- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Fixed Port Campus Switches Configuration Examples-B70D022-6W100
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Manual Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 16-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 18-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 19-BGP Configuration Examples
- 20-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 21-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 22-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 23-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 25-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 26-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 27-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- 28-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 29-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 30-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 31-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 32-ACL Configuration Examples
- 33-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 34-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 35-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 36-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 37-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 38-AAA Configuration Examples
- 39-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 40-Portal Configuration Examples
- 41-SSH Configuration Examples
- 42-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 43-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 44-CFD Configuration Examples
- 45-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 46-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 47-BFD Configuration Examples
- 48-NTP Configuration Examples
- 49-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 50-NQA Configuration Examples
- 51-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 52-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 53-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 54-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 55-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 56-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 57-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 58-MCE Configuration Examples
- 59-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 60-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 61-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 62-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 63-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 64-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 65-IRF Configuration Examples
- 66-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 67-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 68-VCF Fabric Configuration Examples
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 66-MPLS TE Configuration Examples | 211.62 KB |
Example: Establishing MPLS TE tunnels with RSVP-TE
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Configuring MPLS TE forwarding adjacency
Applicable hardware and software versions
Example: Configuring MPLS TE FRR
Applicable hardware and software versions
Introduction
This document provides MPLS TE configuration examples.
Prerequisites
This document is not restricted to specific software or hardware versions.
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of MPLS TE.
Example: Establishing MPLS TE tunnels with RSVP-TE
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, use RSVP-TE to establish two MPLS TE tunnels between Switch A and Switch D. The MPLS TE tunnel for Enterprise A requires a bandwidth of 20000 kbps. The MPLS TE tunnel for Enterprise B requires a bandwidth of 30000 kbps.
The maximum bandwidth of the link that each tunnel traverses is 50000 kbps and the maximum reservable bandwidth is 40000 kbps.
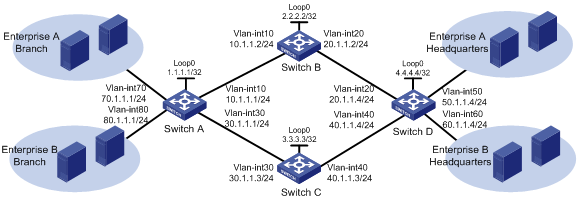
Analysis
To establish MPLS TE tunnels through RSVP-TE, you must perform the following tasks:
· Enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE on nodes that the MPLS TE tunnels traverse.
· On each interface that the MPLS TE tunnels traverse, configure link TE attributes, including the maximum link bandwidth and the maximum reservable bandwidth.
· On each node that the MPLS TE tunnels traverse, configure the IGP TE extension to advertise the link TE attributes, which generates a TEDB on each node.
Based on the TEDB, CSPF calculates the shortest, TE constraints-compliant path to the tunnel destination. If you do not configure the IGP TE extension, the path is created based on IGP routing. The supported IGP TE extensions are OSPF TE and ISIS TE. This example uses OSPF TE.
· Create a tunnel interface on the ingress node of each MPLS TE tunnel, and perform the following tasks on the tunnel interface:
¡ Specify the tunnel destination address.
¡ Specify the tunnel bandwidth as required (20000 kbps for Enterprise A and 30000 kbps for Enterprise B).
¡ Specify the MPLS TE signaling protocol as RSVP-TE.
RSVP-TE advertises labels to establish CRLSPs and reserves bandwidth resources on each node along the calculated path.
· On the ingress node of each MPLS TE tunnel, configure static routing to direct traffic to the MPLS TE tunnel.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6520XE-HI switch series |
Supported in Release 11xx |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Not supported |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4520V2 switch series (except the MS4520V2-30F switch) |
Not supported |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
Restrictions and guidelines
Before configuration, disable the spanning tree feature globally or map each VLAN to an MSTI.
Procedures
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Configure IP addresses and masks for interfaces on Switch A, including the loopback interface, as shown in Figure 1.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] port ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] ip address 10.1.1.1 24
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] quit
[SwitchA] vlan 30
[SwitchA-vlan30] port ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchA-vlan30] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 30
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] ip address 30.1.1.1 24
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] quit
[SwitchA] vlan 70
[SwitchA-vlan70] port ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-vlan70] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 70
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface70] ip address 70.1.1.1 24
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface70] quit
[SwitchA] vlan 80
[SwitchA-vlan80] port ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[SwitchA-vlan80] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 80
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface80] ip address 80.1.1.1 24
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface80] quit
[SwitchA] interface loopback 0
[SwitchA-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[SwitchA-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure other devices in the same way that Switch A is configured. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF to ensure IP connectivity among the switches:
# Configure Switch A.
[SwitchA] ospf
[SwitchA-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchA-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Switch B.
[SwitchB] ospf
[SwitchB-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchB-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Switch C.
[SwitchC] ospf
[SwitchC-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchC-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Switch D.
[SwitchD] ospf
[SwitchD-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchD-ospf-1] quit
# Execute the display ip routing-table command on each switch to verify that the switches have learned the routes to one another, including the routes to the loopback interfaces. The following shows the output on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 26 Routes : 26
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.2.2.2/32 O_INTRA 10 1 10.1.1.2 Vlan10
3.3.3.3/32 O_INTRA 10 1 30.1.1.3 Vlan30
4.4.4.4/32 O_INTRA 10 2 10.1.1.2 Vlan10
8.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 8.1.1.1 Tun2
8.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 8.1.1.1 Tun2
8.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
8.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 8.1.1.1 Tun2
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Vlan10
10.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Vlan10
10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Vlan10
20.1.1.0/24 O_INTRA 10 2 10.1.1.2 Vlan10
30.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 30.1.1.1 Vlan30
30.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 30.1.1.1 Vlan30
30.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
30.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 30.1.1.1 Vlan30
40.1.1.0/24 Static 1 0 0.0.0.0 Tun2
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
3. Configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE:
# Configure Switch A.
[SwitchA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
[SwitchA] mpls te
[SwitchA-te] quit
[SwitchA] rsvp
[SwitchA-rsvp] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] mpls enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] mpls te enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] rsvp enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 30
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] mpls enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] mpls te enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] rsvp enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] quit
# Configure Switch B.
[SwitchB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[SwitchB] mpls te
[SwitchB-te] quit
[SwitchB] rsvp
[SwitchB-rsvp] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] mpls enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] mpls te enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] rsvp enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 20
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface20] mpls enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface20] mpls te enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface20] rsvp enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure Switch C.
[SwitchC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
[SwitchC] mpls te
[SwitchC-te] quit
[SwitchC] rsvp
[SwitchC-rsvp] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 30
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface30] mpls enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface30] mpls te enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface30] rsvp enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface30] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 40
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface40] mpls enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface40] mpls te enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface40] rsvp enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface40] quit
# Configure Switch D.
[SwitchD] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
[SwitchD] mpls te
[SwitchD-te] quit
[SwitchD] rsvp
[SwitchD-rsvp] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 20
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface20] mpls enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface20] mpls te enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface20] rsvp enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface20] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 40
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface40] mpls enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface40] mpls te enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface40] rsvp enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface40] quit
4. Configure MPLS TE attributes of links:
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch A.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 30
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface30] quit
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch B.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface10] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 20
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface20] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface20] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface20] quit
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch C.
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 30
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface30] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface30] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface30] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 40
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface40] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface40] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface40] quit
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch D.
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 20
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface20] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface20] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface20] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 40
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface40] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface40] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface40] quit
5. Configure OSPF TE to advertise link TE attributes:
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch A. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchA] ospf
[SwitchA-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch A.
[SwitchA-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchA-ospf-1] quit
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch B. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchB] ospf
[SwitchB-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch B.
[SwitchB-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchB-ospf-1] quit
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch C. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchC] ospf
[SwitchC-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch C.
[SwitchC-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchC-ospf-1] quit
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch D. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchD] ospf
[SwitchD-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch D.
[SwitchD-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchD-ospf-1] quit
6. Configure MPLS TE tunnels on Switch A:
# Configure MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 1 to forward traffic of Enterprise A.
[SwitchA] interface tunnel 1 mode mpls-te
[SwitchA-Tunnel1] ip address 7.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Specify the tunnel destination address as the LSR ID of Switch D, use RSVP-TE to establish the tunnel, and assign 20000 kbps bandwidth to the tunnel.
[SwitchA-Tunnel1] destination 4.4.4.4
[SwitchA-Tunnel1] mpls te signaling rsvp-te
[SwitchA-Tunnel1] mpls te bandwidth 20000
# Enable route recording for MPLS TE tunnel 1.
[SwitchA-Tunnel1] mpls te record-route
[SwitchA-Tunnel1] quit
# Configure MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 2 to forward traffic of Enterprise B.
[SwitchA] interface tunnel 2 mode mpls-te
[SwitchA-Tunnel2] ip address 8.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Specify the tunnel destination address as the LSR ID of Switch D, use RSVP-TE to establish the tunnel, and assign 30000 kbps bandwidth to the tunnel.
[SwitchA-Tunnel2] destination 4.4.4.4
[SwitchA-Tunnel2] mpls te signaling rsvp-te
[SwitchA-Tunnel2] mpls te bandwidth 30000
# Enable route recording for MPLS TE tunnel 2.
[SwitchA-Tunnel2] mpls te record-route
[SwitchA-Tunnel2] quit
7. Configure static routing on Switch A to direct traffic to the MPLS TE tunnels:
# Configure a static route to direct traffic destined for 50.1.1.0/24 to MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 1.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 50.1.1.0 24 tunnel 1 preference 1
# Configure a static route to direct traffic destined for 60.1.1.0/24 to MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 2.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 60.1.1.0 24 tunnel 2 preference 1
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display interface tunnel brief command on Switch A. The output shows that the two tunnel interfaces are up.
[SwitchA] display interface tunnel brief
Brief information on interfaces in route mode:
Link: ADM - administratively down; Stby - standby
Protocol: (s) - spoofing
Interface Link Protocol Primary IP Description
Tun1 UP UP 7.1.1.1
Tun2 UP UP 8.1.1.1
# Execute the display mpls te tunnel-interface command on Switch A to display detailed information about the MPLS TE tunnels.
[SwitchA] display mpls te tunnel-interface
Tunnel Name : Tunnel 1
Tunnel State : Up (Main CRLSP up, Shared-resource CRLSP down)
Tunnel Attributes :
LSP ID : 27415 Tunnel ID : 1
Admin State : Normal
Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.1 Egress LSR ID : 4.4.4.4
Signaling : RSVP-TE Static CRLSP Name : -
Resv Style : SE
Tunnel mode : -
Reverse-LSP name : -
Reverse-LSP LSR ID : - Reverse-LSP Tunnel ID: -
Class Type : CT0 Tunnel Bandwidth : 20000 kbps
Reserved Bandwidth : 20000 kbps
Setup Priority : 7 Holding Priority : 7
Affinity Attr/Mask : 0/0
Explicit Path : -
Backup Explicit Path : -
Metric Type : TE
Record Route : Enabled Record Label : Disabled
FRR Flag : Disabled Bandwidth Protection : Disabled
Backup Bandwidth Flag: Disabled Backup Bandwidth Type: -
Backup Bandwidth : -
Bypass Tunnel : No Auto Created : No
Route Pinning : Disabled
Retry Limit : 3 Retry Interval : 2 sec
Reoptimization : Disabled Reoptimization Freq : -
Backup Type : None Backup LSP ID : -
Auto Bandwidth : Disabled Auto Bandwidth Freq : -
Min Bandwidth : - Max Bandwidth : -
Collected Bandwidth : -
Tunnel Name : Tunnel 2
Tunnel State : Up (Main CRLSP up, Shared-resource CRLSP down)
Tunnel Attributes :
LSP ID : 27302 Tunnel ID : 2
Admin State : Normal
Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.1 Egress LSR ID : 4.4.4.4
Signaling : RSVP-TE Static CRLSP Name : -
Resv Style : SE
Tunnel mode : -
Reverse-LSP name : -
Reverse-LSP LSR ID : - Reverse-LSP Tunnel ID: -
Class Type : CT0 Tunnel Bandwidth : 30000 kbps
Reserved Bandwidth : 30000 kbps
Setup Priority : 7 Holding Priority : 7
Affinity Attr/Mask : 0/0
Explicit Path : -
Backup Explicit Path : -
Metric Type : TE
Record Route : Enabled Record Label : Disabled
FRR Flag : Disabled Bandwidth Protection : Disabled
Backup Bandwidth Flag: Disabled Backup Bandwidth Type: -
Backup Bandwidth : -
Bypass Tunnel : No Auto Created : No
Route Pinning : Disabled
Retry Limit : 3 Retry Interval : 2 sec
Reoptimization : Disabled Reoptimization Freq : -
Backup Type : None Backup LSP ID : -
Auto Bandwidth : Disabled Auto Bandwidth Freq : -
Min Bandwidth : - Max Bandwidth : -
Collected Bandwidth : -
# Execute the display ip routing-table command on Switch A. The output shows two static route entries with output interfaces of Tunnel 1 and Tunnel 2.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 30 Routes : 31
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.2.2.2/32 O_INTRA 10 1 10.1.1.2 Vlan10
3.3.3.3/32 O_INTRA 10 1 30.1.1.3 Vlan30
4.4.4.4/32 O_INTRA 10 2 10.1.1.2 Vlan10
30.1.1.3 Vlan30
7.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 7.1.1.1 Tun1
7.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 7.1.1.1 Tun1
7.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
7.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 7.1.1.1 Tun1
8.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 8.1.1.1 Tun2
8.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 8.1.1.1 Tun2
8.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
8.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 8.1.1.1 Tun2
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Vlan10
10.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Vlan10
10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Vlan10
50.1.1.0/24 Static 1 0 0.0.0.0 Tun1
30.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 30.1.1.1 Vlan30
30.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 30.1.1.1 Vlan30
30.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
30.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 30.1.1.1 Vlan30
60.1.1.0/24 Static 1 0 0.0.0.0 Tun2
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
# Execute the display rsvp lsp verbose command on Switch A to verify the following information:
· Tunnel 1 uses path Switch A—Switch B—Switch D, and has a bandwidth of 20000 kbps.
· Tunnel 2 uses path Switch A—Switch C—Switch D, and has a bandwidth of 30000 kbps.
[SwitchA] display rsvp lsp verbose
Tunnel name: SwitchA_t1
Destination: 4.4.4.4 Source: 1.1.1.1
Tunnel ID: 1 LSP ID: 27415
LSR type: Ingress Direction: Unidirectional
Setup priority: 7 Holding priority: 7
In-Label: - Out-Label: 1146
In-Interface: - Out-Interface: Vlan10
Nexthop: 10.1.1.2 Exclude-any: 0
Include-Any: 0 Include-all: 0
Mean rate (CIR): 20000 kbps Mean burst size (CBS): 1000.00 bytes
Path MTU: 1500 Class type: CT0
RRO number: 6
10.1.1.1/32 Flag: 0x00 (No FRR)
10.1.1.2/32 Flag: 0x00 (No FRR)
2.2.2.2/32 Flag: 0x20 (No FRR/Node-ID)
20.1.1.2/32 Flag: 0x00 (No FRR)
20.1.1.4/32 Flag: 0x00 (No FRR)
4.4.4.4/32 Flag: 0x20 (No FRR/Node-ID)
Fast Reroute protection: None
Tunnel name: SwitchA_t2
Destination: 4.4.4.4 Source: 1.1.1.1
Tunnel ID: 2 LSP ID: 27302
LSR type: Ingress Direction: Unidirectional
Setup priority: 7 Holding priority: 7
In-Label: - Out-Label: 1150
In-Interface: - Out-Interface: Vlan30
Nexthop: 30.1.1.3 Exclude-any: 0
Include-Any: 0 Include-all: 0
Mean rate (CIR): 30000 kbps Mean burst size (CBS): 1000.00 bytes
Path MTU: 1500 Class type: CT0
RRO number: 6
30.1.1.1/32 Flag: 0x00 (No FRR)
30.1.1.3/32 Flag: 0x00 (No FRR)
3.3.3.3/32 Flag: 0x20 (No FRR/Node-ID)
40.1.1.3/32 Flag: 0x00 (No FRR)
40.1.1.4/32 Flag: 0x00 (No FRR)
4.4.4.4/32 Flag: 0x20 (No FRR/Node-ID)
Fast Reroute protection: None
Configuration files
· Switch A:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 30
#
vlan 70
#
vlan 80
#
mpls te
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface30
ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface70
ip address 70.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface80
ip address 80.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 30
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 70
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 80
#
interface Tunnel1 mode mpls-te
ip address 7.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mpls te bandwidth ct0 20000
mpls te record-route
destination 4.4.4.4
#
interface Tunnel2 mode mpls-te
ip address 8.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mpls te bandwidth ct0 30000
mpls te record-route
destination 4.4.4.4
#
ip route-static 50.1.1.0 24 Tunnel1 preference 1
ip route-static 60.1.1.0 24 Tunnel2 preference 1
#
· Switch B:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
#
vlan 10
#
vlan 20
#
mpls te
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface10
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 10
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
· Switch C:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
network 30.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
#
vlan 30
#
vlan 40
#
mpls te
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface30
ip address 30.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface40
ip address 40.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 40
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 30
#
· Switch D:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
#
vlan 20
#
vlan 40
#
vlan 50
#
vlan 60
#
mpls te
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface20
ip address 20.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface40
ip address 40.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface50
ip address 50.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
#
interface Vlan-interface60
ip address 60.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 40
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 20
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 50
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/4
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 60
#
Example: Configuring MPLS TE forwarding adjacency
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D run OSPF.
Establish an MPLS TE tunnel from Device B to Device D that uses the path Device B—Device C—Device D, and configure MPLS TE forwarding adjacency for the tunnel.
Before the tunnel is established, traffic from Device A to Device D is forwarded through the direct link Device A—Device D. After the tunnel is established, the traffic is forwarded through the MPLS TE tunnel.
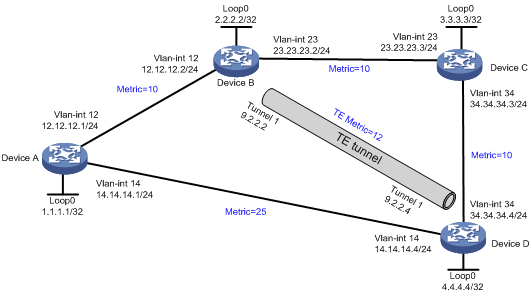
Analysis
· Enable MPLS TE on nodes and interfaces that the MPLS TE tunnels traverse.
· To make forwarding adjacency take effect, you must establish two MPLS TE tunnels in opposite directions between Device B and Device D, and enable forwarding adjacency on both devices.
· For the MPLS TE tunnel to use the path Device B—Device C—Device D, configure the path as the explicit path for the tunnel.
· For traffic from Device A to Device D to be forwarded through the MPLS TE tunnel, make sure the tunnel's metric is less than 15 (metric 25 minus 10). This example uses 12.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6520XE-HI switch series |
Supported in Release 11xx |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Not supported |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4520V2 switch series (except the MS4520V2-30F switch) |
Not supported |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
Procedures
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces, configure basic OSPF, and set OSPF costs. (Details not shown.) For the configuration, see "Configuration files."
2. Enable MPLS TE on each node and interface that the MPLS TE tunnel traverses:
# On Device B, configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[DeviceB] mpls te
[DeviceB-te] quit
[DeviceB] rsvp
[DeviceB-rsvp] quit
[DeviceB] interface vlan-interface 23
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface23] mpls enable
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface23] mpls te enable
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface23] rsvp enable
[DeviceB-Vlan-interface23] quit
# On Device C, configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
[DeviceC] mpls te
[DeviceC-te] quit
[DeviceC] rsvp
[DeviceC-rsvp] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 23
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface23] mpls enable
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface23] mpls te enable
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface23] rsvp enable
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface23] quit
[DeviceC] interface vlan-interface 34
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface34] mpls enable
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface34] mpls te enable
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface34] rsvp enable
[DeviceC-Vlan-interface34] quit
# On Device D, configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
[DeviceD] mpls te
[DeviceD-te] quit
[DeviceD] rsvp
[DeviceD-rsvp] quit
[DeviceD] interface vlan-interface 34
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface34] mpls enable
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface34] mpls te enable
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface34] rsvp enable
[DeviceD-Vlan-interface34] quit
3. Configure OSPF TE to advertise link TE attributes:
# On Device B, enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception, and enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0. By default, opaque LSA advertisement and reception are enabled.
[DeviceB] ospf
[DeviceB-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
[DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
# On Device C, enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception, and enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0. By default, opaque LSA advertisement and reception are enabled.
[DeviceC] ospf
[DeviceC-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
[DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceC-ospf-1] quit
# On Device D, enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception, and enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0. By default, opaque LSA advertisement and reception are enabled.
[DeviceD] ospf
[DeviceD-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
[DeviceD-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[DeviceD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceD-ospf-1] quit
4. Configure MPLS TE tunnels:
# On Device B, configure MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 1, and specify the tunnel destination address as the LSR ID of Device D.
[DeviceB] interface tunnel 1 mode mpls-te
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] ip address 9.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] destination 4.4.4.4
# Configure MPLS TE to use RSVP-TE to establish the tunnel.
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] mpls te signaling rsvp-te
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] quit
# Configure an explicit path named tun1.
[DeviceB] explicit-path tun1
[DeviceB-explicit-path-tun1] nexthop 23.23.23.3
[DeviceB-explicit-path-tun1] nexthop 34.34.34.4
[DeviceB-explicit-path-tun1]quit
# Specify explicit path tun1 for the tunnel.
[DeviceB] interface tunnel 1
[DeviceB–Tunnel1] mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path tun1
# Enable forwarding adjacency for the tunnel.
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] mpls te igp advertise
# Enable OSPF on tunnel interface Tunnel 1 and set the OSPF cost to 12 for the tunnel interface.
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] ospf 1 area 0
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] ospf cost 12
[DeviceB-Tunnel1] quit
# On Device D, configure MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 1, and specify the tunnel destination address as the LSR ID of Device B.
[DeviceD] interface tunnel 1 mode mpls-te
[DeviceD-Tunnel1] ip address 9.2.2.4 255.255.255.0
[DeviceD-Tunnel1] destination 2.2.2.2
# Configure MPLS TE to use RSVP-TE to establish the tunnel.
[DeviceD-Tunnel1] mpls te signaling rsvp-te
[DeviceD-Tunnel1] quit
# Configure an explicit path named tun1.
[DeviceD] explicit-path tun1
[DeviceD-explicit-path-tun1] nexthop 34.34.34.3
[DeviceD-explicit-path-tun1] nexthop 23.23.23.2
[DeviceD-explicit-path-tun1]quit
# Specify explicit path tun1 for the tunnel.
[DeviceD] interface tunnel 1
[DeviceD–Tunnel1] mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path tun1
# Enable forwarding adjacency for the tunnel.
[DeviceD-Tunnel1] mpls te igp advertise
# Enable OSPF on tunnel interface Tunnel 1 and set the OSPF cost to 12 for the tunnel interface.
[DeviceD-Tunnel1] ospf 1 area 0
[DeviceD-Tunnel1] ospf cost 12
[DeviceD-Tunnel1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display interface tunnel brief command on Device B and Device D. This example uses Device B. The output shows that Tunnel 1 is up.
[DeviceB] display interface tunnel brief
Brief information on interfaces in route mode:
Link: ADM - administratively down; Stby - standby
Protocol: (s) - spoofing
Interface Link Protocol Primary IP Description
Tun1 UP UP 9.2.2.2
# Display routing table information on Device A. The output shows that the next hop of the route to Device D is Device B, and the cost is 22 (10 plus 12). The MPLS TE tunnel has been used during IGP route calculation.
[Device A] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 24 Routes : 24
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.2.2.2/32 O_INTRA 10 10 12.12.12.2 Vlan12
3.3.3.3/32 O_INTRA 10 20 12.12.12.2 Vlan12
4.4.4.4/32 O_INTRA 10 22 12.12.12.2 Vlan12
9.2.2.0/24 O_INTRA 10 22 12.12.12.2 Vlan12
10.1.0.3/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
12.12.12.0/24 Direct 0 0 12.12.12.1 Vlan12
12.12.12.0/32 Direct 0 0 12.12.12.1 Vlan12
12.12.12.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
12.12.12.255/32 Direct 0 0 12.12.12.1 Vlan12
14.14.14.0/24 Direct 0 0 14.14.14.1 Vlan14
14.14.14.0/32 Direct 0 0 14.14.14.1 Vlan14
14.14.14.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
14.14.14.255/32 Direct 0 0 14.14.14.1 Vlan14
23.23.23.0/24 O_INTRA 10 20 12.12.12.2 Vlan12
34.34.34.0/24 O_INTRA 10 30 12.12.12.2 Vlan12
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
Configuration files
· Device A:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
network 12.12.12.0 0.0.0.255
network 14.14.14.0 0.0.0.255
#
vlan 12
#
vlan 14
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface12
ip address 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 10
#
interface Vlan-interface14
ip address 14.14.14.1 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 25
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 12
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 14
#
· Device B:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
network 12.12.12.0 0.0.0.255
network 23.23.23.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
#
vlan 12
#
vlan 23
#
mpls te
#
explicit-path tun1
nexthop index 1 23.23.23.3 include strict
nexthop index 101 34.34.34.4 include strict
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface12
ip address 12.12.12.2 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 10
#
interface Vlan-interface23
ip address 23.23.23.2 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 10
mpls enable
mpls te enable
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 12
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 23
#
interface Tunnel1 mode mpls-te
ip address 9.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 12
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path tun1
mpls te igp advertise
destination 4.4.4.4
#
· Device C:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
network 23.23.23.0 0.0.0.255
network 34.34.34.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
#
vlan 23
#
vlan 34
#
mpls te
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface23
ip address 23.23.23.3 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 10
mpls enable
mpls te enable
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface34
ip address 34.34.34.3 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 10
mpls enable
mpls te enable
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 34
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 23
#
· Device D:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
network 14.14.14.0 0.0.0.255
network 34.34.34.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
#
vlan 14
#
vlan 34
#
mpls te
#
explicit-path tun1
nexthop index 1 34.34.34.3 include strict
nexthop index 101 23.23.23.2 include strict
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface14
ip address 14.14.14.4 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 25
#
interface Vlan-interface34
ip address 34.34.34.4 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 10
mpls enable
mpls te enable
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 34
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 14
#
interface Tunnel1 mode mpls-te
ip address 9.2.2.4 255.255.255.0
ospf cost 12
ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path tun1
mpls te igp advertise
destination 2.2.2.2
#
Example: Configuring MPLS TE FRR
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, on the primary CRLSP Switch A—Switch B—Switch C—Switch D, configure MPLS TE FRR to protect the link Switch B—Switch C. When the link between Switch B and Switch C fails, MPLS TE can immediately switch traffic to the bypass tunnel Switch B—Switch E—Switch C.
The primary CRLSP and the bypass tunnel each require a bandwidth of 30000 kbps. The maximum bandwidth of the link that each tunnel traverses is 50000 kbps and the maximum reservable bandwidth is 40000 kbps.
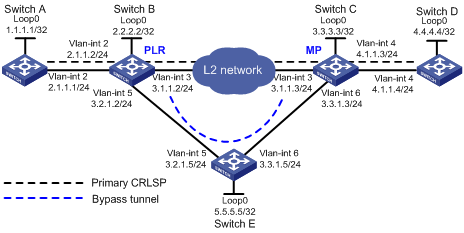
Analysis
To implement MPLS TE FRR, you must perform the following tasks:
· Enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE on each switch for primary and bypass tunnel establishment.
· Configure explicit paths for the primary CRLSP and the bypass tunnel as required.
· Configure BFD for RSVP-TE on Switch B and Switch C for quick detection of the link failure.
BFD can immediately detect the failure of the protected link and notify RSVP-TE of the failure.
· Configure MPLS TE FRR on the ingress node of the primary CRLSP to ensure that traffic can be immediately switched to the bypass tunnel when BFD detects the failure of the protected link.
· If multiple bypass tunnels are specified for a primary CRLSP, MPLS TE selects an optimal bypass tunnel to protect the primary CRLSP. To make sure an optimal bypass tunnel is always selected, set the optimal bypass tunnel selection interval to 5 seconds on the PLR. The default interval for selecting an optimal bypass tunnel is 300 seconds.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6520XE-HI switch series |
Supported in Release 11xx |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Not supported |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4520V2 switch series (except the MS4520V2-30F switch) |
Not supported |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure MPLS TE FRR, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· Before configuration, disable the spanning tree feature globally or map each VLAN to an MSTI.
· Only MPLS TE tunnels established through RSVP-TE support FRR.
· Do not configure both FRR and RSVP authentication on the same interface.
· Use bypass tunnels to protect only critical interfaces or links when bandwidth is insufficient. Bypass tunnels are pre-established and require extra bandwidth.
· Make sure the bandwidth assigned to the bypass tunnel is no less than the total bandwidth needed by all primary CRLSPs to be protected by the bypass tunnel. Otherwise, some primary CRLSPs might not be protected by the bypass tunnel.
· A bypass tunnel typically does not forward data when the primary CRLSP operates correctly. For a bypass tunnel to also forward data during tunnel protection, you must assign adequate bandwidth to the bypass tunnel.
· A bypass tunnel cannot be used for services such as VPN.
· You cannot configure FRR for a bypass tunnel. A bypass tunnel cannot act as a primary CRLSP.
· Make sure the protected node or interface is not on the bypass tunnel.
· After you associate a primary CRLSP that does not require bandwidth protection with a bypass tunnel that provides bandwidth protection, the primary CRLSP occupies the bandwidth that the bypass tunnel protects. The bandwidth is protected on a first-come-first-served basis. The primary CRLSP that needs bandwidth protection cannot preempt the one that does not need bandwidth protection.
· After an FRR, the primary CRLSP will be down if you modify the bandwidth that the bypass tunnel can protect and your modification results in one of the following:
¡ The CT type changes.
¡ The bypass tunnel cannot protect adequate bandwidth as configured.
¡ FRR protection type (whether or not to provide bandwidth protection for the primary CRLSP) changes.
Procedures
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces:
# Configure IP addresses and masks for interfaces on Switch A, including the loopback interface, as shown in Figure 3.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] vlan 2
[SwitchA-vlan2] port ten-gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchA-vlan2] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 2
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] ip address 2.1.1.1 24
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] quit
[SwitchA] interface loopback 0
[SwitchA-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[SwitchA-LoopBack0] quit
# Configure other devices in the same way that Switch A is configured. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF to ensure IP connectivity among the switches:
# Configure Switch A.
[SwitchA] ospf
[SwitchA-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchA-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Switch B.
[SwitchB] ospf
[SwitchB-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchB-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Switch C.
[SwitchC] ospf
[SwitchC-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchC-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Switch D.
[SwitchD] ospf
[SwitchD-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 4.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchD-ospf-1] quit
# Configure Switch E.
[SwitchE] ospf
[SwitchE-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
[SwitchE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchE-ospf-1] quit
# Execute the display ip routing-table command on each switch to verify that the switches have learned the routes to one another, including the routes to the loopback interfaces. The following shows the output on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 21 Routes : 21
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 Vlan2
2.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 Vlan2
2.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 Vlan2
2.2.2.2/32 O_INTRA 10 1 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
3.1.1.0/24 O_INTRA 10 2 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
3.2.1.0/24 O_INTRA 10 2 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
3.3.1.0/24 O_INTRA 10 3 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
3.3.3.3/32 O_INTRA 10 2 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
4.1.1.0/24 O_INTRA 10 3 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
4.4.4.4/32 O_INTRA 10 3 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
5.5.5.5/32 O_INTRA 10 2 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
3. Configure an LSR ID, and enable MPLS, MPLS TE, and RSVP-TE on each switch. Enable BFD for RSVP-TE on Switch B and Switch C:
# Configure Switch A.
[SwitchA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
[SwitchA] mpls te
[SwitchA-te] quit
[SwitchA] rsvp
[SwitchA-rsvp] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 2
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] mpls enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] mpls te enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] rsvp enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] quit
# Configure Switch B.
[SwitchB] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
[SwitchB] mpls te
[SwitchB-te] quit
[SwitchB] rsvp
[SwitchB-rsvp] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 2
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] mpls enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] mpls te enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] rsvp enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] mpls enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] mpls te enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] rsvp enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] rsvp bfd enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 5
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface5] mpls enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface5] mpls te enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface5] rsvp enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface5] quit
# Configure Switch C.
[SwitchC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
[SwitchC] mpls te
[SwitchC-te] quit
[SwitchC] rsvp
[SwitchC-rsvp] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] mpls enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] mpls te enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] rsvp enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] rsvp bfd enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 4
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface4] mpls enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface4] mpls te enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface4] rsvp enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface4] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 6
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface6] mpls enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface6] mpls te enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface6] rsvp enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface6] quit
# Configure Switch D.
[SwitchD] mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
[SwitchD] mpls te
[SwitchD-te] quit
[SwitchD] rsvp
[SwitchD-rsvp] quit
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 4
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface4] mpls enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface4] mpls te enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface4] rsvp enable
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface4] quit
# Configure Switch E.
[SwitchE] mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5
[SwitchE] mpls te
[SwitchE-te] quit
[SwitchE] rsvp
[SwitchE-rsvp] quit
[SwitchE] interface vlan-interface 5
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface5] mpls enable
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface5] mpls te enable
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface5] rsvp enable
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface5] quit
[SwitchE] interface vlan-interface 6
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface6] mpls enable
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface6] mpls te enable
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface6] rsvp enable
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface6] quit
4. Configure MPLS TE attributes of links:
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch A.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 2
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface2] quit
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch B.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 2
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface2] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 5
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface5] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface5] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface5] quit
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch C.
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface3] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 4
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface4] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface4] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface4] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 6
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface6] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface6] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface6] quit
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch D.
[SwitchD] interface vlan-interface 4
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface4] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface4] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchD-Vlan-interface4] quit
# Configure the maximum link bandwidth and maximum reservable bandwidth on Switch E.
[SwitchE] interface vlan-interface 5
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface5] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface5] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface5] quit
[SwitchE] interface vlan-interface 6
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface6] mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface6] mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
[SwitchE-Vlan-interface6] quit
5. Configure OSPF TE to advertise link TE attributes:
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch A. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchA] ospf
[SwitchA-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch A.
[SwitchA-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchA-ospf-1] quit
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch B. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchB] ospf
[SwitchB-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch B.
[SwitchB-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchB-ospf-1] quit
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch C. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchC] ospf
[SwitchC-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch C.
[SwitchC-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchC-ospf-1] quit
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch D. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchD] ospf
[SwitchD-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch D.
[SwitchD-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchD-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchD-ospf-1] quit
# Enable opaque LSA advertisement and reception on Switch E. By default, the opaque LSA advertisement and reception capability is enabled.
[SwitchE] ospf
[SwitchE-ospf-1] opaque-capability enable
# Enable MPLS TE for OSPF area 0 on Switch E.
[SwitchE-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] mpls te enable
[SwitchE-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchE-ospf-1] quit
6. Configure an MPLS TE tunnel on Switch A (the ingress node of the primary CRLSP):
# Configure an explicit path named pri-path for the primary CRLSP.
[SwitchA] explicit-path pri-path
[SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] nexthop 2.1.1.2
[SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] nexthop 3.1.1.3
[SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] nexthop 4.1.1.4
[SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] nexthop 4.4.4.4
[SwitchA-explicit-path-pri-path] quit
# Configure MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 4 for the primary CRLSP.
[SwitchA] interface tunnel4 mode mpls-te
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Specify the tunnel destination address as the LSR ID of Switch D, configure MPLS TE to use RSVP-TE to establish the tunnel, and assign 30000 kbps bandwidth to the tunnel.
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] destination 4.4.4.4
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] mpls te signaling rsvp-te
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] mpls te bandwidth 30000
# Specify the explicit path to be used as pri-path.
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path pri-path
# Enable FRR for the MPLS TE tunnel.
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] mpls te fast-reroute
[SwitchA-Tunnel4] quit
# Execute the display interface tunnel brief command on Switch A. The output shows that tunnel interface Tunnel 4 is up.
[SwitchA] display interface tunnel brief
Brief information on interfaces in route mode:
Link: ADM - administratively down; Stby - standby
Protocol: (s) - spoofing
Interface Link Protocol Primary IP Description
Tun4 UP UP 10.1.1.1
# Execute the display mpls te tunnel-interface command on Switch A to display detailed information about the MPLS TE tunnel.
[SwitchA] display mpls te tunnel-interface
Tunnel Name : Tunnel 4
Tunnel State : Up (Main CRLSP up, Shared-resource CRLSP down)
Tunnel Attributes :
LSP ID : 37325 Tunnel ID : 4
Admin State : Normal
Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.1 Egress LSR ID : 4.4.4.4
Signaling : RSVP-TE Static CRLSP Name : -
Resv Style : SE
Tunnel mode : -
Reverse-LSP name : -
Reverse-LSP LSR ID : - Reverse-LSP Tunnel ID: -
Class Type : CT0 Tunnel Bandwidth : 30000 kbps
Reserved Bandwidth : 30000 kbps
Setup Priority : 7 Holding Priority : 7
Affinity Attr/Mask : 0/0
Explicit Path : pri-path
Backup Explicit Path : -
Metric Type : TE
Record Route : Enabled Record Label : Enabled
FRR Flag : Enabled Bandwidth Protection : Disabled
Backup Bandwidth Flag: Disabled Backup Bandwidth Type: -
Backup Bandwidth : -
Bypass Tunnel : No Auto Created : No
Route Pinning : Disabled
Retry Limit : 3 Retry Interval : 2 sec
Reoptimization : Disabled Reoptimization Freq : -
Backup Type : None Backup LSP ID : -
Auto Bandwidth : Disabled Auto Bandwidth Freq : -
Min Bandwidth : - Max Bandwidth : -
Collected Bandwidth : -
7. Configure a bypass tunnel on Switch B (the PLR):
# Configure an explicit path named by-path for the bypass tunnel.
[SwitchB] explicit-path by-path
[SwitchB-explicit-path-by-path] nexthop 3.2.1.5
[SwitchB-explicit-path-by-path] nexthop 3.3.1.3
[SwitchB-explicit-path-by-path] nexthop 3.3.3.3
[SwitchB-explicit-path-by-path] quit
# Configure MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 5 for the bypass tunnel.
[SwitchB] interface tunnel 5 mode mpls-te
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
# Specify the tunnel destination address as the LSR ID of Switch C and configure MPLS TE to use RSVP-TE to establish the tunnel.
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] destination 3.3.3.3
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] mpls te signaling rsvp-te
# Set the bandwidth that the bypass tunnel can protect to 30000 kbps.
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] mpls te backup bandwidth 30000
# Specify the explicit path to be used as by-path.
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path by-path
[SwitchB-Tunnel5] quit
# Bind the bypass tunnel to the protected interface.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] mpls te fast-reroute bypass-tunnel tunnel 5
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] quit
# Execute the display interface tunnel brief command on Switch B. The output shows that tunnel interface Tunnel 5 is up.
[SwitchB] display interface tunnel brief
Brief information on interfaces in route mode:
Link: ADM - administratively down; Stby - standby
Protocol: (s) - spoofing
Interface Link Protocol Primary IP Description
Tun5 UP DOWN 11.1.1.1
8. Configure a static route on Switch A to direct traffic destined for 4.1.1.0/24 to MPLS TE tunnel interface Tunnel 4.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 4.1.1.0 24 tunnel 4 preference 1
Verifying the configuration
# Execute the display mpls lsp command on each switch. The output shows the LSP entries. Switch B has two CRLSPs. The bypass tunnel backs up the primary CRLSP.
[SwitchA] display mpls lsp
FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE
1.1.1.1/4/37325 RSVP -/1150 Vlan2
2.1.1.2 Local -/- Vlan2
Tunnel4 Local -/- NHLFE1026
[SwitchB] display mpls lsp
FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE
1.1.1.1/4/37325 RSVP 1150/1147 Vlan3
Backup 1150/1147 Tun5
2.2.2.2/5/18928 RSVP -/1149 Vlan5
3.1.1.3 Local -/- Vlan3
3.2.1.5 Local -/- Vlan5
Tunnel5 Local -/- NHLFE1027
[SwitchC] display mpls lsp
FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE
1.1.1.1/4/37325 RSVP 1147/3 Vlan4
2.2.2.2/5/18928 RSVP 3/- -
4.1.1.4 Local -/- Vlan4
# Shut down the protected interface VLAN-interface 3 on the PLR (Switch B).
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] shutdown
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] quit
# Execute the display interface tunnel 4 brief command on Switch A to display information about the primary CRLSP. The output shows that the tunnel interface is still up.
[SwitchA] display interface tunnel 4 brief
Brief information on interfaces in route mode:
Link: ADM - administratively down; Stby - standby
Protocol: (s) - spoofing
Interface Link Protocol Primary IP Description
Tun4 UP UP 10.1.1.1
# Execute the display mpls te tunnel-interface command on Switch A to display detailed information about the tunnel interface.
[SwitchA] display mpls te tunnel-interface
Tunnel Name : Tunnel 4
Tunnel State : Up (Main CRLSP up, Shared-resource CRLSP being set up)
Tunnel Attributes :
LSP ID : 37325 Tunnel ID : 4
Admin State : Normal
Ingress LSR ID : 1.1.1.1 Egress LSR ID : 4.4.4.4
Signaling : RSVP-TE Static CRLSP Name : -
Resv Style : SE
Tunnel mode : -
Reverse-LSP name : -
Reverse-LSP LSR ID : - Reverse-LSP Tunnel ID: -
Class Type : CT0 Tunnel Bandwidth : 30000 kbps
Reserved Bandwidth : 30000 kbps
Setup Priority : 7 Holding Priority : 7
Affinity Attr/Mask : 0/0
Explicit Path : pri-path
Backup Explicit Path : -
Metric Type : TE
Record Route : Enabled Record Label : Enabled
FRR Flag : Enabled Bandwidth Protection : Disabled
Backup Bandwidth Flag: Disabled Backup Bandwidth Type: -
Backup Bandwidth : -
Bypass Tunnel : No Auto Created : No
Route Pinning : Disabled
Retry Limit : 3 Retry Interval : 2 sec
Reoptimization : Disabled Reoptimization Freq : -
Backup Type : None Backup LSP ID : -
Auto Bandwidth : Disabled Auto Bandwidth Freq : -
Min Bandwidth : - Max Bandwidth : -
Collected Bandwidth : -
# Execute the display mpls lsp command on Switch B. The output shows that the bypass tunnel is in use.
[SwitchB] display mpls lsp
FEC Proto In/Out Label Interface/Out NHLFE
1.1.1.1/4/37325 RSVP 1150/1147 Tun5
2.2.2.2/5/18928 RSVP -/1149 Vlan5
3.2.1.5 Local -/- Vlan5
Tunnel5 Local -/- NHLFE1027
# On the PLR, configure the interval for selecting an optimal bypass tunnel as 5 seconds.
[SwitchB] mpls te
[SwitchB-te] fast-reroute timer 5
[SwitchB-te] quit
# On the PLR, bring up the protected interface VLAN-interface 3.
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 3
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] undo shutdown
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface3] quit
# Execute the display interface tunnel 4 brief command on Switch A. The output shows that the tunnel interface is in up state.
[SwitchA] display interface tunnel 4 brief
Brief information on interfaces in route mode:
Link: ADM - administratively down; Stby - standby
Protocol: (s) - spoofing
Interface Link Protocol Primary IP Description
Tun4 UP UP 10.1.1.1
# Wait for about 5 seconds, execute the display mpls lsp verbose command on Switch B. The output shows that Tunnel 5 is bound to interface VLAN-interface 3 but is not in use.
[SwitchB] display mpls lsp verbose
Destination : 4.4.4.4
FEC : 1.1.1.1/4/53319
Protocol : RSVP
LSR Type : Transit
Service : -
In-Label : 1150
Path ID : 0x540000003.1
State : Active
Out-Label : 1150
Nexthop : 3.1.1.3
Out-Interface: Vlan3
BkLabel : 1150
BkInterface : Tun5
Destination : 3.3.3.3
FEC : 2.2.2.2/5/16429
Protocol : RSVP
LSR Type : Ingress
Service : -
NHLFE ID : 1025
State : Active
Out-Label : 1151
Nexthop : 3.2.1.5
Out-Interface: Vlan5
Destination : 3.1.1.3
FEC : 3.1.1.3
Protocol : Local
LSR Type : Ingress
Service : -
NHLFE ID : 1027
State : Active
Nexthop : 3.1.1.3
Out-Interface: Vlan3
Destination : 3.2.1.5
FEC : 3.2.1.5
Protocol : Local
LSR Type : Ingress
Service : -
NHLFE ID : 1024
State : Active
Nexthop : 3.2.1.5
Out-Interface: Vlan5
Destination : 3.3.3.3
FEC : Tunnel5
Protocol : Local
LSR Type : Ingress
Service : -
NHLFE ID : 268435461
State : Active
Out-Interface: NHLFE1025
# Execute the display ip routing-table command on Switch A. The output shows a static route entry with interface Tunnel 4 as the output interface.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 25 Routes : 25
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 Vlan2
2.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 Vlan2
2.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
2.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 2.1.1.1 Vlan2
2.2.2.2/32 O_INTRA 10 1 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
3.1.1.0/24 O_INTRA 10 2 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
3.2.1.0/24 O_INTRA 10 2 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
3.3.1.0/24 O_INTRA 10 3 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
3.3.3.3/32 O_INTRA 10 2 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
4.1.1.0/24 Static 1 0 0.0.0.0 Tun4
4.4.4.4/32 O_INTRA 10 3 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
5.5.5.5/32 O_INTRA 10 2 2.1.1.2 Vlan2
10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Tun4
10.1.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Tun4
10.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 10.1.1.1 Tun4
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
224.0.0.0/4 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
224.0.0.0/24 Direct 0 0 0.0.0.0 NULL0
255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
Configuration files
· Switch A:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
network 2.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1
#
vlan 2
#
mpls te
#
explicit-path pri-path
nexthop index 1 2.1.1.2 include strict
nexthop index 101 3.1.1.3 include strict
nexthop index 201 4.1.1.4 include strict
nexthop index 301 4.4.4.4 include strict
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface2
ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 2
#
interface Tunnel4 mode mpls-te
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mpls te bandwidth ct0 30000
mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path pri-path
mpls te fast-reroute
destination 4.4.4.4
#
ip route-static 4.1.1.0 24 Tunnel4 preference 1
#
· Switch B:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 2.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
network 3.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 3.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2
#
vlan 2 to 3
#
vlan 5
#
mpls te
fast-reroute timer 5
#
explicit-path by-path
nexthop index 1 3.2.1.5 include strict
nexthop index 101 3.3.1.3 include strict
nexthop index 201 3.3.3.3 include strict
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface2
ip address 2.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface3
ip address 3.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
mpls te fast-reroute bypass-tunnel Tunnel5
rsvp enable
rsvp bfd enable
#
interface Vlan-interface5
ip address 3.2.1.2 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 2
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 3
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 5
#
interface Tunnel5 mode mpls-te
ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
mpls te backup bandwidth ct0 30000
mpls te path preference 1 explicit-path by-path
destination 3.3.3.3
#
· Switch C:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 3.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 3.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
network 4.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3
#
vlan 3 to 4
#
vlan 6
#
mpls te
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface3
ip address 3.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
rsvp bfd enable
#
interface Vlan-interface4
ip address 4.1.1.3 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface6
ip address 3.3.1.3 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 4
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 3
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 6
#
· Switch D:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 4.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.4
#
vlan 4
#
mpls te
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface4
ip address 4.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 4
#
· Switch E:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 3.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 3.3.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
mpls te enable
#
mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.5
#
vlan 5 to 6
#
mpls te
#
rsvp
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
#
interface Vlan-interface5
ip address 3.2.1.5 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Vlan-interface6
ip address 3.3.1.5 255.255.255.0
mpls enable
mpls te enable
mpls te max-link-bandwidth 50000
mpls te max-reservable-bandwidth 40000
rsvp enable
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 5
#
interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode bridge
port access vlan 6
#

