- Table of Contents
-
- 06-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA Configuration
- 02-802.1X Configuration
- 03-MAC Authentication Configuration
- 04-Triple Authentication Configuration
- 05-Port Security Configuration
- 06-User Profile Configuration
- 07-HABP Configuration
- 08-Public Key Configuration
- 09-PKI Configuration
- 10-SSH2.0 Configuration
- 11-SSL Configuration
- 12-TCP Attack Protection Configuration
- 13-IP Source Guard Configuration
- 14-ARP Attack Protection Configuration
- 15-ND Attack Defense Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-Triple Authentication Configuration | 124.47 KB |
Content
Triple authentication configuration·
Introduction to triple authentication
Triple authentication mechanism
Triple authentication configuration task list
Triple authentication configuration examples
Triple authentication basic function configuration example
Triple authentication supporting VLAN assignment and Auth-Fail VLAN configuration example
This chapter includes these sections:
· Introduction to triple authentication
· Triple authentication configuration task list
· Triple authentication configuration examples
|
|
NOTE: · The term "switch" or "device" in this chapter refers to the switching engine on a WX3000E wireless switch. · The WX3000E series comprises WX3024E and WX3010E wireless switches. · The port numbers in this chapter are for illustration only. |
Introduction to triple authentication
Overview
Triple authentication enables a Layer 2 access port to perform MAC and 802.1X authentication. A terminal can access the network if it passes one type of authentication.
Triple authentication is suitable for a LAN that comprises terminals that require different authentication services. For example, the triple authentication-enabled access port in Figure 1 can perform MAC authentication for the printer, 802.1X authentication for a PC installed with the 802.1X client, and port authentication for the other PC.
Figure 1 Triple authentication network diagram
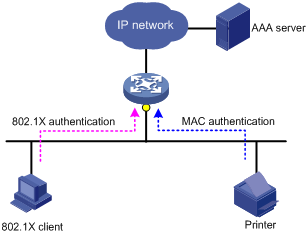
|
|
NOTE: For more information about MAC authentication and 802.1X authentication, see the chapters ”MAC authentication configuration,” and “802.1X configuration” in the Security Configuration Guide. |
Triple authentication mechanism
The three types of authentication are triggered by different packets:
· The access port performs MAC authentication for a terminal when it receives an ARP or DHCP broadcast packet from the terminal for the first time. If the terminal passes MAC authentication, the terminal can access the network. If the MAC authentication fails, the access port performs 802.1X authentication.
· The access port performs 802.1X authentication when it receives an EAP packet from an 802.1X client. If the unicast trigger function of 802.1X is enabled on the access port, any packet from an 802.1X client can trigger an 802.1X authentication.
If a terminal triggers different types of authentication, the authentications are processed at the same time. The failure of one type of authentication does not affect the others. When a terminal passes one type of authentication, the other types of authentication being performed are terminated. Then, whether the other types of authentication can be triggered varies:
· If a terminal passes 802.1X authentication, no other types of authentication will be triggered for the terminal.
· If the terminal passes MAC authentication, 802.1X authentication can be triggered. When the terminal passes 802.1X authentication, the 802.1X authentication information will overwrite the MAC authentication information for the terminal.
Extended functions
A triple authentication enabled access port also supports these extended functions:
· Auth-Fail VLAN or MAC authentication guest VLAN
· Detection of online terminals
VLAN assignment
After a terminal passes authentication, the authentication server assigns an authorized VLAN to the access port for the access terminal. The terminal can then access the network resources in the authorized VLAN.
Auth-Fail VLAN or MAC authentication guest VLAN
After a terminal fails authentication, the access port:
· Adds the terminal to an Auth-Fail VLAN, if it uses 802.1X authentication service.
· Adds the terminal to a MAC authentication guest VLAN, if it uses MAC authentication service.
A terminal may undergo all three types of authentication. If it fails to pass all types of authentication, the access port adds the terminal to the 802.1X Auth-Fail VLAN.
ACL assignment
You can specify an authorization ACL for an authenticated user to control its access to network resources. After the user passes MAC authentication, the authentication server, either the local access device or a RADIUS server, assigns the ACL onto the access port to filter traffic for the user.
You must configure the ACLs on the access device, whether the authentication server is the access device or a remote AAA server.
Detection of online terminals
· You can enable the online handshake or periodic re-authentication function to detect online 802.1X clients at a configurable interval.
· You can enable an offline detection timer to detect online MAC authentication terminals at a configurable interval.
|
|
NOTE: For more information about the extended functions, see the chapters “802.1X configuration,” and “MAC authentication configuration.” |
Triple authentication configuration task list
Complete the following tasks to configure triple authentication:
|
Task |
Remarks |
Reference |
|
|
Configure 802.1X authentication |
Required Configure at least one type of authentication |
MAC-based access control (macbased) is required. H3C does not recommend you configure guest VLANs. |
802.1X configuration in the Security Configuration Guide. |
|
Configure MAC authentication |
— |
MAC authentication configuration in the Security Configuration Guide. |
|
Triple authentication configuration examples
Triple authentication basic function configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, the terminals are connected to a switch to access the IP network. Configure triple authentication on the Layer-2 interface of the switch that connects to the terminals so that a terminal passing one of the three authentication methods, 802.1X authentication and MAC authentication, can access the IP network. More specifically,
· Configure static IP addresses in network 192.168.1.0/24 for the terminals.
· Use the remote RADIUS server to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting and configure the switch to send usernames carrying no ISP domain names to the RADIUS server.
Figure 2 Network diagram for triple authentication basic configuration
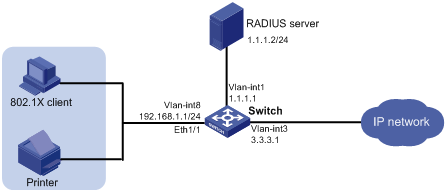
Configuration procedure
|
|
NOTE: Complete the configuration on the RADIUS server and make sure the authentication, authorization, and accounting functions work normally. In this example, configure on the RADIUS server an 802.1X user (with username userdot), and a MAC authentication user (with a username and password both being the MAC address of the printer 001588f80dd7). |
1. Configure 802.1X authentication
# Enable 802.1X authentication globally.
[Switch] dot1x
# Enable 802.1X authentication (MAC-based access control required) on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x port-method macbased
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
2. Configure MAC authentication
# Enable MAC authentication globally.
[Switch] mac-authentication
# Enable MAC authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mac-authentication
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
3. Configure a RADIUS scheme
# Create a RADIUS scheme named rs1.
[Switch] radius scheme rs1
# Specify the server type for the RADIUS scheme, which must be extended when the CAMS or iMC server is used.
[Switch-radius-rs1] server-type extended
# Specify the primary authentication and accounting servers and keys.
[Switch-radius-rs1] primary authentication 1.1.1.2
[Switch-radius-rs1] primary accounting 1.1.1.2
[Switch-radius-rs1] key authentication radius
[Switch-radius-rs1] key accounting radius
# Specify usernames sent to the RADIUS server to carry no domain names.
[Switch-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-domain
[Switch-radius-rs1] quit
4. Configure an ISP domain
# Create an ISP domain named triple.
[Switch] domain triple
# Configure the default AAA methods for all types of users in the domain.
[Switch-isp-triple] authentication default radius-scheme rs1
[Switch-isp-triple] authorization default radius-scheme rs1
[Switch-isp-triple] accounting default radius-scheme rs1
[Switch-isp-triple] quit
# Configure domain triple as the default domain. If a username input by a user includes no ISP domain name, the authentication scheme of the default domain is used.
[Switch] domain default enable triple
Verification
User userdot uses the 802.1X client to initiate authentication. After inputting the correct username and password, the user can pass 802.1X authentication. The printer can pass MAC authentication after being connected to the network.
Use the display connection command to view online users.
[Switch] display connection
Slot: 1
Index=31 , Username=userdot@triple
IP=192.168.1.3
IPv6=N/A
MAC=0002-0002-0001
Index=32 , Username=001588f80dd7@triple
IP=192.168.1.4
IPv6=N/A
MAC=0015-88f8-0dd7
Total 2 connection(s) matched on slot 1.
Total 2 connection(s) matched.
Triple authentication supporting VLAN assignment and Auth-Fail VLAN configuration example
Network requirement
As shown in Figure 3, the terminals are connected to a switch to access the IP network. Configure triple authentication on the Layer-2 interface of the switch which connects to the terminals so that a terminal passing one of the three authentication methods, 802.1X authentication, and MAC authentication, can access the IP network. More specifically,
· 802.1X terminals use IP addresses in 192.168.1.0/24 before authentication, and request IP addresses in 3.3.3.0/24 through DHCP after passing authentication. If the terminal fails authentication, it uses an IP address in 2.2.2.0/24.
· After passing authentication, the printer obtains the IP address 3.3.3.111/24 that is bound with its MAC address through DHCP.
· Use the remote RADIUS server to perform authentication, authorization, and accounting and configure the switch to remove the ISP domain names from usernames sent to the RADIUS server.
· Configure VLAN 3 as the authorized VLAN on the RADIUS server. Users passing authentication are added to this VLAN.
· Configure VLAN 2 as the Auth-Fail VLAN on the access device. Users failing authentication are added to this VLAN, and are allowed to access only the Update server.
Figure 3 Network diagram for triple authentication supporting VLAN assignment and Auth-Fail VLAN
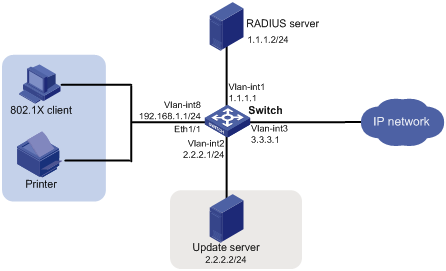
Configuration procedure
|
|
NOTE: · When using an external DHCP server, ensure that the terminals can get IP addresses from the server before and after authentication. · Complete the configuration on the RADIUS server, and make sure the authentication, authorization, and accounting functions work normally. In this example, configure on the RADIUS server an 802.1X user (with username userdot), a MAC authentication user (with a username and password both being the MAC address of the printer 001588f80dd7), and an authorized VLAN (VLAN 3). · Complete the configuration of PKI domain pkidm and acquire the local and CA certificates. For more information, see the chapter “PKI configuration.” · Complete the editing of a self-defined default authentication page file, compress the file to a zip file named defaultfile and save the zip file at the root directory. |
1. Configure DHCP
# Configure VLANs and IP addresses for the VLAN interfaces, and add ports to specific VLANs (omitted).
# Enable DHCP.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] dhcp enable
# Exclude the IP address of the update server from assignment.
[Switch] dhcp server forbidden-ip 2.2.2.2
# Configure IP address pool 1, including the address range, lease and gateway address. A short lease is recommended to shorten the time terminals use to re-acquire IP addresses after the terminals passing or failing authentication.
[Switch] dhcp server ip-pool 1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-1] network 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Switch-dhcp-pool-1] expired day 0 hour 0 minute 1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-1] gateway-list 192.168.1.1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-1] quit
|
|
NOTE: A short lease is recommended to shorten the time that terminals use to re-acquire IP addresses after passing or failing authentication. However, in some applications, a terminal can require a new IP address before the lease duration expires. For example, the iNode 802.1X client automatically renews its IP address after disconnecting from the server. |
# Configure IP address pool 2, including the address range, lease and gateway address. A short lease is recommended to shorten the time terminals use to re-acquire IP addresses after the terminals pass authentication.
[Switch] dhcp server ip-pool 2
[Switch-dhcp-pool-2] network 2.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Switch-dhcp-pool-2] expired day 0 hour 0 minute 1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-2] gateway-list 2.2.2.1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-2] quit
# Configure IP address pool 3, including the address range, lease and gateway address. A short lease is recommended to shorten the time terminals use to re-acquire IP addresses after the terminals are offline.
[Switch] dhcp server ip-pool 3
[Switch-dhcp-pool-3] network 3.3.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0
[Switch-dhcp-pool-3] expired day 0 hour 0 minute 1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-3] gateway-list 3.3.3.1
[Switch-dhcp-pool-3] quit
# Configure IP address pool 4, and bind the printer MAC address 0015-e9a6-7cfe to the IP address 3.3.3.111/24 in this address pool.
[Switch] dhcp server ip-pool 4
[Switch-dhcp-pool-4] static-bind ip-address 3.3.3.111 mask 255.255.255.0
[Switch-dhcp-pool-4] static-bind mac-address 0015-e9a6-7cfe
[Switch-dhcp-pool-4] quit
2. Configure 802.1X authentication
# Enable 802.1X authentication globally.
[Switch] dot1x
# Enable 802.1X authentication (MAC-based access control required) on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and specify VLAN 2 as the Auth-Fail VLAN.
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x port-method macbased
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x auth-fail vlan 2
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
3. Configure MAC authentication
# Enable MAC authentication globally.
[Switch] mac-authentication
# Enable MAC authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, and specify VLAN 2 as the Auth-Fail VLAN
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mac-authentication
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mac-authentication guest-vlan 2
[Switch–GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
4. Configure a RADIUS scheme
# Create a RADIUS scheme named rs1.
[Switch] radius scheme rs1
# Specify the server type for the RADIUS scheme, which must be extended when the CAMS or iMC server is used.
[Switch-radius-rs1] server-type extended
# Specify the primary authentication and accounting servers and keys.
[Switch-radius-rs1] primary authentication 1.1.1.2
[Switch-radius-rs1] primary accounting 1.1.1.2
[Switch-radius-rs1] key authentication radius
[Switch-radius-rs1] key accounting radius
# Specify usernames sent to the RADIUS server to carry no domain names.
[Switch-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-domain
[Switch-radius-rs1] quit
5. Configure an ISP domain
# Create an ISP domain named triple.
[Switch] domain triple
# Configure the default AAA methods for all types of users in the domain.
[Switch-isp-triple] authentication default radius-scheme rs1
[Switch-isp-triple] authorization default radius-scheme rs1
[Switch-isp-triple] accounting default radius-scheme rs1
[Switch-isp-triple] quit
# Configure domain triple as the default domain. If a username input by a user includes no ISP domain name, the authentication scheme of the default domain is used.
[Switch] domain default enable triple
Verification
User userdot uses the 802.1X client to initiate authentication. After inputting the correct username and password, the user can pass 802.1X authentication. The printer can pass MAC authentication after being connected to the network.
Use the display connection command to view connection information about online users.
[Switch] display connection
Slot: 1
Index=31 , Username=userdot@triple
IP=3.3.3.2
IPv6=N/A
MAC=0002-0002-0001
Index=32 , Username=001588f80dd7@triple
IP=N/A
IPv6=N/A
MAC=0015-88f8-0dd7
Total 2 connection(s) matched on slot 1.
Total 2 connection(s) matched.
Use the display mac-vlan all command to view the MAC-VLAN entries of online users. VLAN 3 is the authorized VLAN.
[Switch] display mac-vlan all
The following MAC VLAN addresses exist:
S:Static D:Dynamic
MAC ADDR MASK VLAN ID PRIO STATE
--------------------------------------------------------
0002-0002-0001 ffff-ffff-ffff 3 0 D
0015-88f8-0dd7 ffff-ffff-ffff 3 0 D
Total MAC VLAN address count:2
Use the display dhcp server ip-in-use command to view the IP addresses assigned to online users.
[Switch] display dhcp server ip-in-use all
Pool utilization: 0.59%
IP address Client-identifier/ Lease expiration Type
Hardware address
3.3.3.2 0002-0002-0001 Dec 15 2009 17:41:02 Auto:COMMITTED
3.3.3.3 0015-e9a6-7cfe Unlimited Manual
--- total 2 entry ---
When a terminal fails authentication, it is added to VLAN 2. You can also use the display commands to view the MAC-VLAN entry and IP address of the terminal.

