- Table of Contents
-
- H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches Switching Engine Configuration Guide-6W103
- 00-Preface
- 01-CLI Configuration
- 02-Login Configuration
- 03-Configuration File Management Configuration
- 04-VLAN Configuration
- 05-Auto Detect Configuration
- 06-Voice VLAN Configuration
- 07-GVRP Configuration
- 08-Basic Port Configuration
- 09-Link Aggregation Configuration
- 10-Port Isolation Configuration
- 11-Port Security-Port Binding Configuration
- 12-DLDP Configuration
- 13-MAC Address Table Management Configuration
- 14-MSTP Configuration
- 15-802.1x and System Guard Configuration
- 16-AAA Configuration
- 17-MAC Address Authentication Configuration
- 18-IP Address and Performance Configuration
- 19-DHCP Configuration
- 20-ACL Configuration
- 21-QoS-QoS Profile Configuration
- 22-Mirroring Configuration
- 23-ARP Configuration
- 24-SNMP-RMON Configuration
- 25-Multicast Configuration
- 26-NTP Configuration
- 27-SSH Configuration
- 28-File System Management Configuration
- 29-FTP-SFTP-TFTP Configuration
- 30-Information Center Configuration
- 31-System Maintenance and Debugging Configuration
- 32-VLAN-VPN Configuration
- 33-HWPing Configuration
- 34-DNS Configuration
- 35-Smart Link-Monitor Link Configuration
- 36-PoE-PoE Profile Configuration
- 37-Routing Protocol Configuration
- 38-UDP Helper Configuration
- 39-Acronyms
- 40-Index
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 06-Voice VLAN Configuration | 237.23 KB |
Table of Contents
How the Device Identifies Voice Traffic
Configuring Operation Mode for Voice VLAN
Support for Voice VLAN on Various Ports
Configuring a Voice VLAN to Operate in Automatic Mode
Configuring a Voice VLAN to Operate in Manual Mode
Displaying and Maintaining Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN Configuration Example
Voice VLAN Configuration Example (Automatic Mode)
Voice VLAN Configuration Example (Manual Mode)
![]()
The sample output information in this manual was created on the WX3024. The output information on your device may vary.
Voice VLAN Overview
Voice VLANs are VLANs configured specially for voice traffic. By adding the ports connected with voice devices to voice VLANs, you can have voice traffic transmitted within voice VLANs and perform QoS-related configuration for voice traffic as required, thus ensuring the transmission priority of voice traffic and voice quality.
How an IP Phone Works
IP phones can convert analog voice signals into digital signals to enable them to be transmitted in IP-based networks. Used in conjunction with other voice devices, IP phones can offer large-capacity and low-cost voice communication solutions. As network devices, IP phones need IP addresses to operate properly in a network. Normally, an IP telephone automatically acquires an IP address from a DHCP server in its network.
When an IP phone applies for an IP address from a DHCP server, the IP phone can also apply for the following extensive information from the DHCP server through the Option184 field:
l IP address of the network call processor (NCP)
l IP address of the secondary NCP server
l Voice VLAN configuration
l Failover call routing
![]()
The following contents just describe the IP address acquiring process of IP phones in general. Different IP phones may work differently. Refer to the IP Phones User Manual for details.
Following describes the way an IP phone acquires an IP address.
Figure 1-1 Network diagram for IP phones
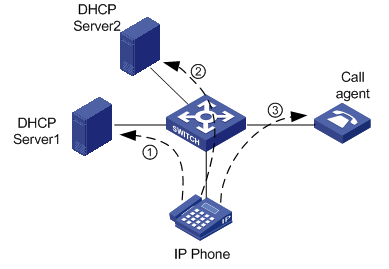
As shown in Figure 1-1, the IP phone needs to work in conjunction with the DHCP server and the NCP to establish a path for voice data transmission. An IP phone goes through the following three phases to become capable of transmitting voice data.
1) After the IP phone is powered on, it sends an untagged DHCP request message containing four special requests in the Option 184 field besides the request for an IP address. The message is broadcast in the default VLAN of the receiving port. After receiving the DHCP request message, DHCP Server1, which resides in the default VLAN of the port receiving the message, responds as follows:
l If DHCP Server1 does not support Option 184, it returns the IP address assigned to the IP phone but ignores the other four special requests in the Option 184 field. Without information about voice VLAN, the IP phone can only send untagged packets in the default VLAN of the port the IP phone is connected to. In this case, you need to manually configure the default VLAN of the port as a voice VLAN.
![]()
In cases where an IP phone obtains an IP address from a DHCP server that does not support Option 184, the IP phone directly communicates through the gateway after it obtains an IP address. It does not go through step 2 and step 3 described below.
l If DHCP Server1 supports Option 184, it returns the IP address assigned to the IP phone, the IP address of the NCP, the voice VLAN ID, and so on.
2) On acquiring the voice VLAN ID from DHCP Server1, the IP phone ignores the IP address assigned by DHCP Server1 and sends a new DHCP request message carrying the voice VLAN tag to the voice VLAN. After receiving the DHCP request, DHCP Server2 residing in the voice VLAN assigns a new IP address to the IP phone and sends a tagged response message to the IP phone. After the IP phone receives the tagged response message, it sends voice data packets tagged with the voice VLAN tag. In this case, the port on the device connecting to the IP phone must be configured to allow packets tagged with the voice VLAN tag to pass.
3) After the IP phone acquires the IP address assigned by DHCP Server2, the IP phone establishes a connection to the NCP specified by DHCP Server1 and downloads corresponding software. After that, the IP phone can communicate properly.
![]()
l An untagged packet carries no VLAN tag.
l A tagged packet carries the tag of a VLAN.
How the Device Identifies Voice Traffic
The device determines whether a received packet is a voice packet by checking its source MAC address. Packets with their source MAC addresses complying with the configured OUI (organizationally unique identifier) addresses are treated as voice packets. Ports receiving packets of this type will be added to the voice VLAN automatically for transmitting voice data.
You can configure OUI addresses for voice packets or specify to use the default OUI addresses.
![]()
An OUI address is a globally unique identifier assigned to a vendor by IEEE. You can determine which vendor a device belongs to according to the OUI address which forms the first 24 bits of a MAC address. The WX3000 supports OUI address mask configuration. You can adjust the matching depth of MAC address by setting different OUI address masks.
The following table lists the five default OUI addresses on the device.
Table 1-1 Default OUI addresses preset on the device
|
Number |
OUI address |
Vendor |
|
1 |
0003-6b00-0000 |
Cisco phones |
|
2 |
000f-e200-0000 |
H3C Aolynk phones |
|
3 |
00d0-1e00-0000 |
Pingtel phones |
|
4 |
00e0-7500-0000 |
Polycom phones |
|
5 |
00e0-bb00-0000 |
3Com phones |
Configuring Operation Mode for Voice VLAN
A voice VLAN can operate in two modes: automatic and manual. You can configure the operation mode for the voice VLAN according to data traffic passing through a port.
Processing mode of untagged packets sent by IP voice devices
l Automatic mode. A WX3000 device automatically adds a port connecting an IP voice device to the voice VLAN by learning the source MAC address in the untagged packet sent by the IP voice device when it is powered on. The voice VLAN uses the aging mechanism to maintain the number of ports in the voice VLAN. When the aging timer expires, the ports whose OUI addresses are not updated (that is, no voice traffic passes) will be removed from the voice VLAN. In automatic mode, ports can not be added to or removed from a voice VLAN manually.
l Manual mode: In this mode, you need to add a port to a voice VLAN or remove a port from a voice VLAN manually.
Processing mode of tagged packets sent by IP voice devices
Tagged packets from IP voice devices are forwarded based on their tagged VLAN IDs, whether the automatic or manual mode is used.
![]()
l If the voice traffic transmitted by an IP voice device carries VLAN tags, and 802.1x authentication and guest VLAN is enabled on the port which the IP voice device is connected to, assign different VLAN IDs for the voice VLAN, the default VLAN of the port, and the 802.1x guest VLAN to ensure the effective operation of these functions.
l If the voice traffic transmitted by an IP voice device carries no VLAN tag, the default VLAN of the port which the IP voice device is connected to must be configured as the voice VLAN. In this case, the 802.1x authentication is unavailable.
Support for Voice VLAN on Various Ports
Voice VLAN packets can be forwarded by access ports, trunk ports, and hybrid ports. You can enable a trunk or hybrid port belonging to other VLANs to forward voice and service packets simultaneously by enabling the voice VLAN.
The support for different types of voice traffic (that is, tagged traffic and untagged traffic) varies with port mode and port type, as listed in Table 1-2.
Table 1-2 Matching relationship between port types and voice traffic types
|
Port voice VLAN mode |
Voice traffic type |
Port type |
Supported or not |
|
Automatic mode |
Tagged voice traffic |
Access |
Not supported |
|
Trunk |
Supported Make sure the default VLAN of the port exists and is not a voice VLAN. And the access port permits the traffic of the default VLAN. |
||
|
Hybrid |
Supported Make sure the default VLAN of the port exists and is not a voice VLAN. The default VLAN must be in the list of the tagged VLANs whose traffic is permitted by the access port. |
||
|
Untagged voice traffic |
Access |
Not supported, because the default VLAN of the port must be a voice VLAN and the access port is in the voice VLAN. This can be done by adding the port to the voice VLAN manually. |
|
|
Trunk |
|||
|
Hybrid |
|||
|
Manual mode |
Tagged voice traffic |
Access |
Not supported |
|
Trunk |
Supported Make sure the default VLAN of the port exists and is not a voice VLAN. And the access port permits the traffic of the default VLAN. |
||
|
Hybrid |
Supported Make sure the default VLAN of the port exists and is in the list of the tagged VLANs whose traffic is permitted by the access port. |
||
|
Untagged voice traffic |
Access |
Supported Make sure the default VLAN of the port is a voice VLAN. |
|
|
Trunk |
Supported Make sure the default VLAN of the port is a voice VLAN and the port permits the traffic of the VLAN. |
||
|
Hybrid |
Supported Make sure the default VLAN of the port is a voice VLAN and is in the list of untagged VLANs whose traffic is permitted by the port. |
Security Mode of Voice VLAN
On the WX3000 devices, a voice VLAN can operate in the security mode. Voice VLANs operating in this mode only permit voice data, enabling you to perform voice traffic-specific priority configuration. With the security mode disabled, both voice data and service data can be transmitted in a voice VLAN.
Voice VLAN Configuration
Configuration Prerequisites
l Create the corresponding VLAN before configuring a voice VLAN.
l VLAN 1 (the default VLAN) cannot be configured as a voice VLAN.
Configuring a Voice VLAN to Operate in Automatic Mode
Follow these steps to configure a voice VLAN to operate in automatic mode:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set an OUI address that can be identified by the voice VLAN |
voice vlan mac-address oui mask oui-mask [ description text ] |
Optional By default, the device determines the voice traffic according to the default OUI address. |
|
Enable the voice VLAN security mode |
voice vlan security enable |
Optional By default, the voice VLAN security mode is enabled. |
|
Set the aging time for the voice VLAN |
voice vlan aging minutes |
Optional The default aging time is 1,440 minutes. |
|
Enable the voice VLAN function globally |
voice vlan vlan-id enable |
Required |
|
Enter Ethernet port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required |
|
Enable the voice VLAN function on a port |
voice vlan enable |
Required By default, voice VLAN is disabled. |
|
Enable the voice VLAN legacy function on the port |
voice vlan legacy |
Optional By default, voice VLAN legacy is disabled. |
|
Set the voice VLAN operation mode on a port to automatic. |
voice vlan mode auto |
Optional The default voice VLAN operation mode on a port is automatic. |
![]()
l For a voice VLAN operating in automatic mode, it does not support the adding of an Access port, and thus a voice VLAN cannot function when configuring with the VLAN VPN function.
l For a voice VLAN operating in automatic mode, it only supports that the Hybrid port to process the tagged voice traffic. However, the protocol VLAN feature requires the Hybrid port to remove tags from the packets, see VLAN in H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches Switching Engine Configuration Guide for details. Therefore, a VLAN cannot be configured as a voice VLAN and a protocol VLAN simultaneously.
l For a port operating in automatic mode, a default VLAN cannot be configured as a voice VLAN; otherwise the system prompts you for unsuccessful configuration.
![]()
When the voice VLAN is working normally, if the device restarts, in order to make the established voice connections work normally, the system does not need to be triggered by the voice traffic to add the port in automatic mode to the local devices of the voice VLAN but does so immediately after the restart.
Configuring a Voice VLAN to Operate in Manual Mode
Follow these steps to configure a voice VLAN to operate in manual mode:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
||
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
||
|
Set an OUI address that can be identified by the voice VLAN |
voice vlan mac-address oui mask oui-mask [ description text ] |
Optional Without this address, the default OUI address is used. |
||
|
Enable the voice VLAN security mode |
voice vlan security enable |
Optional By default, the voice VLAN security mode is enabled. |
||
|
Set the aging time for a voice VLAN |
voice vlan aging minutes |
Optional The default aging time is 1,440 minutes. |
||
|
Enable the voice VLAN function globally |
voice vlan vlan-id enable |
Required |
||
|
Enter port view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
Required |
||
|
Enable voice VLAN on a port |
voice vlan enable |
Required By default, voice VLAN is disabled on a port. |
||
|
Enable the voice VLAN legacy function on the port |
voice vlan legacy |
Optional By default, voice VLAN legacy is disabled. |
||
|
Set voice VLAN operation mode on a port to manual |
undo voice vlan mode auto |
Required The default voice VLAN operation mode on a port is automatic. |
||
|
Quit to system view |
quit |
— |
||
|
Add a port in manual mode to the voice VLAN |
Access port |
Enter VLAN view |
vlan vlan-id |
Required By default, all the ports belong to VLAN 1. |
|
Add the port to the VLAN |
port interface-list |
|||
|
Trunk or Hybrid port |
Enter port view |
interface interface-type interface-num |
||
|
Add the port to the VLAN |
port trunk permit vlan vlan-id port hybrid vlan vlan-id { tagged | untagged } |
|||
|
Configure the voice VLAN to be the default VLAN of the port |
port trunk pvid vlan vlan-id port hybrid pvid vlan vlan-id |
Optional Refer to Table 1-2 to determine whether or not this operation is needed. |
||
![]()
l The voice VLAN function can be enabled for only one VLAN at one time.
l If the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is enabled on a port, voice VLAN feature cannot be enabled on it.
l Voice VLAN function can be enabled only for the static VLAN. A dynamic VLAN cannot be configured as a voice VLAN.
l When ACL number applied to a port reaches to its threshold, voice VLAN cannot be enabled on this port. You can use the display voice vlan error-info command to locate such ports.
l When a voice VLAN operates in security mode, the device in it permits only the packets whose source addresses are the identified voice OUI addresses. Packets whose source addresses cannot be identified, including certain authentication packets (such as 802.1x authentication packets), will be dropped. Therefore, you are suggested not to transmit both voice data and service data in a voice VLAN. If you have to do so, make sure that the voice VLAN does not operate in security mode.
l The voice VLAN legacy feature realizes the communication between the WX3000 series devices and other vendor's voice devices by automatically adding the voice VLAN tag to the voice data coming from other vendors’ voice device. The voice vlan legacy command can be executed before voice VLAN is enabled globally and on a port, but it takes effect only after voice VLAN is enabled globally and on the port.
To add a Trunk port or a Hybrid port to the voice VLAN, refer to Basic Port Configurations in H3C WX3000 Series Unified Switches Switching Engines Command Reference for the related command.
Displaying and Maintaining Voice VLAN
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display the information about ports on which voice VLAN configuration fails |
display voice vlan error-info |
You can execute the display command in any view. |
|
Display the voice VLAN configuration status |
display voice vlan status |
|
|
Display the currently valid OUI addresses |
display voice vlan oui |
|
|
Display the ports operating in the current voice VLAN |
display vlan vlan-id |
Voice VLAN Configuration Example
Voice VLAN Configuration Example (Automatic Mode)
Network requirements
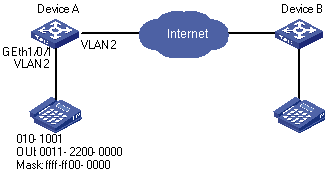
Create a voice VLAN and configure it to operate in automatic mode to enable the port to which an IP phone is connected to join or exit the voice VLAN automatically and voice traffic to be transmitted within the voice VLAN, as shown in Figure 1-2.
l Create VLAN 2 and configure it as a voice VLAN, with the aging time being 100 minutes.
l The IP phone sends tagged packets. It is connected to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, a hybrid port, with VLAN 6 being its default VLAN. Set this port to operate in automatic mode.
l You need to add a user-defined OUI address 0011-2200-000, with the mask being ffff-ff00-0000 and the description string being “test”.
Figure 1-2 Network diagram for voice VLAN configuration (automatic mode)
Configuration procedure
# Create VLAN 2 and VLAN 6.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 2
[DeviceA-vlan2] quit
[DeviceA] vlan 6
[DeviceA-vlan6] quit
# Set the aging time for the voice VLAN.
[DeviceA] voice vlan aging 100
# Add a user-defined OUI address 0011-2200-000 and set the description string to “test”.
[DeviceA] voice vlan mac-address 0011-2200-0000 mask ffff-ff00-0000 description test
# Enable the voice VLAN function globally.
[DeviceA] voice vlan 2 enable
# Configure the vocie VLAN to operate in automatic mode on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. This operation is optional. By default, a voice VLAN operates in automatic mode on a port.
[DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] voice vlan mode auto
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type hybrid
# Configure VLAN 6 as the default VLAN of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to permit packets with the tag of VLAN 6.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port hybrid pvid vlan 6
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 6 tagged
# Enable the voice VLAN function on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] voice vlan enable
Voice VLAN Configuration Example (Manual Mode)
Network requirements
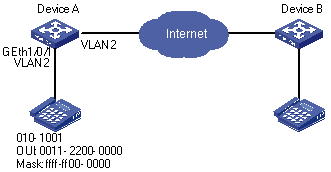
Create a voice VLAN and configure it to operate in manual mode. Add the port to which an IP phone is connected to the voice VLAN to enable voice traffic to be transmitted within the voice VLAN, as shown in Figure 1-3.
l Create VLAN 2 and configure it as a voice VLAN. Set the voice VLAN to operate in security mode
l The IP phone sends untagged packets. It is connected to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, a hybrid port. Set this port to operate in manual mode.
l You need to add a user-defined OUI address 0011-2200-000, with the mask being ffff-ff00-0000 and the description string being “test”.
Figure 1-3 Network diagram for voice VLAN configuration (manual mode)
Configuration procedure
# Enable the security mode for the voice VLAN so that the ports in the voice VLAN permit valid voice packets only. This operation is optional. The security mode is enabled by default.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] voice vlan security enable
# Add a user-defined OUI address 0011-2200-000 and set the description string to “test”.
[DeviceA] voice vlan mac-address 0011-2200-0000 mask ffff-ff00-0000 description test
# Create VLAN 2 and configure it as a voice VLAN.
[DeviceA] vlan 2
[DeviceA-vlan2] quit
[DeviceA] voice vlan 2 enable
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to operate in manual mode.
[DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo voice vlan mode auto
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type hybrid
# Configure the voice VLAN as the default VLAN of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and add the voice VLAN to the list of untagged VLANs whose traffic is permitted by the port.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port hybrid pvid vlan 2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 2 untagged
# Enable the voice VLAN function on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] voice vlan enable
Verification
# Display the OUI addresses, the corresponding OUI address masks and the corresponding description strings that the system supports.
<DeviceA> display voice vlan oui
Oui Address Mask Description
0003-6b00-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 Cisco phone
000f-e200-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 H3C Aolynk phone
0011-2200-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 test
00d0-1e00-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 Pingtel phone
00e0-7500-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 Polycom phone
00e0-bb00-0000 ffff-ff00-0000 3Com phone
# Display the status of the current voice VLAN.
<DeviceA> display voice vlan status
Voice Vlan status: ENABLE
Voice Vlan ID: 2
Voice Vlan security mode: Security
Voice Vlan aging time: 1440 minutes
Current voice vlan enabled port mode:
PORT MODE
----------------------------------------
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 MANUAL

