- Table of Contents
-
- 06-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA Configuration
- 02-802.1X Configuration
- 03-MAC Authentication Configuration
- 04-Triple Authentication Configuration
- 05-Port Security Configuration
- 06-User Profile Configuration
- 07-HABP Configuration
- 08-Public Key Configuration
- 09-PKI Configuration
- 10-SSH2.0 Configuration
- 11-SSL Configuration
- 12-TCP Attack Protection Configuration
- 13-IP Source Guard Configuration
- 14-ARP Attack Protection Configuration
- 15-ND Attack Defense Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 15-ND Attack Defense Configuration | 105.10 KB |
ND attack defense configuration
Introduction to ND attack defense
Enabling source MAC consistency check for ND packets
Configuring the ND detection function
Displaying and maintaining ND detection
ND detection configuration example
This chapter includes these sections:
· Introduction to ND attack defense
· Enabling source MAC consistency check for ND packets
· Configuring the ND detection function
· ND detection configuration example
|
|
NOTE: · The term "switch" or "device" in this chapter refers to the switching engine on a WX3000E wireless switch. · The WX3000E series comprises WX3024E and WX3010E wireless switches. · The port numbers in this chapter are for illustration only. |
Introduction to ND attack defense
The IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (ND) protocol provides rich functions, such as address resolution, neighbor reachability detection, duplicate address detection, router/prefix discovery and address autoconfiguration, and redirection. However, it does not provide any security mechanisms. Attackers can easily exploit the ND protocol to attack hosts and gateways by sending forged packets.
The ND protocol implements its function by using five types of ICMPv6 messages:
· Neighbor Solicitation (NS)
· Neighbor Advertisement (NA)
· Router Solicitation (RS)
· Router Advertisement (RA)
· Redirect (RR)
An attacker can attack a network by sending forged ICMPv6 messages, as shown in Figure 1:
· Sends forged NS/NA/RS packets with the IPv6 address of a victim host. The gateway and other hosts update the ND entry for the victim host with incorrect address information. As a result, all packets intended for the victim host are sent to the attacking host rather than the victim host.
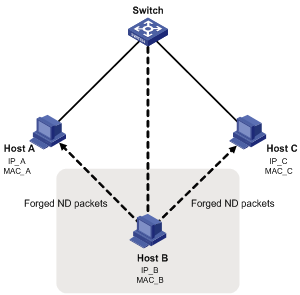
All forged ND packets have two common features:
· The Ethernet frame header and the source link layer address option of the ND packet contain different source MAC addresses.
· The mapping between the source IPv6 address and the source MAC address in the Ethernet frame header is invalid.
To identify forged ND packets, H3C developed the source MAC consistency check and ND detection features.
|
|
NOTE: For more information about the five functions of the ND protocol, see the Layer 3 Configuration Guide. |
Enabling source MAC consistency check for ND packets
Use source MAC consistency check on a gateway to filter out ND packets that carry different source MAC addresses in the Ethernet frame header and the source link layer address option.
Follow these steps to enable source MAC consistency check for ND packets:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable source MAC consistency check for ND packets |
ipv6 nd mac-check enable |
Required Disabled by default. |
Configuring the ND detection function
Introduction to ND detection
Use the ND detection function on access devices to verify the source of ND packets. If an ND packet comes from a spoofing host or gateway, it is discarded.
The ND detection function operates on a per VLAN basis. In an ND detection-enabled VLAN, a port is either ND-trusted or ND-untrusted:
· An ND-trusted port does not check ND packets for address spoofing.
· An ND-untrusted port checks all ND packets but RA and RR messages in the VLAN for source spoofing. RA and RR messages are considered illegal and discarded directly.
The ND detection function checks an ND packet by looking up the IPv6 static bindings table of the IP source guard function, ND snooping table, and DHCPv6 snooping table in the following steps:
1. Looks up the IPv6 static bindings table of IP source guard, based on the source IPv6 address and the source MAC address in the Ethernet frame header of the ND packet. If an exact match is found, the ND packet is forwarded. If an entry matches the source IPv6 address but not the source MAC address, the ND packet is discarded. If no entry matches the source IPv6 address, the ND detection function continues to look up the DHCPv6 snooping table and the ND snooping table.
2. If an exact match is found in either the DHCPv6 snooping or ND snooping table, the ND packet is forwarded. If no match is found in either table, the packet is discarded. If neither the DHCPv6 snooping table nor the ND snooping table is available, the ND packet is discarded.
|
|
NOTE: · To create IPv6 static bindings with IP source guard, use the user-bind ipv6 command. For more information, see the chapter “IP source guard configuration.” · The DHCPv6 snooping table is created automatically by the DHCPv6 snooping module. For more information, see the Layer 3 Configuration Guide. · The ND snooping table is created automatically by the ND snooping module. For more information, see the Layer 3 Configuration Guide. |
Configuring ND detection
Follow these steps to configure ND detection:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
–– |
|
Enter VLAN view |
vlan vlan-id |
–– |
|
Enable ND Detection |
ipv6 nd detection enable |
Required Disabled by default. |
|
Quit system view |
quit |
–– |
|
Enter Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
–– |
|
Configure the port as an ND-trusted port |
ipv6 nd detection trust |
Optional A port does not trust sources of ND packets by default. |
|
|
NOTE: · ND detection performs source check by using the binding tables of IP source guard, DHCPv6 snooping, and ND snooping. To prevent an ND-untrusted port from discarding legal ND packets in an ND detection-enabled VLAN, ensure that at least one of the three functions is available. · When creating an IPv6 static binding with IP source guard for ND detection in a VLAN, specify the VLAN ID for the binding. If not, no ND packets in the VLAN can match the binding. |
Displaying and maintaining ND detection
|
To do… |
Use the command |
Remarks |
|
Display the ND detection configuration |
display ipv6 nd detection [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display the statistics of discarded packets when the ND detection checks the user legality |
display ipv6 nd detection statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Clear the statistics by ND detection |
reset ipv6 nd detection statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
Available in user view |
ND detection configuration example
Network requirements
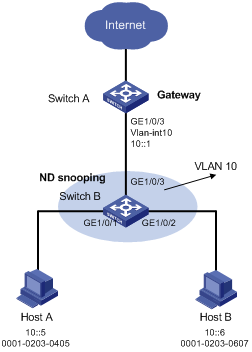
As shown in Figure 2, Host A and Host B connect to Switch A, the gateway, through Switch B. Host A has the IPv6 address 10::5 and MAC address 0001-0203-0405. Host B has the IPv6 address 10::6 and MAC address 0001-0203-0607.
Enable ND detection on Switch B to filter out forged ND packets.
Network diagram
Figure 2 Network diagram for ND detection configuration
Configuration procedure
1. Configuring Switch A
# Enable IPv6 forwarding.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ipv6
# Create VLAN 10.
[SwitchA] vlan 10
[SwitchA-vlan10] quit
# Assign port GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 10.
[SwitchA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 10
[SwitchA-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Assign an IPv6 address to VLAN-interface 10.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] ipv6 address 10::1/64
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface10] quit
2. Configuring Switch B
# Enable IPv6 forwarding.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ipv6
# Create VLAN 10.
[SwitchB] vlan 10
[SwitchB-vlan10] quit
# Assign ports GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 to VLAN 10.
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 10
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
# Enable ND snooping in VLAN 10.
[SwitchB] vlan 10
[SwitchB-vlan 10] ipv6 nd snooping enable
# Enable ND detection in VLAN 10.
[SwitchB-vlan 10] ipv6 nd detection enable
[SwitchB-vlan 10] quit
# Configure the uplink port GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as an ND-trusted port, and the downlink ports GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as ND-untrusted ports (the default).
[SwitchB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[SwitchB-GigabitEthernet 1/0/3] ipv6 nd detection trust
The configuration enables Switch B to check all incoming ND packets of ports GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 based on the ND snooping table.

