- Table of Contents
-
- H3C Fixed Port Campus Switches Configuration Examples-B70D022-6W100
- 01-Login Management Configuration Examples
- 02-RBAC Configuration Examples
- 03-Software Upgrade Examples
- 04-ISSU Configuration Examples
- 05-Software Patching Examples
- 06-Ethernet Link Aggregation Configuration Examples
- 07-Port Isolation Configuration Examples
- 08-Spanning Tree Configuration Examples
- 09-VLAN Configuration Examples
- 10-VLAN Tagging Configuration Examples
- 11-DHCP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 12-Cross-Subnet Dynamic IP Address Allocation Configuration Examples
- 13-IPv6 over IPv4 Manual Tunneling with OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 14-ISATAP Tunnel and 6to4 Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 15-GRE Tunnel Configuration Examples
- 16-GRE with OSPF Configuration Examples
- 17-OSPF Configuration Examples
- 18-IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 19-BGP Configuration Examples
- 20-Policy-Based Routing Configuration Examples
- 21-OSPFv3 Configuration Examples
- 22-IPv6 IS-IS Configuration Examples
- 23-Routing Policy Configuration Examples
- 24-IGMP Snooping Configuration Examples
- 25-IGMP Configuration Examples
- 26-BIDIR-PIM Configuration Examples
- 27-Multicast VPN Configuration Examples
- 28-MLD Snooping Configuration Examples
- 29-IPv6 Multicast VLAN Configuration Examples
- 30-Basic MPLS Configuration Examples
- 31-MPLS L3VPN Configuration Examples
- 32-ACL Configuration Examples
- 33-Control Plane-Based QoS Policy Configuration Examples
- 34-Traffic Policing Configuration Examples
- 35-GTS and Rate Limiting Configuration Examples
- 36-Priority Mapping and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 37-Traffic Filtering Configuration Examples
- 38-AAA Configuration Examples
- 39-Port Security Configuration Examples
- 40-Portal Configuration Examples
- 41-SSH Configuration Examples
- 42-IP Source Guard Configuration Examples
- 43-Ethernet OAM Configuration Examples
- 44-CFD Configuration Examples
- 45-DLDP Configuration Examples
- 46-VRRP Configuration Examples
- 47-BFD Configuration Examples
- 48-NTP Configuration Examples
- 49-SNMP Configuration Examples
- 50-NQA Configuration Examples
- 51-Mirroring Configuration Examples
- 52-sFlow Configuration Examples
- 53-OpenFlow Configuration Examples
- 54-MAC Address Table Configuration Examples
- 55-Static Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration Examples
- 56-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples
- 57-MVRP Configuration Examples
- 58-MCE Configuration Examples
- 59-Congestion Avoidance and Queue Scheduling Configuration Examples
- 60-Attack Protection Configuration Examples
- 61-Smart Link Configuration Examples
- 62-RRPP Configuration Examples
- 63-BGP Route Selection Configuration Examples
- 64-IS-IS Route Summarization Configuration Examples
- 65-IRF Configuration Examples
- 66-MPLS TE Configuration Examples
- 67-VXLAN Configuration Examples
- 68-VCF Fabric Configuration Examples
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 56-IP Unnumbered Configuration Examples | 78.69 KB |
Introduction
This document provides IP unnumbered configuration examples.
This feature enables an interface to borrow an IP address from another interface on the device when the borrowing interface does not have any IP addresses. The borrowing interface is called IP unnumbered interface.
Prerequisites
The configuration examples in this document were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
This document assumes that you have basic knowledge of IP unnumbered.
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure IP unnumbered, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· Loopback interfaces cannot borrow IP addresses of other interfaces.
· An interface cannot borrow an IP address from an unnumbered interface.
Example: Configuring IP unnumbered
Network configuration
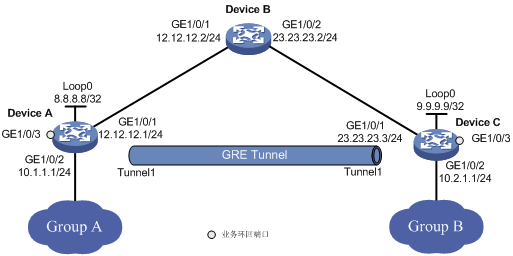
As shown in Figure 1, Group A and Group B are two private IPv4 networks. Device A and Device C will establish a GRE tunnel to interconnect Group 1 and Group 2.
To save IP address space, configure tunnel interface Tunnel 1 to borrow an IP address from the loopback interface loopback 0.
Applicable hardware and software versions
The following matrix shows the hardware and software versions to which this configuration example is applicable:
|
Hardware |
Software version |
|
S6520XE-HI switch series |
Supported in Release 11xx |
|
S5560X-EI switch series |
Supported in Release 111x |
|
S5500V2-EI switch series |
Supported in Release 111x |
|
MS4520V2-30F switch |
Supported in Release 111x |
|
S5560S-EI switch series S5560S-SI switch series |
Supported in Release 612x |
|
S5130S-HI switch series S5130S-EI switch series S5130S-SI switch series S5130S-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5120V2-SI switch series S5120V2-LI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S3100V3-EI switch series S3100V3-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2 switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5110V2-SI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000V3-EI switch series |
Not supported |
|
S5000E-X switch series |
Not supported |
|
WAS6000 switch series |
Not supported |
|
E128C switch E152C switch E500C switch series E500D switch series |
Not supported |
|
MS4520V2 switch series (except the MS4520V2-30F switch) |
Supported in Release 612x |
|
MS4320V2 switch series MS4300V2 switch series MS4320 switch series MS4200 switch series |
Not supported |
|
WS5850-WiNet switch series |
Supported in Release 612x |
|
WS5820-WiNet switch series WS5810-WiNet switch series |
Not supported |
Procedures
|
|
IMPORTANT: For the S6520XE-HI switch series, create a service loopback group and specify the unicast tunnel service for the group before you create a GRE tunnel. |
Configuring Device A
1. Assign IP addresses to the interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and loopback 0.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 12.12.12.1 24
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] interface loopback 0
[DeviceA-LoopBack0] ip address 8.8.8.8 32
[DeviceA-LoopBack0] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way an IP address is assigned to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF:
[DeviceA] ospf 1
# Create Area 0 and specify GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 whose IP address is on network 12.12.12.0/24 to run OSPF in Area 0.
[DeviceA-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.12.12.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceA-ospf-1] quit
3. Configure a GRE tunnel:
# Create service loopback group 1 and specify the unicast tunnel service for the group.
[DeviceA] service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to the service loopback group.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create a tunnel interface Tunnel 1, and specify the tunnel mode as GRE/IPv4.
[DeviceA] interface tunnel 1 mode gre
# Specify 12.12.12.1 as the source address of interface Tunnel 1.
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] source 12.12.12.1
# Specify 23.23.23.3 as the destination address of interface Tunnel 1.
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] destination 23.23.23.3
# Configure interface Tunnel 1 to borrow an IP address from loopback 0.
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 0
[DeviceA-Tunnel1] quit
# Configure a static route from Device A through the tunnel interface to Group B.
[DeviceA] ip route-static 10.2.1.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 1
Configuring Device B
1. Assign IP addresses to the interfaces:
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 12.12.12.2 24
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Assign an IP address to GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 in the same way an IP address is assigned to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF:
# Enable OSPF process 1.
[DeviceB] ospf 1
# Create Area 0 and specify GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 whose IP address is on network 12.12.12.0/24 to run OSPF in Area 0.
[DeviceB-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 12.12.12.0 0.0.0.255
# Create Area 0 and specify GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 whose IP address is on network 23.23.23.0/24 to run OSPF in Area 0.
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 23.23.23.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
Configuring Device C
1. Assign IP addresses to the interfaces:
# Assign IP addresses to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and loopback 0.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 23.23.23.3 24
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceC] interface loopback 0
[DeviceC-LoopBack0] ip address 9.9.9.9 32
[DeviceC-LoopBack0] quit
# Assign IP addresses to other interfaces in the same way an IP address is assigned to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF:
# Enable OSPF process 1.
[DeviceC] ospf 1
# Create Area 0 and specify GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 whose IP address is on network 23.23.23.0/24 to run OSPF in Area 0.
[DeviceC-ospf-1] area 0
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 23.23.23.0 0.0.0.255
[DeviceC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[DeviceC-ospf-1] quit
3. Configure a GRE tunnel:
# Create service loopback group 1 and specify the unicast tunnel service for the group.
[DeviceC] service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
# Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to the service loopback group.
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port service-loopback group 1
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Create a tunnel interface Tunnel 1, and specify the tunnel mode as GRE/IPv4.
[DeviceC] interface tunnel 1 mode gre
# Specify 23.23.23.3 as the source address of interface Tunnel 1.
[DeviceC-Tunnel1] source 23.23.23.3
# Specify 12.12.12.1 as the destination address of interface Tunnel 1.
[DeviceC-Tunnel1] destination 12.12.12.1
# Configure interface Tunnel 1 to borrow an IP address from loopback 0.
[DeviceC-Tunnel1] ip address unnumbered interface loopback 0
[DeviceC-Tunnel1] quit
# Configure a static route from Device C through the tunnel interface to Group A.
[DeviceC] ip route-static 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 tunnel 1
Verifying the configuration
This example uses Device A to verify the configuration.
# Verify that the interface Tunnel 1 has borrowed the IP address 8.8.8.8/32 from loopback 0.
[DeviceA] display interface tunnel 1
Tunnel1
Current state: UP
Line protocol state: UP
Description: Tunnel1 Interface
Bandwidth: 64kbps
Maximum transmission unit: 1476
Internet Address: 8.8.8.8/32 (Unnumbered)
Tunnel source 12.12.12.1, destination 23.23.23.3
Tunnel keepalive disabled
Tunnel TTL 255
Tunnel protocol/transport GRE/IP
GRE key disabled
Checksumming of GRE packets disabled
Last clearing of counters: Never
Last 300 seconds input rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Last 300 seconds output rate: 0 bytes/sec, 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
Input: 11 packets, 924 bytes, 0 drops
Output: 10 packets, 840 bytes, 0 drops
# Verify that GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Device A can ping the IP address of GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Device C.
[DeviceA] ping -a 10.1.1.1 10.2.1.1
Ping 10.2.1.1 (10.2.1.1) from 10.1.1.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 10.2.1.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=32.641 ms
56 bytes from 10.2.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=4.881 ms
56 bytes from 10.2.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=4.816 ms
56 bytes from 10.2.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=26.393 ms
56 bytes from 10.2.1.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=43.003 ms
--- Ping statistics for 10.2.1.1 ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 4.816/22.347/43.003/15.241 ms
Configuration files
|
|
IMPORTANT: The port link-mode bridge command is available only on the following switches: · S6520XE-HI switch series. · S5560X-EI switch series. · S5500V2-EI switch series. · MS4520V2-30F switch. For the S6520XE-HI switch series, a service loopback group of the unicast tunnel service type is required before you create a GRE tunnel. |
· Device A:
#
service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 12.12.12.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 8.8.8.8 255.255.255.255
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port service-loopback group 1
#
interface Tunnel1 mode gre
ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack0
source 12.12.12.1
destination 23.23.23.3
#
ip route-static 10.2.1.0 24 Tunnel1
#
· Device B:
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 12.12.12.0 0.0.0.255
network 23.23.23.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 12.12.12.2 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 23.23.23.2 255.255.255.0
#
· Device C:
#
service-loopback group 1 type tunnel
#
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 23.23.23.0 0.0.0.255
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 9.9.9.9 255.255.255.255
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port link-mode route
ip address 23.23.23.3 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
port link-mode route
ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
port link-mode bridge
port service-loopback group 1
#
interface Tunnel1 mode gre
ip address unnumbered interface LoopBack0
source 23.23.23.3
destination 12.12.12.1
#
ip route-static 10.1.1.0 24 Tunnel1
#