- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Data Center Switches M-LAG Configuration Guide-6W100
- 00-M-LAG network planning
- 01-M-LAG+IPv4 and IPv6 Dual-Active VLAN Gateway Configuration Example
- 02-Multi-Layer M-LAG+STP+Dual-Active VLAN Gateway Configuration Examples
- 03-Multi-Layer M-LAG+Dual-Active VLAN Gateway+OSPF Configuration Examples
- 04-Multi-tier M-LAG+Spine Gateways+ECMP Paths to External Network Configuration Example
- 05-M-LAG and VRRP Configuration Example
- 06-M-LAG+RDMA Configuration Example
- 07-M-LAG and EVPN Distributed Gateway (IS-IS for underlay routing) Configuration Example
- 08-M-LAG and EVPN Distributed Gateway (BGP for Underlay Routing) Configuration Example
- 09-M-LAG+EVPN Distributed Gateway (OSPF on Underlay Network)+DHCP Relay+Microsegmentation+Service Chain Configuration Example
- 10-M-LAG+EVPN Centralized Gateway Configuration Example
- 11-Access to M-LAG Through Dynamic Routing and Distributed EVPN Gateways Configuration Example
- 12-M-LAG+EVPN+Monitor Link Configuration Examples
- 13-M-LAG and MVXLAN Configuration Example
- 14-M-LAG and DCI Configuration Example
- 15-M-LAG+EVPN DC Switchover Upon Border Failure Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 12-M-LAG+EVPN+Monitor Link Configuration Examples | 205.88 KB |
Example: Configuring M-LAG, EVPN, and Monitor Link
Configuring the M-LAG member devices
Configuring the links towards the downstream server
Configuring the links towards Device C
Configuring the links towards the M-LAG system
Configuring the links towards the servers and Network
Configuring the links towards the M-LAG system
Configuring the link towards Server 1
Configuring routing on the M-LAG member devices
Configuring routing on Device C
Testing network convergence upon single points of failure
Verifying functionality of the M-LAG system
Verifying connectivity between Server 1 and Server 2
Verifying connectivity between Server 1 and Server 3
Verifying connectivity between Server 1 and Network
Verifying traffic failover upon uplink failure
Verifying spanning tree configuration
Upgrading the M-LAG member devices
Verifying the traffic interruption time during the upgrade
Example: Configuring M-LAG, EVPN, and Monitor Link
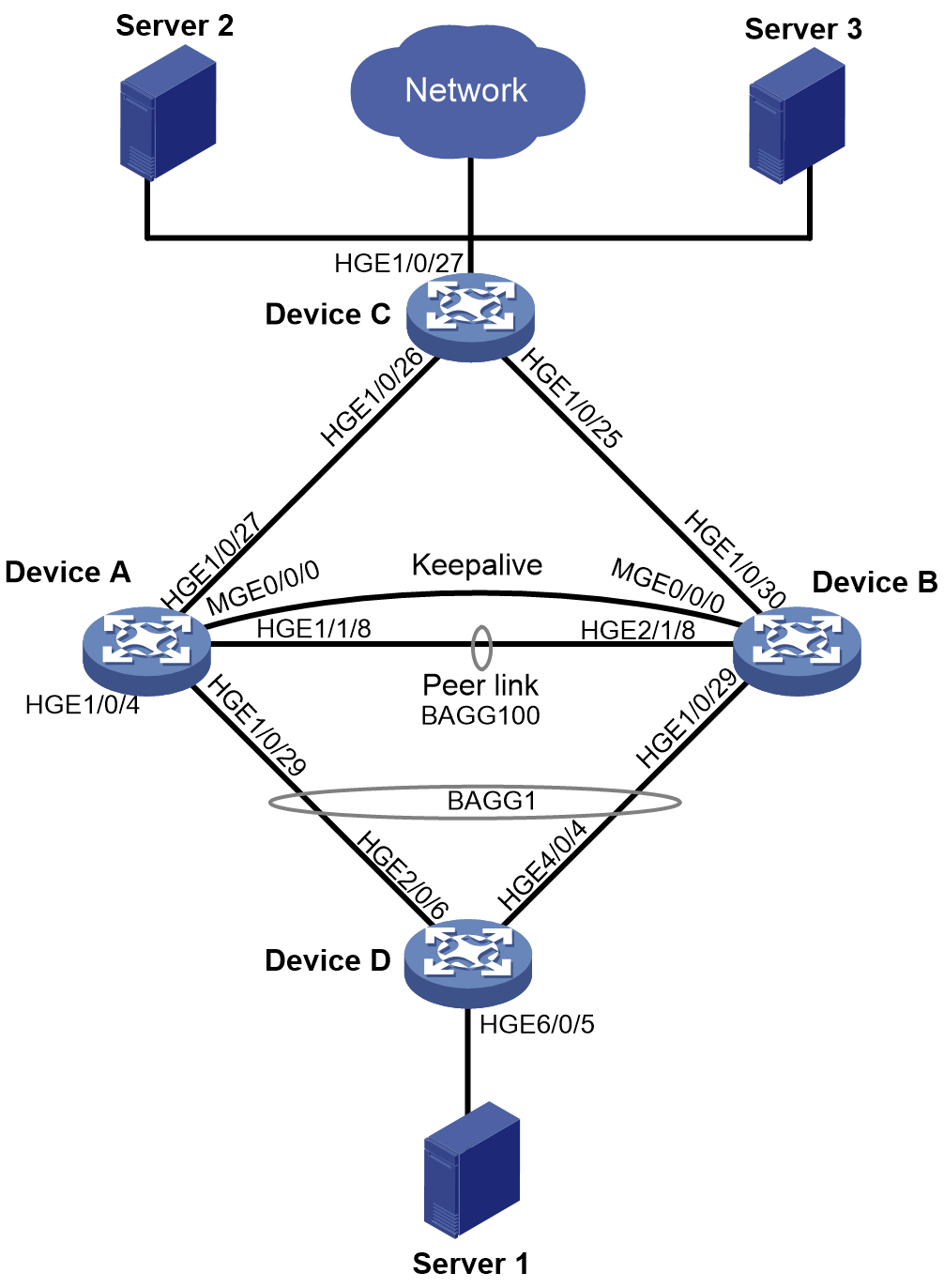
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, configure the network as follows:
· Set up an M-LAG system with Device A and Device B.
· Connect Server 1 to the M-LAG system via Device D.
· Connect Device C to Server 2, Server 3, and Network (public network).
· Configure ECMP routes between the M-LAG system and Device C.
Perform the following tasks to ensure network connectivity:
· Configure Device A and Device B as distributed gateways.
· Configure Device C as a distributed gateway and border gateway.
· Assign Server 1 to Server 2 to one VXLAN, and assign Server 3 to another VXLAN.
· Configure Monitor Link to enable one M-LAG member device to shut down its downlink interface upon uplink interface failure for traffic to fail over to the other M-LAG member device.
Configure spanning tree to eliminate loops:
· Enable spanning tree on the M-LAG member devices.
· Enable BPDU guard on the M-LAG member devices to protect them from forged BPDU attacks.
|
Interface |
IP address |
Remarks |
|
|
Device A |
HGE 1/0/27 |
10.130.0.161/31 |
Connected to HGE 1/0/26 on Device C. |
|
HGE 1/0/29 |
N/A |
Connected to HGE 2/0/6 on Device D. |
|
|
MGE 0/0/0 |
10.130.8.105/24 |
Connected to MGE 0/0/0 on Device A. |
|
|
Vlan-int 100 |
192.168.1.1/30 |
Connected to VLAN-interface 100 on Device B. Used for Layer 3 communication between the M-LAG member devices, BGP peer relationship setup, and traffic failover. |
|
|
Vsi-int 5000 |
120.241.147.49/26 |
Distributed EVPN gateway interface. |
|
|
Vsi-int 1 |
N/A |
L3VNI-associated VSI interface. |
|
|
LoopBack 0 |
10.130.11.1/32 |
VTEP IP address used for setting up BGP EVPN peer relationships. |
|
|
LoopBack 1 |
10.130.12.1/32 |
Virtual VTEP IP address. |
|
|
Device B |
HGE 1/0/25 |
N/A |
Connected to HGE 1/0/26 on Device A. |
|
HGE 1/0/29 |
N/A |
Connected to HGE 4/0/4 on Device D. |
|
|
HGE 1/0/30 |
10.130.1.161/31 |
Connected to HGE 1/0/25 on Device C. |
|
|
MGE 0/0/0 |
10.130.8.106/24 |
Connected to MGE 0/0/0 on Device B. |
|
|
Vlan-int 100 |
192.168.1.2/30 |
Connected to VLAN-interface 100 on Device A. Used for Layer 3 communication between the M-LAG member devices, BGP peer relationship setup, and traffic failover. |
|
|
Vsi-int 5000 |
120.241.147.49/26 |
Distributed EVPN gateway interface. |
|
|
Vsi-int 1 |
N/A |
L3VNI-associated VSI interface. |
|
|
LoopBack 0 |
10.130.11.2/32 |
VTEP IP address used for setting up BGP EVPN peer relationships. |
|
|
LoopBack 1 |
10.130.12.1/32 |
Virtual VTEP IP address. |
|
|
Device C |
HGE 1/0/25 |
10.130.1.160/31 |
Connected to HGE 1/0/30 on Device B. |
|
HGE 1/0/26 |
10.130.0.160/31 |
Connected to HGE 1/0/27 on Device A |
|
|
HGE 1/0/27 |
N/A |
Connected to Network, Server 2, and Server 3. |
|
|
Vlan-int 5 |
192.168.255.1 |
Connected to Network. |
|
|
Vsi-int 5000 |
120.241.147.49/26 |
Distributed EVPN gateway interface. |
|
|
Vsi-int 1000 |
11.0.0.1/26 |
Gateway interface for Server 3. |
|
|
Vsi-int 1 |
N/A |
L3VNI-associated VSI interface. |
|
|
LoopBack 1 |
10.130.12.253/32 |
VTEP IP address used for setting up BGP EVPN peer relationships. |
|
|
Device D |
HGE 2/0/6 |
N/A |
Connected to HGE 1/0/29 on Device A. |
|
HGE 4/0/4 |
N/A |
Connected to HGE 1/0/29 on Device B. |
|
|
HGE 6/0/5 |
N/A |
Connected to Server 1. |
Applicable product matrix
|
IMPORTANT: In addition to running an applicable software version, you must also install the most recent patch, if any. |
|
Device |
Software version |
|
S12500X-AF, S6890 |
R2825 |
|
S6805, S6825, S6850, S9850 |
R6710 |
|
S12500G-AF |
R7625 |
|
S6800, S6860 |
R6710 |
|
S9820-64H, S9820-8C |
Not supported |
|
S6812, S6813 |
F6628P22 and higher |
Analysis
To enable successful traffic failover upon failure of one M-LAG member device, configure Device A and Device B to set up BGP peer relationships by using VLAN-interface 100.
Restrictions and guidelines
In this example, all devices use factory defaults. When you configure M-LAG on a live network, make sure the following requirements are met:
· Device A and Device B use the same M-LAG system MAC address.
· Each device has a unique router ID.
Configuring the M-LAG member devices
Procedure summary
· Configuring the links towards the downstream server
· Configuring the links towards Device C
Configuring interfaces
|
Device A |
Device B |
Description |
Remarks |
|
interface LoopBack 0 |
interface LoopBack 0 |
Create loopback 0. |
N/A |
|
description evpn_ip |
description evpn_ip |
Configure a description for the interface to indicate its purpose. |
N/A |
|
ip address 10.130.11.1 32 |
ip address 10.130.11.2 32 |
Assign an IP address to the interface. |
Unique VTEP IP address. |
|
interface LoopBack 1 |
interface LoopBack 1 |
Create loopback 1. |
N/A |
|
description VTEP |
description VTEP |
Configure a description for the interface. |
N/A |
|
ip address 10.130.12.1 32 |
ip address 10.130.12.1 32 |
Assign an IP address to the interface to indicate its purpose. |
Virtual VTEP IP address. |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
ip vpn-instance Mgt |
ip vpn-instance Mgt |
Create a VPN instance. |
Bound to the management Ethernet interface. |
|
ip vpn-instance WAN |
ip vpn-instance WAN |
Create another VPN instance and enter its view. |
Bound to the VSI interface acting as a gateway for service traffic. |
|
route-distinguisher 10.130.11.1:400 |
route-distinguisher 10.130.11.2:400 |
Configure an RD for the VPN instance. |
An RD uniquely identifies a VPN instance. Configure unique RDs on different devices. |
|
address-family ipv4 |
address-family ipv4 |
Enter IPv4 address family view of the VPN instance. |
N/A |
|
vpn-target 65000:10000 import-extcommunity |
vpn-target 65000:10000 import-extcommunity |
Configure import targets. |
Route targets are used to control advertisement of VPN routes. · Export target attribute—A PE sets the export target attribute for VPN routes before advertising them to other PEs. · Import target attribute—A PE checks the export target attribute of VPN routes received from other PEs. If the export target attribute matches the import target attribute of a VPN instance, the PE adds the routes to the routing table of the VPN instance. |
|
vpn-target 65000:10000 export-extcommunity |
vpn-target 65000:10000 export-extcommunity |
Configure export targets. |
Route targets are used to control advertisement of VPN routes. · Export target attribute—A PE sets the export target attribute for VPN routes before advertising them to other PEs. · Import target attribute—A PE checks the export target attribute of VPN routes received from other PEs. If the export target attribute matches the import target attribute of a VPN instance, the PE adds the routes to the routing table of the VPN instance. |
|
address-family evpn |
address-family evpn |
Enter EVPN view of the VPN instance. |
N/A |
|
vpn-target 65000:10000 import-extcommunity |
vpn-target 65000:10000 import-extcommunity |
Configure import targets. |
Route targets are used to control advertisement of VPN routes. · Export target attribute—A PE sets the export target attribute for VPN routes before advertising them to other PEs. · Import target attribute—A PE checks the export target attribute of VPN routes received from other PEs. If the export target attribute matches the import target attribute of a VPN instance, the PE adds the routes to the routing table of the VPN instance. |
|
vpn-target 65000:10000 export-extcommunity |
vpn-target 65000:10000 export-extcommunity |
Configure export targets. |
Route targets are used to control advertisement of VPN routes. · Export target attribute—A PE sets the export target attribute for VPN routes before advertising them to other PEs. · Import target attribute—A PE checks the export target attribute of VPN routes received from other PEs. If the export target attribute matches the import target attribute of a VPN instance, the PE adds the routes to the routing table of the VPN instance. |
|
quit |
quit |
Exit the current view. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
interface M-GigabitEthernet0/0/0 |
interface M-GigabitEthernet0/0/0 |
Enter management Ethernet interface view. |
N/A |
|
ip binding vpn-instance Mgt |
ip binding vpn-instance Mgt |
Bind the interface to a VPN instance. |
N/A |
|
ip address 10.130.8.105 24 |
ip address 10.130.8.106 24 |
Assign an IP address to the management Ethernet interface. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
vlan 50 100 |
vlan 50 100 |
Create VLAN 50 and VLAN 100. |
N/A |
|
interface Vlan-interface100 |
interface Vlan-interface100 |
Create a VLAN interface. |
Layer 3 interface used for interconnecting the M-LAG member devices. |
|
ip address 192.168.1.1 30 |
ip address 192.168.1.2 30 |
Assign an IP address to the VLAN interface. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
interface Vsi-interface 5000 |
interface Vsi-interface 5000 |
Create a VSI interface and enter its view. |
Distributed EVPN gateway interface. |
|
ip binding vpn-instance WAN |
ip binding vpn-instance WAN |
Bind the VSI interface to VPN instance WAN. |
N/A |
|
ip address 120.241.147.49 26 |
ip address 120.241.147.49 26 |
Assign an IP address to the VSI interface. |
N/A |
|
mac-address 0000-5e00-aa01 |
mac-address 0000-5e00-aa01 |
Assign a MAC address to the VSI interface. |
N/A |
|
distributed-gateway local |
distributed-gateway local |
Specify the VSI interface as a distributed gateway interface. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
vsi 5000 |
vsi 5000 |
Create a VSI and enter its view. |
N/A |
|
gateway vsi-interface 5000 |
gateway vsi-interface 5000 |
Specify a gateway interface for the VSI. |
N/A |
|
arp suppression enable |
arp suppression enable |
Enable ARP flood suppression. |
N/A |
|
vxlan 5000 |
vxlan 5000 |
Create a VXLAN and enter its view. |
N/A |
|
evpn encapsulation vxlan |
evpn encapsulation vxlan |
Enter VSI EVPN instance view. |
N/A |
|
route-distinguisher 10.130.11.1:5000 |
route-distinguisher 10.130.11.2:5000 |
Configure an RD for the EVPN instance. |
An RD uniquely identifies a VPN instance. Configure unique RDs on different devices. |
|
vpn-target 65000:5000 export-extcommunity |
vpn-target 65000:5000 export-extcommunity |
Configure import targets. |
Route targets are used to control advertisement of VPN routes. · Export target attribute—A PE sets the export target attribute for VPN routes before advertising them to other PEs. · Import target attribute—A PE checks the export target attribute of VPN routes received from other PEs. If the export target attribute matches the import target attribute of a VPN instance, the PE adds the routes to the routing table of the VPN instance. |
|
vpn-target 65000:5000 import-extcommunity |
vpn-target 65000:5000 import-extcommunity |
Configure export targets. |
Route targets are used to control advertisement of VPN routes. · Export target attribute—A PE sets the export target attribute for VPN routes before advertising them to other PEs. · Import target attribute—A PE checks the export target attribute of VPN routes received from other PEs. If the export target attribute matches the import target attribute of a VPN instance, the PE adds the routes to the routing table of the VPN instance. |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to VSI view. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
interface Vsi-interface 1 |
interface Vsi-interface 1 |
Create a VSI interface. |
L3VNI-associated VSI interface. |
|
ip binding vpn-instance WAN |
ip binding vpn-instance WAN |
Bind the VSI interface to VPN instance WAN. |
N/A |
|
l3-vni 10000 |
l3-vni 10000 |
Assign an L3VNI to the VSI interface. |
N/A |
Configuring the links towards the downstream server
|
Device A |
Device B |
Description |
Remarks |
|
l2vpn enable |
l2vpn enable |
Enable L2VPN. |
N/A |
|
vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable |
vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable |
Disable remote ARP learning. |
N/A |
|
vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable |
vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable |
Disable remote MAC learning. |
N/A |
|
evpn m-lag group 10.130.12.1 |
evpn m-lag group 10.130.12.1 |
Configure a virtual VTEP IP address. |
Used by the M-LAG member devices to establish tunnels with peer devices. |
|
evpn global-mac 0000-5e01-0e01 |
evpn global-mac 0000-5e01-0e01 |
Configure an EVPN global MAC address for L3VNI-associated VSI interfaces. |
N/A |
|
m-lag system-mac 0000-5e01-0ffe |
m-lag system-mac 0000-5e01-0ffe |
Configure an M-LAG system MAC address. |
Configure the same M-LAG system MAC address on the M-LAG member devices. |
|
m-lag system-number 1 |
m-lag system-number 2 |
Configure an M-LAG system number. |
Configure different M-LAG system numbers on the M-LAG member devices. |
|
m-lag role priority 100 |
m-lag role priority 150 |
Set the M-LAG role priority. |
The lower the value, the higher the priority. |
|
m-lag system-priority 32768 |
m-lag system-priority 32768 |
Set the M-LAG system priority. |
Configure the same M-LAG system priority on the M-LAG member devices. |
|
m-lag auto-recovery reload-delay 240 |
m-lag auto-recovery reload-delay 240 |
Enable M-LAG system auto-recovery and set the reload delay timer. |
To avoid incorrect role preemption, make sure the reload delay timer is longer than the amount of time required for the device to restart. |
|
m-lag keepalive ip destination 10.130.8.106 source 10.130.8.105 vpn-instance Mgt |
m-lag keepalive ip destination 10.130.8.105 source 10.130.8.106 vpn-instance Mgt |
Configure M-LAG keepalive packet parameters. |
N/A |
|
m-lag standalone enable |
m-lag standalone enable |
Enable M-LAG standalone mode. |
N/A |
|
stp global enable |
stp global enable |
Enable spanning tree globally. |
N/A |
|
stp bpdu-protection |
stp bpdu-protection |
Enable BPDU guard globally. |
N/A |
|
interface bridge-aggregation 100 |
interface bridge-aggregation 100 |
Create Bridge-Aggregation 100, which will be configured as the peer-link interface. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
interface HundredGigE 1/0/26 |
interface HundredGigE 1/0/25 |
Enter Ethernet interface view. |
N/A |
|
port link-mode bridge |
port link-mode bridge |
Configure the Ethernet interface to work in Layer 2 mode. |
N/A |
|
port link-aggregation group 100 |
port link-aggregation group 100 |
Assign HundredGigE 1/0/25 to Layer 2 aggregation group 100. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
interface bridge-aggregation 100 |
interface bridge-aggregation 100 |
Enter the view of Bridge-Aggregation 100. |
N/A |
|
link-aggregation mode dynamic |
link-aggregation mode dynamic |
Configure Bridge-Aggregation 100 to work in dynamic aggregation mode. |
N/A |
|
port m-lag peer-link 1 |
port m-lag peer-link 1 |
Configure Bridge-Aggregation 100 as a peer-link interface. |
N/A |
|
port link-type trunk |
port link-type trunk |
Configure the Layer 2 aggregate interface as a trunk port. |
N/A |
|
port trunk permit vlan all |
port trunk permit vlan all |
Configure the trunk port to permit all VLANs. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
interface bridge-aggregation 1 |
interface bridge-aggregation 1 |
Create Bridge-Aggregation 1, which is connected to Device D. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
Interface HundredGigE 1/0/29 |
interface HundredGigE 1/0/29 |
Enter Ethernet interface view. |
N/A |
|
port link-mode bridge |
port link-mode bridge |
Configure the Ethernet interface to work in Layer 2 mode. |
N/A |
|
port link-aggregation group 1 |
port link-aggregation group 1 |
Assign the Ethernet interface to aggregation group 1. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
interface bridge-aggregation 1 |
interface bridge-aggregation 1 |
Enter the view of Bridge-Aggregation 1. |
N/A |
|
undo mac-address static source-check enable |
undo mac-address static source-check enable |
Disable static source check. |
The S12500X-AF, S12500G-AF, and S6890 switches do not support this command. |
|
link-aggregation mode dynamic |
link-aggregation mode dynamic |
Configure the aggregate interface to work in dynamic aggregation mode. |
N/A |
|
port m-lag group 1 |
port m-lag group 1 |
Assign the aggregate interface to an M-LAG group. |
N/A |
|
port link-type trunk |
port link-type trunk |
Configure the Layer 2 aggregate interface as a trunk port. |
N/A |
|
undo port trunk permit vlan 1 |
undo port trunk permit vlan 1 |
Forbid traffic of VLAN 1. |
N/A |
|
port trunk permit vlan 50 |
port trunk permit vlan 50 |
Permit traffic of VLAN 50. |
N/A |
|
service-instance 50 |
service-instance 50 |
Create Ethernet service instance 50. |
N/A |
|
encapsulation s-vid 50 |
encapsulation s-vid 50 |
Configure the Ethernet service instance to match packets with outer VLAN tag 50. |
N/A |
|
xconnect vsi 5000 |
xconnect vsi 5000 |
Map the Ethernet service instance to VSI 5000. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to VSI view. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
Configuring the links towards Device C
|
Device A |
Device B |
Description |
|
interface HundredGigE 1/0/27 |
interface HundredGigE 1/0/30 |
Enter Ethernet interface view. |
|
port link-mode route |
port link-mode route |
Configure the interface to work in Layer 3 mode. |
|
description TO_Device-C |
description TO_Device-C |
Configure a description. |
|
ip address 10.130.0.161 31 |
ip address 10.130.1.161 31 |
Assign an IP address to the interface. |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
Configuring M-LAG MAD
|
Device A |
Device B |
Description |
|
m-lag mad default-action none |
m-lag mad default-action none |
Set the default M-LAG MAD action to NONE. |
|
m-lag mad include interface HundredGigE 1/0/27 |
m-lag mad include interface HundredGigE 1/0/30 |
Specify an interface to be shut down by M-LAG MAD when the M-LAG system splits. |
|
m-lag mad include interface HundredGigE 1/0/29 |
m-lag mad include interface HundredGigE 1/0/29 |
Specify an interface to be shut down by M-LAG MAD when the M-LAG system splits. |
Configuring monitoring
|
Device A |
Device B |
Description |
|
undo monitor-link disable |
undo monitor-link disable |
Enable Monitor Link globally. |
|
monitor-link group 1 |
monitor-link group 1 |
Create a monitor link group and enter its view. |
|
port HundredGigE 1/0/27 uplink |
port HundredGigE 1/0/30 uplink |
Assign uplink interfaces to the monitor link group. |
|
port HundredGigE 1/0/29 downlink |
port HundredGigE 1/0/29 downlink |
Assign downlink interfaces to the monitor link group. |
Configuring Device C
Procedure summary
· Configuring the links towards the
· Configuring the links towards the servers and Network
Configuring the interfaces
|
Description |
|
|
interface LoopBack 1 |
Create a loopback interface and enter its view. |
|
description VTEP |
Configure a description for the interface to indicate its purpose. |
|
ip address 10.130.12.253 32 |
Assign an IP address to the interface. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
ip vpn-instance Mgt |
Create VPN instance Mgt. |
|
ip vpn-instance WAN |
Create L3VPN instance WAN. |
|
route-distinguisher 10.130.12.253:400 |
Configure an RD for the VPN instance. |
|
address-family ipv4 |
Enter IPv4 address family view of the VPN instance. |
|
vpn-target 65000:10000 import-extcommunity |
Configure import targets. |
|
vpn-target 65000:10000 export-extcommunity |
Configure export targets. |
|
address-family evpn |
Enter EVPN view of the VPN instance. |
|
vpn-target 65000:10000 import-extcommunity |
Configure import targets. |
|
vpn-target 65000:10000 export-extcommunity |
Configure export targets. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
interface M-GigabitEthernet0/0/0 |
Enter management Ethernet interface view. |
|
ip binding vpn-instance Mgt |
Bind the management Ethernet interface to VPN instance Mgt. |
|
ip address 10.130.8.104 24 |
Assign an IP address to the management Ethernet interface. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
vlan 5 10 50 |
Create VLAN 5, VLAN 10, and VLAN 100. |
|
interface Vlan-interface 5 |
Create a VLAN interface. |
|
ip binding vpn-instance WAN |
Bind the VLAN interface to VPN instance WAN. |
|
ip address 192.168.255.1 30 |
Assign an IP address to the VLAN interface. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
interface Vsi-interface 5000 |
Create a VSI interface. |
|
ip binding vpn-instance WAN |
Bind the VSI interface to VPN instance WAN. |
|
ip address 120.241.147.49 26 |
Assign an IP address to the VSI interface. |
|
mac-address 0000-5e00-aa01 |
Assign a MAC address to the VSI interface. |
|
distributed-gateway local |
Specify the VSI interface as a distributed gateway interface. |
|
vsi 5000 |
Create a VSI. |
|
gateway vsi-interface 5000 |
Specify a gateway interface for the VSI. |
|
arp suppression enable |
Enable ARP flood suppression. |
|
vxlan 5000 |
Create a VXLAN. |
|
evpn encapsulation vxlan |
Enter VSI EVPN instance view. |
|
route-distinguisher 10.130.12.253:5000 |
Configure an RD for the EVPN instance. |
|
vpn-target 65000:5000 export-extcommunity |
Configure import targets. |
|
vpn-target 65000:5000 import-extcommunity |
Configure export targets. |
|
quit |
Return to VSI view. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
interface Vsi-interface1 |
Create a VSI interface. |
|
ip binding vpn-instance WAN |
Bind the VSI interface to VPN instance WAN. |
|
l3-vni 10000 |
Assign an L3VNI to the VSI interface. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
interface Vsi-interface1000 |
Create a VSI interface. |
|
ip binding vpn-instance WAN |
Bind the VSI interface to VPN instance WAN. |
|
ip address 11.0.0.1 26 |
Assign an IP address to the VSI interface. |
|
mac-address 0000-5e00-aa02 |
Assign a MAC address to the VSI interface. |
|
distributed-gateway local |
Specify the VSI interface as a distributed gateway interface. |
|
vsi 1000 |
Create a VSI. |
|
gateway vsi-interface 1000 |
Specify a gateway interface for the VSI. |
|
arp suppression enable |
Enable ARP flood suppression. |
|
vxlan 1000 |
Enter VXLAN view. |
|
evpn encapsulation vxlan |
Enter VSI EVPN instance view. |
|
route-distinguisher 10.130.12.253:1000 |
Configure an RD for the EVPN instance. |
|
vpn-target 65000:1000 export-extcommunity |
Configure import targets. |
|
vpn-target 65000:1000 import-extcommunity |
Configure export targets. |
|
quit |
Return to VSI view. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
Configuring the links towards the M-LAG system
|
Device C |
Description |
|
l2vpn enable |
Enable L2VPN. |
|
vxlan tunnel arp-learning disable |
Disable remote ARP learning. |
|
vxlan tunnel mac-learning disable |
Disable remote MAC learning. |
|
interface HundredGigE 1/0/26 |
Enter the view of the interface connected to Device A. |
|
port link-mode route |
Configure the interface to work at Layer 3 mode. |
|
description TO_Device-A |
Configure a description for the interface. |
|
ip address 10.130.0.160 31 |
Assign an IP address to the interface. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
interface HundredGigE 1/0/25 |
Enter the view of the interface connected to Device B. |
|
port link-mode route |
Configure the interface to work at Layer 3 mode. |
|
description TO_Device-B |
Configure a description for the interface. |
|
ip address 10.130.1.160 31 |
Assign an IP address to the interface. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
Configuring the links towards the servers and Network
|
Device C |
Description |
|
interface HundredGigE 1/0/27 |
Enter the view of the physical interface facing the servers and Network. |
|
port link-mode bridge |
Configure the interface to work at Layer 2 mode. |
|
port link-type trunk |
Set the link type to trunk. |
|
undo port trunk permit vlan 1 |
Forbid traffic of VLAN 1. |
|
port trunk permit vlan 5 10 50 |
Permit traffic of VLAN 5, VLAN 10, and VLAN 50. |
|
service-instance 50 |
Create an Ethernet service instance. |
|
encapsulation s-vid 50 |
Configure a frame match criterion for the Ethernet service instance. |
|
xconnect vsi 5000 |
Map the Ethernet service instance to a VSI. |
|
service-instance 10 |
Create an Ethernet service instance. |
|
encapsulation s-vid 10 |
Configure a frame match criterion for the Ethernet service instance. |
|
xconnect vsi 1000 |
Map the Ethernet service instance to a VSI. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
Configuring Device D
Procedure summary
· Configuring the links towards the
· Configuring the link towards Server 1
Configuring the links towards the M-LAG system
|
Device D |
Description |
|
vlan 50 |
Create VLAN 50. |
|
interface bridge-aggregation 1 |
Create an aggregate interface. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
interface HundredGigE 2/0/6 |
Enter Ethernet interface view. |
|
port link-mode bridge |
Configure the Ethernet interface to work in Layer 2 mode. |
|
port link-aggregation group 1 |
Assign the Ethernet interface to aggregation group 1. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
interface HundredGigE 4/0/4 |
Enter Ethernet interface view. |
|
port link-mode bridge |
Configure the Ethernet interface to work in Layer 2 mode. |
|
port link-aggregation group 1 |
Assign the Ethernet interface to aggregation group 1. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
|
interface bridge-aggregation 1 |
Create an aggregate interface. |
|
link-aggregation mode dynamic |
Configure the aggregate interface to work in dynamic aggregation mode. |
|
port link-type trunk |
Set the link type of the aggregate interface to trunk. |
|
undo port trunk permit vlan 1 |
Forbid traffic of VLAN 1. |
|
port trunk permit vlan 50 |
Permit traffic of VLAN 50. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
Configuring the link towards Server 1
|
Device D |
Description |
|
stp global enable |
Enable spanning tree globally. |
|
interface HundredGigE 6/0/5 |
Enter the view of the interface connected to Server 1. |
|
port link-mode bridge |
Configure the interface to work at Layer 2 mode. |
|
port link-type access |
Set the link type to access. |
|
port access vlan 50 |
Configure the interface to permit traffic of VLAN 50 as an access port. |
|
stp edged-port |
Configure the interface as a spanning tree edge port. |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
Configuring routing
Procedure summary
· Configuring routing on the M-LAG member devices
· Configuring routing on Device C
Configuring routing on the M-LAG member devices
|
Device A |
Device B |
Description |
Purpose/Remarks |
|
bgp 1 |
bgp 1 |
Enable BGP instance default, specify 1 as the local AS number, and enter BGP instance view. |
Used for creating underlay routes. |
|
bgp update-delay on-startup 240 |
bgp update-delay on-startup 240 |
Configure BGP to delay sending route updates on reboot. |
The delay timer must be longer than the time spent on BGP relationship establishment after the BGP process restarts. |
|
non-stop-routing |
non-stop-routing |
Enable BGP NSR. |
N/A |
|
router-id 10.130.11.1 |
router-id 10.130.11.2 |
Configure a router ID. |
Configure unique router IDs for the devices in the same AS. |
|
group ibgp internal |
group ibgp internal |
Create IBGP peer group ibgp. |
N/A |
|
group spine external |
group spine external |
Create EBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer spine as-number 2 |
peer spine as-number 2 |
Specify AS number 2 for the EBGP peer group. |
N/A |
|
peer spine route-update-interval 0 |
peer spine route-update-interval 0 |
Set the interval to 0 for sending the same update to peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer 10.130.0.160 group spine |
peer 10.130.1.160 group spine |
Assign peers with a 10.130.x.160 IP address to EBGP peer group spine. |
Set up peer relationships between the M-LAG member devices and Device C. |
|
peer 192.168.1.2 group ibgp |
peer 192.168.1.1 group ibgp |
Assign peers with a 192.168.1.x address to IBGP peer group ibgp. |
Set up peer relationships between the M-LAG member devices and Device C. |
|
address-family ipv4 unicast |
address-family ipv4 unicast |
Create the BGP-VPN IPv4 unicast address family and enter its view. |
N/A |
|
balance ebgp 8 |
balance ebgp 8 |
Enable load balancing and set the maximum number of EBGP ECMP routes for load balancing to 8. |
N/A |
|
network 10.130.11.1 255.255.255.255 |
network 10.130.11.2 255.255.255.255 |
Configure BGP to advertise a local network. |
N/A |
|
network 10.130.12.1 255.255.255.255 |
network 10.130.12.1 255.255.255.255 |
Configure BGP to inject local network 10.130.12.1/32 into the BGP routing table. |
N/A |
|
peer ibgp enable |
peer ibgp enable |
Enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with peer group ibgp. |
N/A |
|
peer ibgp next-hop-local |
peer ibgp next-hop-local |
Set the local router as the next hop for BGP routes sent to the IBGP peer group. |
N/A |
|
peer spine enable |
peer spine enable |
Enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to BGP view. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
bgp 65000 instance evpn |
bgp 65000 instance evpn |
Enable BGP instance evpn, specify 65000 as the local AS number, and enter BGP instance view. |
Used for creating overlay routes. |
|
bgp update-delay on-startup 240 |
bgp update-delay on-startup 240 |
Configure BGP to delay sending route updates on reboot. |
The delay timer must be longer than the time spent on BGP relationship establishment after the BGP process restarts. |
|
non-stop-routing |
non-stop-routing |
Enable BGP NSR. |
N/A |
|
router-id 10.130.11.1 |
router-id 10.130.11.2 |
Configure a router ID. |
Configure unique router IDs for the devices in the same AS. |
|
group spine internal |
group spine internal |
Create IBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer spine connect-interface LoopBack0 |
peer spine connect-interface LoopBack0 |
Specify source interface Loopback 0 for establishing TCP links towards peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer 10.130.12.253 group spine |
peer 10.130.12.253 group spine |
Assign the peer at 10.130.12.253 to IBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
address-family l2vpn evpn |
address-family l2vpn evpn |
Create the BGP EVPN address family and enter its view. |
N/A |
|
nexthop evpn-m-lag group-address |
nexthop evpn-m-lag group-address |
Set the next hop of advertised EVPN routes to the virtual VTEP address of the M-LAG system. |
N/A |
|
peer spine enable |
peer spine enable |
Enable the device to exchange BGP EVPN routes with peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to BGP view. |
N/A |
|
quit |
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
Configuring routing on Device C
|
Device C |
Description |
Remarks |
|
bgp 2 |
Enable BGP instance default, specify 2 as the local AS number, and enter BGP instance view. |
N/A |
|
bgp update-delay on-startup 240 |
Configure BGP to delay sending route updates on reboot. |
The delay timer must be longer than the time spent on BGP relationship establishment after the BGP process restarts. |
|
non-stop-routing |
Enable BGP NSR. |
N/A |
|
group spine external |
Create EBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer spine as-number 1 |
Specify AS number 1 for the EBGP peer group. |
N/A |
|
peer spine route-update-interval 0 |
Set the interval to 0 for sending the same update to peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer 10.130.0.161 group spine |
Assign the peer at 10.130.0.161 to EBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer 10.130.1.161 group spine |
Assign the peer at 10.130.1.161 to EBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
address-family ipv4 unicast |
Enter BGP IPv4 unicast address family view. |
N/A |
|
balance ebgp 8 |
Enable load balancing and set the maximum number of EBGP ECMP routes for load balancing to 8. |
N/A |
|
network 10.130.12.253 255.255.255.255 |
Configure BGP to inject local network 10.130.12.253/32 into the BGP routing table. |
N/A |
|
peer spine enable |
Enable BGP to exchange IPv4 unicast routing information with peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
quit |
Return to BGP view. |
N/A |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
bgp 65000 instance evpn |
Enable BGP instance evpn, specify 65000 as the local AS number, and enter BGP instance view. |
N/A |
|
bgp update-delay on-startup 240 |
Configure BGP to delay sending route updates on reboot. |
The delay timer must be longer than the time spent on BGP relationship establishment after the BGP process restarts. |
|
non-stop-routing |
Enable BGP NSR. |
N/A |
|
router-id 10.130.12.253 |
Configure a router ID. |
N/A |
|
group spine internal |
Create IBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer spine connect-interface LoopBack1 |
Specify source interface Loopback 1 for establishing TCP links towards peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer 10.130.11.1 group spine |
Assign the peer at 10.130.11.1 to IBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
peer 10.130.11.2 group spine |
Assign the peer at 10.130.11.2 to IBGP peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
address-family l2vpn evpn |
Create the BGP EVPN address family and enter its view. |
N/A |
|
peer spine enable |
Enable BGP to exchange BGP EVPN routing information with peer group spine. |
N/A |
|
ip vpn-instance WAN |
Enter the view of BGP-VPN instance WAN. |
N/A |
|
address-family ipv4 unicast |
Enter BGP-VPN IPv4 unicast address family view. |
N/A |
|
default-route imported |
Import default routes to the BGP routing table. |
N/A |
|
balance 16 |
Enable load balancing and set the maximum number of BGP ECMP routes for load balancing to 16. |
N/A |
|
quit |
Return to BGP view. |
N/A |
|
quit |
Return to system view. |
N/A |
|
ip route-static vpn-instance WAN 0.0.0.0 0 Vlan-interface5 192.168.255.2 description to-evpn-wan |
Configure a static route for Network. |
N/A |
|
ip route-static vpn-instance Mgt 10.0.0.0 8 10.130.8.1 |
Configure a static route for the management Ethernet interface. |
N/A |
Traffic forwarding models
Traffic characteristics
The forwarding model matrix provides the following characteristics of traffic:
· No.—Traffic number, which can be U-S2, U-S3, or U-N.
¡ U—Underlay traffic.
¡ S—Server.
¡ N—Network.
· Traffic type—Type of traffic, which can only be known IPv4 unicast.
· Direction—Direction of traffic, which can only be south to north.
· Forwarding path—Nodes that traffic traverses.
· Traffic simulation—Traffic simulation method. Typically a tester is used to simulate traffic.
· Load—Traffic size, which can be light (less than 1000 flows).
· Traffic direction to firewalls/LB—Not applicable.
Underlay forwarding models
|
No. |
Traffic type |
Direction |
Forwarding path |
Traffic simulation |
Load |
Traffic direction to firewalls/LB |
|
U-S2 |
Known unicast |
South to north |
Server 1 > Device A/B > Device C > Server 2 |
Tester |
Light |
N/A |
|
U-S3 |
Known unicast |
South to north |
Server 1 > Device A/B > Device C > Server 3 |
Tester |
Light |
N/A |
|
U-N1 |
Known unicast |
South to north |
Server 1 > Device A/B > Device C > Network |
Tester |
Light |
N/A |
Testing network convergence upon single points of failure
Table 1 Network convergence upon single points of failure
|
Device |
Failure type |
Traffic interruption time |
|
M-LAG member device |
Link failure |
≤ 500 ms |
|
Link failure recovery |
≤ 500 ms |
|
|
Uplink failure |
≤ 500 ms |
|
|
Peer link failure |
≤ 500 ms |
|
|
Peer link failure recovery |
≤ 500 ms |
|
|
Keepalive link failure |
0 ms |
|
|
Keepalive link failure recovery |
0 ms |
|
|
Concurrent failure of the keepalive link and peer link |
≤ 5000 ms |
|
|
Recovery of the keepalive link and peer link from failure |
≤ 1000 ms |
|
|
Upgrade |
≤ 500 ms (device-by-device upgrade) |
Verifying the configuration
Verifying functionality of the M-LAG system
The following steps use Device A as an example.
# Verify that Device A and Device B have established an M-LAG system.
[DeviceA] display m-lag summary
Flags: A -- Aggregate interface down, B -- No peer M-LAG interface configured
C -- Configuration consistency check failed
Peer-link interface: BAGG100
Peer-link interface state (cause): UP
Keepalive link state (cause): UP
M-LAG interface information
M-LAG interface M-LAG group Local state (cause) Peer state Remaining down time (s)
BAGG1 1 UP UP -
# Verify the keepalive packet statistics.
[DeviceA] display m-lag keepalive
Neighbor keepalive link status: Up
Neighbor is alive for: 69 s 921 ms
Keepalive packet transmission status:
Sent: Successful
Received: Successful
Last received keepalive packet information:
Source IP address: 10.130.8.106
Time: 2022/01/03 15:30:44
Action: Accept
M-LAG keepalive parameters:
Destination IP address: 10.130.8.106
Source IP address: 10.130.8.105
Keepalive UDP port : 6400
Keepalive VPN name : Mgt
Keepalive interval : 1000 ms
Keepalive timeout : 5 sec
Keepalive hold time: 3 sec
# Verify the M-LAG system settings.
[DeviceA] display m-lag system
System information
Local system number: 1 Peer system number: 2
Local system MAC: 0000-5e01-0ffe Peer system MAC: 0000-5e01-0ffe
Local system priority: 32768 Peer system priority: 32768
Local bridge MAC: f474-8882-ee00 Peer bridge MAC: 0000-fc00-6504
Local effective role: Primary Peer effective role: Secondary
Health level: 0
Standalone mode on split: Disabled
In standalone mode: No
System timer information
Timer State Value (s) Remaining time (s)
Auto recovery Disabled 240 -
Restore delay Disabled 30 -
Consistency-check delay Disabled 15 -
Standalone delay Disabled - -
Role to None delay Disabled 60 -
# Verify information about the interfaces on the M-LAG system.
[DeviceA] display m-lag verbose
Flags: A -- Home_Gateway, B -- Neighbor_Gateway, C -- Other_Gateway,
D -- PeerLink_Activity, E -- DRCP_Timeout, F -- Gateway_Sync,
G -- Port_Sync, H -- Expired
Peer-link interface/Peer-link interface ID: BAGG100/1
State: UP
Cause: -
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): HGE 1/0/26 (26)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 25
M-LAG interface/M-LAG group ID: BAGG1/1
Local M-LAG interface state: UP
Peer M-LAG interface state: UP
M-LAG group state: UP
Local M-LAG interface down cause: -
Remaining M-LAG DOWN time: -
Local M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=N/A, Effective=0000-5e01-0ffe
Peer M-LAG interface LACP MAC: Config=N/A, Effective=0000-5e01-0ffe
Local M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=32768
Peer M-LAG interface LACP priority: Config=32768, Effective=32768
Local DRCP flags/Peer DRCP flags: ABDFG/ABDFG
Local Selected ports (index): HGE 1/0/29(45)
Peer Selected ports indexes: 29
Verifying routing information
# Verify that Device A has underlay BGP peers.
[DeviceA] display bgp peer ipv4
BGP local router ID: 10.130.11.1
Local AS number: 1
Total number of peers: 2 peers in established state: 2
* - Dynamically created peer
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
10.130.0.160 2 3743 3744 0 1 01:02:17 Established
192.168.1.2 1 600024 600043 0 3 0166h40m Established
# Verify that Device A has overlay BGP peers.
[DeviceA] display bgp instance evpn peer l2vpn evpn
BGP local router ID: 10.130.11.1
Local AS number: 65000
Total number of peers: 1 peers in established state: 1
* - Dynamically created peer
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
10.130.12.253 65000 10232 11134 0 4 0166h52m Established
# Verify that Device B has underlay BGP peers.
[DeviceB] display bgp peer ipv4
BGP local router ID: 10.130.11.2
Local AS number: 1
Total number of peers: 2 peers in established state: 2
* - Dynamically created peer
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
10.130.1.160 2 3925 3926 0 1 01:21:55 Established
192.168.1.1 1 601092 602000 0 3 0166h52m Established
# Verify that Device B has overlay BGP peers.
[DeviceB] display bgp instance evpn peer l2vpn evpn
BGP local router ID: 10.130.11.2
Local AS number: 65000
Total number of peers: 1 peers in established state: 1
* - Dynamically created peer
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
10.130.12.253 65000 12539 11149 0 4 0166h59m Established
# Verify that Device C has underlay BGP peers.
[DeviceC] display bgp peer ipv4
BGP local router ID: 10.130.12.253
Local AS number: 2
Total number of peers: 2 peers in established state: 2
* - Dynamically created peer
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
10.130.0.161 1 5211 5209 0 3 01:26:42 Established
10.130.1.161 1 502 501 0 3 01:08:16 Established
# Verify that Device C has overlay BGP peers.
[DeviceB] display bgp instance evpn peer l2vpn evpn
BGP local router ID: 10.130.12:253
Local AS number: 65000
Total number of peers: 2 peers in established state: 2
* - Dynamically created peer
Peer AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ PrefRcv Up/Down State
10.130.11.1 65000 11156 10252 0 3 0167h12m Established
10.130.11.2 65000 11157 12549 0 3 0167h07m Established
Verifying connectivity between Server 1 and Server 2
Verify that Server 1 and Server 2, which are in the same VXLAN, have Layer 2 connectivity.
Verifying connectivity between Server 1 and Server 3
Verify that Server 1 and Server 2, which are in different VXLANs, have Layer 3 connectivity.
Verifying connectivity between Server 1 and Network
Verify that Server 1 on a private network and Network on the public network have Layer 3 connectivity.
Verifying traffic failover upon uplink failure
Configure Monitor Link.
monitor-link group 1
port HGE 1/0/30 uplink Uplink interface
port ethernet 1/0/29 downlink Associated member port of an M-LAG group
monitor-link group 2
port HGE 1/0/27 uplink Uplink interface
port ethernet 1/0/29 downlink Associated member port of an M-LAG group
Disconnect the interface connected to Device C on Device A or Device B.
Verify that Server 1, Server 2, Server 3, and Network can communicate with one another.
Verifying spanning tree configuration
# Verify that spanning tree is operating correctly.
<DeviceA> display stp brief
MST ID Port Role STP State Protection
0 HundredGigE1/0/27 DESI FORWARDING NONE
0 Bridge-Aggregation1 (M-LAG) DESI FORWARDING NONE
<DeviceB> display stp brief
MST ID Port Role STP State Protection
0 HundredGigE1/0/30 DESI FORWARDING NONE
0 Bridge-Aggregation1 (M-LAG) DESI FORWARDING NONE
Upgrading the M-LAG member devices
Checking the environment
Execute the commands in "Verifying the configuration" and the following commands to verify that the device is available for an upgrade.
|
Leaf 1 |
Leaf 2 |
Description |
|
display device |
display device |
Displays device information. |
|
display boot-loader |
display boot-loader |
Displays current software images and startup software images. |
|
display version |
display version |
Displays system version information. |
Upgrading the device
See H3C Switches M-LAG System Upgrade & Replacement & Expansion Guide.
Verifying the traffic interruption time during the upgrade
Verify that the traffic interruption time is shorter than 500 ms during a switchover and shorter than 150 ms during fallback. For more information, see "Testing network convergence upon single points of failure."
Verifying the upgrade result
Execute the commands in "Verifying the configuration" and the following commands to verify that the device is upgraded successfully.
|
Leaf 1 |
Leaf 2 |
Description |
|
display device |
display device |
Displays device information. |
|
display boot-loader |
display boot-loader |
Displays current software images and startup software images. |
|
display version |
display version |
Displays system version information. |