- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Fixed Port Campus Switches Configuration Examples-B70D022-6W100
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Manual Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 16-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 18-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 19-BGP Configuration Examples
- 20-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 21-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 22-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 23-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 25-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 26-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 27-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- 28-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 29-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 30-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 31-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 32-ACL Configuration Examples
- 33-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 34-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 35-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 36-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 37-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 38-AAA Configuration Examples
- 39-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 40-Portal Configuration Examples
- 41-SSH Configuration Examples
- 42-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 43-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 44-CFD Configuration Examples
- 45-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 46-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 47-BFD Configuration Examples
- 48-NTP Configuration Examples
- 49-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 50-NQA Configuration Examples
- 51-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 52-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 53-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 54-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 55-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 56-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 57-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 58-MCE Configuration Examples
- 59-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 60-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 61-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 62-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 63-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 64-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 65-IRF Configuration Examples
- 66-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 67-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 68-VCF Fabric Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 16-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples | 104.79 KB |
Example: Configuring GRE with OSPF· 1
Applicable hardware and software versions· 2
Restrictions and guidelines· 3
Verifying the configuration· 6
Introduction
This document provides GRE with OSPF configuration examples.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of GRE and OSPF.
Example: Configuring GRE with OSPF
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, Device A is the gateway of the headquarters. Device B and Device C are the gateways of Branch 1 and Branch 2, respectively. The gateways have obtained public IP addresses from an ISP and can communicate with one another. Configure GRE with OSPF to meet the following requirements:
· The headquarters and the branches communicate with one another through the GRE tunnels established between the headquarters and the branches.
· The gateways learn the routes reaching the destination networks through the tunnel interfaces.
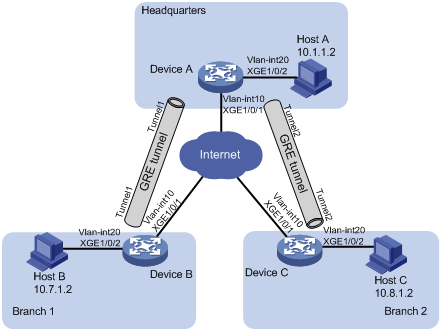
Table 1 Interface and IP address assignment
Device | Interface | IP address | Device | Interface | IP address |
Device A | Vlan-int10 | 191.2.1.1/24 | Device B | Vlan-int10 | 191.3.1.1/24 |
| Vlan-int20 | 10.1.1.1/24 |
| Vlan-int20 | 10.7.1.1/24 |
| Tunnel1 | 10.5.1.1/24 |
| Tunnel1 | 10.5.1.2/24 |
| Tunnel2 | 10.6.1.1/24 |
|
|
|
Device C | Vlan-int10 | 191.4.1.1/24 |
|
|
|
| Vlan-int20 | 10.8.1.1/24 |
|
|
|
| Tunnel2 | 10.6.1.2/24 |
|
|
|
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
Hardware | Software version |
S6520XE-HI switch series | Supported in Release 11xx |
S5560X-EI switch series | Supported in Release 111x |
S5500V2-EI switch series | Supported in Release 111x |
MS4520V2-30F switch | Supported in Release 111x |
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series | Supported in Release 612x |
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series | Not supported |
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series | Not supported |
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series | Not supported |
S5110V2 switch series | Not supported |
S5110V2-SI switch series | Not supported |
S5000V3-EI switch series | Not supported |
S5000E-X switch series | Not supported |
WAS6000 switch series | Not supported |
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series | Not supported |
MS4520V2 switch series (except the MS4520V2-30F switch) | Supported in Release 612x |
MS4320V2 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series | Not supported |
WS5850-WiNet switch series | Supported in Release 612x |
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series | Not supported |
Restrictions and guidelines
On the S6520XE-HI switch series, encapsulated packets cannot be forwarded on Layer 3 according to the destination IP addresses and routing tables. You must create a service loopback group of the tunnel service type to loop encapsulated packets back to the forwarding module for Layer 3 forwarding.
Procedures
Before configuring GRE and OSPF, configure an IPv4 routing protocol on the gateways so that they can reach one another. (Details not shown.)
Configuring Device A
# Configure VLAN-interface 10.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 10
[DeviceA-vlan10] port Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-vlan10] quit
[DeviceA] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceA-vlan-interface10] ip address 191.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceA-vlan-interface10] quit
# Configure other interfaces in the same way VLAN-interface 10 is configured. (Details not shown.)
# Create service loopback group 1, and specify its service type as Tunnel. (Required only on the S6520XE-HI switch series.)
[DeviceA] service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
# Add Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to service loopback group 1. (Required only on the S6520XE-HI switch series.)
[DeviceA] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
[DeviceA-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1
[DeviceA-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create a tunnel interface Tunnel 1, and specify the tunnel mode as GRE/IPv4.
[DeviceA] interface tunnel 1 mode gre
# Configure an IP address for the tunnel interface Tunnel 1.
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] ip address 10.5.1.1 24
# Configure the source interface of the tunnel interface Tunnel 1 as VLAN-interface 10.
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] source vlan-interface 10
# Configure the destination address of the tunnel interface Tunnel 1 as the IP address of VLAN-interface 10 on Device B.
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] destination 191.3.1.1
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] quit
# Create a tunnel interface Tunnel 2, and specify the tunnel mode as GRE/IPv4.
[DeviceA] interface tunnel 2 mode gre
# Configure an IP address for the tunnel interface Tunnel 2.
[DeviceA-Tunnel2] ip address 10.6.1.1 24
# Configure the source interface of the tunnel interface Tunnel 2 as VLAN-interface 10.
[DeviceA-Tunnel2] source vlan-interface 10
# Configure the destination address of the tunnel interface Tunnel 2 as the IP address of VLAN-interface 10 on Device C.
[DeviceA-Tunnel2] destination 191.4.1.1
[DeviceA-Tunnel2] quit
# Configure the OSPF router ID as 10.6.1.1.
[DeviceA] router id 10.6.1.1
# Enable OSPF process 1.
[DeviceA] ospf 1
# Create OSPF area 0.
[DeviceA-ospf-1] area 0
# Enable OSPF on interfaces whose primary IP addresses are on network 10.1.1.0/24, 10.5.1.0/24, or 10.6.1.0/24 in area 0.
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
Configuring Device B
# Configure VLAN-interface 10.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] vlan 10
[DeviceB-vlan10] port Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-vlan10] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 10
[DeviceB-vlan-interface10] ip address 191.3.1.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceB-vlan-interface10] quit
# Configure other interfaces in the same way VLAN-interface 10 is configured. (Details not shown.)
# Create service loopback group 1, and specify its service type as Tunnel. (Required only on the S6520XE-HI switch series.)
[DeviceB] service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
# Add Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to service loopback group 1. (Required only on the S6520XE-HI switch series.)
[DeviceB] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
[DeviceB-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1
[DeviceB-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create a tunnel interface Tunnel 1, and specify the tunnel mode as GRE/IPv4.
[DeviceB] interface tunnel 1 mode gre
# Configure an IP address for the tunnel interface Tunnel 1.
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] ip address 10.5.1.2 24
# Configure the source interface of the tunnel interface Tunnel 1 as VLAN-interface 10.
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] source Vlan-interface 10
# Configure the destination address of the tunnel interface Tunnel 1 as the IP address of VLAN-interface 10 on Device A.
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] destination 191.2.1.1
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] quit
# Configure the OSPF router ID as 10.7.1.1.
[DeviceB] router id 10.7.1.1
# Enable OSPF process 1.
[DeviceB] ospf 1
# Create OSPF area 0.
[DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0
# Enable OSPF on interfaces whose primary IP addresses are on network 10.7.1.0/24 or 10.5.1.0/24 in area 0.
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.7.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
Configuring Device C
# Configure VLAN-interface 10.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] vlan 10
[DeviceC-vlan10] port Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[DeviceC-vlan10] quit
[DeviceC] interface Vlan-interface 10
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] ip address 191.4.1.1 255.255.255.0
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface10] quit
# Configure other interfaces in the same way VLAN-interface 10 is configured. (Details not shown.)
# Create service loopback group 1, and specify its service type as Tunnel. (Required only on the S6520XE-HI switch series.)
[DeviceC] service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
# Add Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to service loopback group 1. (Required only on the S6520XE-HI switch series.)
[DeviceC] interface Ten-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
[DeviceC-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1
[DeviceC-Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create a tunnel interface Tunnel 2, and specify the tunnel mode as GRE/IPv4.
[DeviceC] interface tunnel 2 mode gre
# Configure an IP address for the tunnel interface Tunnel 2.
[DeviceC-Tunnel2] ip address 10.6.1.2 24
# Configure the source interface of the tunnel interface Tunnel 2 as VLAN-interface 10.
[DeviceC-Tunnel2] source Vlan-interface 10
# Configure the destination address of the tunnel interface Tunnel 2 as the IP address of VLAN-interface 10 on Device A.
[DeviceC-Tunnel2] destination 191.2.1.1
[DeviceC-Tunnel2] quit
# Configure the OSPF router ID as 10.8.1.1.
[DeviceC] router id 10.8.1.1
# Enable OSPF process 1.
[DeviceC] ospf 1
# Create OSPF area 0.
[DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0
# Enable OSPF on interfaces whose primary IP addresses are on network 10.8.1.0/24 or 10.6.1.0/24 in area 0.
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.8.1.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that Host A can ping Host B successfully.
C:\> ping 10.7.1.2
Pinging 10.7.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.7.1.2: bytes=32 time=19ms TTL=253
Reply from 10.7.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Reply from 10.7.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Reply from 10.7.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Ping statistics for 10.7.1.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 19ms, Average = 4ms
# Verify that Host A can ping Host C successfully.
C:\> ping 10.8.1.2
Pinging 10.8.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.8.1.2: bytes=32 time=18ms TTL=253
Reply from 10.8.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Reply from 10.8.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Reply from 10.8.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=253
Ping statistics for 10.8.1.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 19ms, Average = 4ms
# Verify that Host B can ping Host C successfully.
C:\> ping 10.8.1.2
Pinging 10.8.1.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 10.8.1.2: bytes=32 time=20ms TTL=251
Reply from 10.8.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=251
Reply from 10.8.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=251
Reply from 10.8.1.2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=251
Ping statistics for 10.8.1.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 19ms, Average = 4ms
Configuration files
| IMPORTANT: The port link-mode bridge command is available only on the following switches: · S6520XE-HI switch series. · S5560X-EI switch series. · S5500V2-EI switch series. · MS4520V2-30F switch. |
· Device A
#
service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 191.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port service-loopback group 1
#
interface Tunnel1 mode gre
source vlan-interface10
destination 191.3.1.1
ip address 10.5.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Tunnel2 mode gre
source vlan-interface10
destination 191.4.1.1
ip address 10.6.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
router id 10.6.1.1
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
· Device B
#
service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 191.3.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 10.7.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port service-loopback group 1
#
interface Tunnel1 mode gre
source Vlan-interface10
destination 191.2.1.1
ip address 10.5.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
router id 10.7.1.1
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.7.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
#
· Device C
#
service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 191.4.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 10.8.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port service-loopback group 1
#
interface Tunnel2 mode gre
source Vlan-interface10
destination 191.2.1.1
ip address 10.6.1.2 255.255.255.0
#
router id 10.8.1.1
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.8.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
#

