- Table of Contents
-
- 06-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA Configuration
- 02-802.1X Configuration
- 03-MAC Authentication Configuration
- 04-Triple Authentication Configuration
- 05-Port Security Configuration
- 06-User Profile Configuration
- 07-HABP Configuration
- 08-Public Key Configuration
- 09-PKI Configuration
- 10-SSH2.0 Configuration
- 11-SSL Configuration
- 12-TCP Attack Protection Configuration
- 13-IP Source Guard Configuration
- 14-ARP Attack Protection Configuration
- 15-ND Attack Defense Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Port Security Configuration | 198.66 KB |
Contents
Support for guest VLAN and Auth-Fail VLAN
Port security configuration task list
Setting port security’s limit on the number of MAC addresses on a port
Setting the port security mode
Configuring port security features
Configuring intrusion protection
Configuring secure MAC addresses
Ignoring authorization information from the server
Displaying and maintaining port security
Port security configuration examples
Configuring the autoLearn mode
Configuring the userLoginWithOUI mode
Configuring the macAddressElseUserLoginSecure mode
Cannot set the port security mode
Cannot configure secure MAC addresses
Cannot change port security mode when a user is online
This chapter includes these sections:
· Port security configuration task list
· Displaying and maintaining port security
· Port security configuration examples
· Troubleshooting port security
|
|
NOTE: · The term "switch" or "device" in this chapter refers to the switching engine on a WX3000E wireless switch. · The WX3000E series comprises WX3024E and WX3010E wireless switches. · The port numbers in this chapter are for illustration only. |
Port security overview
Port security provides MAC-based network access control. It prevents unauthorized access to the network by checking the source MAC address of inbound traffic and prevents access to unauthorized devices by checking the destination MAC address of outbound traffic.
Port security enables you to control MAC address learning and authentication on ports. The feature ensures that a port learns only legal source MAC addresses.
A frame is illegal, if its source MAC address cannot be learned in a port security mode or it is from a client that has failed 802.1X or MAC authentication.
The port security feature can automatically take a pre-defined action on illegal frames. This automatic mechanism enhances network security and reduces human intervention.
|
|
NOTE: The security modes of the port security feature provide extended and combined use of 802.1X authentication and MAC authentication. They apply to scenarios that require both 802.1X authentication and MAC authentication. For scenarios that require only 802.1X authentication or MAC authentication, H3C recommends you configure 802.1X authentication or MAC authentication rather than port security. For more information about 802.1X and MAC authentication, see the chapters “802.1X configuration” and “MAC authentication configuration.” |
Port security features
NTK
The need to know (NTK) feature prevents traffic interception by checking the destination MAC address in the outbound frames. The feature ensures that frames are sent only to hosts that have passed authentication or whose MAC addresses have been learned or configured on the access device.
Intrusion protection
The intrusion protection feature checks the source MAC address in inbound frames for illegal frames and takes a pre-defined action on each detected illegal frame. The action can be disabling the port temporarily, disabling the port permanently, or blocking frames from the illegal MAC address for three minutes (not user configurable).
Port security traps
You can configure the port security module to send traps for port security events such as login, logoff, and MAC authentication. These traps help you monitor user behaviors.
Port security modes
Port security supports the following categories of security modes:
· MAC learning control—Includes two modes, autoLearn and secure. MAC address learning is permitted on a port in autoLearn mode and disabled in secure mode.
· Authentication—Security modes in this category implement MAC authentication, 802.1X authentication, or a combination of these two authentication methods.
Upon receiving a frame, the port in a security mode searches the MAC address table for the source MAC address. If a match is found, the port forwards the frame. If no match is found, the port learns the MAC address or performs authentication, depending on the security mode. If the frame is illegal, the port takes the pre-defined NTK, intrusion protection, or trapping action.
Table 1 describes the port security modes and the security features.
|
Purpose |
Security mode |
Features that can be triggered |
|
|
Turning off the port security feature |
noRestrictions (the default mode) In this mode, port security is disabled on the port and access to the port is not restricted. |
— |
|
|
autoLearn |
NTK/intrusion protection |
||
|
secure |
|||
|
userLogin |
— |
||
|
userLoginSecure |
NTK/intrusion protection |
||
|
userLoginSecureExt |
|||
|
userLoginWithOUI |
|||
|
macAddressWithRadius |
NTK/intrusion protection |
||
|
Performing a combination of MAC authentication and 802.1X authentication |
Or |
macAddressOrUserLoginSecure |
NTK/intrusion protection |
|
macAddressOrUserLoginSecureExt |
|||
|
Else |
macAddressElseUserLoginSecure |
||
|
macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt |
|||
|
· userLogin specifies 802.1X authentication and port-based access control. · macAddress specifies MAC authentication. · Else specifies that the authentication method before Else is applied first. If the authentication fails, whether to turn to the authentication method following Else depends on the protocol type of the authentication request. · Typically, in a security mode with Or, which authentication method is to be used depends on the protocol type of the authentication request. · userLogin with Secure specifies 802.1X authentication and MAC-based access control. · Ext indicates allowing multiple 802.1X users to be authenticated and serviced at the same time. A security mode without Ext allows only one user to pass 802.1X authentication. |
|||
Controlling MAC address learning
1. autoLearn
A port in this mode can learn MAC addresses, and allows frames from learned or configured MAC addresses to pass. The automatically learned MAC addresses are secure MAC addresses. You can also configure secure MAC addresses by using the port-security mac-address security command. A secure MAC address never ages out by default.
When the number of secure MAC addresses reaches the upper limit, the port transitions to secure mode.
The dynamic MAC address learning function in MAC address management is disabled on ports operating in autoLearn mode, but you can configure MAC addresses by using the mac-address dynamic and mac-address static commands.
2. secure
MAC address learning is disabled on a port in secure mode. You configure MAC addresses by using the mac-address static and mac-address dynamic commands.
A port in secure mode allows only frames sourced from secure MAC addresses and manually configured MAC addresses to pass.
Performing 802.1X authentication
1. userLogin
A port in this mode performs 802.1X authentication and implements port-based access control. The port can service multiple 802.1X users. If one 802.1X user passes authentication, all the other 802.1X users of the port can access the network without authentication.
2. userLoginSecure
A port in this mode performs 802.1X authentication and implements MAC-based access control. The port services only one user passing 802.1X authentication.
3. userLoginSecureExt
This mode is similar to the userLoginSecure mode except that this mode supports multiple online 802.1X users.
4. userLoginWithOUI
This mode is similar to the userLoginSecure mode. The difference is that a port in this mode also permits frames from one user whose MAC address contains a specified organizationally unique identifier (OUI).
For wired users, the port performs 802.1X authentication upon receiving 802.1X frames, and performs OUI check upon receiving non-802.1X frames.
Performing MAC authentication
macAddressWithRadius: A port in this mode performs MAC authentication and services multiple users.
Performing a combination of MAC authentication and 802.1X authentication
1. macAddressOrUserLoginSecure
This mode is the combination of the macAddressWithRadius and userLoginSecure modes.
For wired users, the port performs MAC authentication upon receiving non-802.1X frames and performs 802.1X authentication upon receiving 802.1X frames.
2. macAddressOrUserLoginSecureExt
This mode is similar to the macAddressOrUserLoginSecure mode except that a port in this mode supports multiple 802.1X and MAC authentication users.
3. macAddressElseUserLoginSecure
This mode is the combination of the macAddressWithRadius and userLoginSecure modes, with MAC authentication having a higher priority as the Else keyword implies.
For non-802.1X frames, a port in this mode performs only MAC authentication. For 802.1X frames, it performs MAC authentication and then, if the authentication fails, 802.1X authentication.
4. macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt
This mode is similar to the macAddressElseUserLoginSecure mode except that a port in this mode supports multiple 802.1X and MAC authentication users as the keyword Ext implies.
|
|
NOTE: · The maximum number of users a port supports equals the maximum number of MAC addresses that port security allows or the maximum number of concurrent users the authentication mode in use allows, whichever is smaller. For example, if 802.1X allows less concurrent users than port security’s limit on the number of MAC addresses on the port in userLoginSecureExt mode, port security’s limit takes effect. · For more information about configuring MAC address table entries, see the Layer 2 Configuration Guide. |
Support for guest VLAN and Auth-Fail VLAN
An 802.1X guest VLAN is the VLAN that a user is in before initiating authentication. An 802.1X Auth-Fail VLAN or a MAC authentication guest VLAN is the VLAN that a user is in after failing authentication. Support for the guest VLAN and Auth-Fail VLAN features varies with security modes.
· You can use the 802.1X guest VLAN and 802.1X Auth-Fail VLAN features together with port security modes that support 802.1X authentication. For more information about the 802.1X guest VLAN and Auth-Fail VLAN on a port that performs MAC-based access control, see the chapter “802.1X configuration.”
· You can use the MAC authentication VLAN feature together with security modes that support MAC authentication. For more information about the MAC authentication guest VLAN, see the chapter “MAC authentication configuration.”
|
|
NOTE: If you configure both an 802.1X Auth-Fail VLAN and a MAC authentication guest VLAN on a port that performs MAC-based access control, the 802.1X Auth-Fail VLAN has a higher priority. |
Port security configuration task list
Complete the following tasks to configure port security:
|
Task |
Remarks |
|
|
Required |
||
|
Setting port security’s limit on the number of MAC addresses on a port |
Optional |
|
|
Required |
||
|
Optional Configure one or more features as required. |
||
|
Optional |
||
|
Optional |
||
Enabling port security
Configuration prerequisites
Disable 802.1X and MAC authentication globally.
Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to enable port security:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable port security |
port-security enable |
Required The port security is disabled by default . |
Enabling or disabling port security resets the following security settings to the default:
· 802.1X access control mode is MAC-based, and the port authorization state is auto.
· Port security mode is noRestrictions.
When port security is enabled, you cannot manually enable 802.1X or MAC authentication, or change the access control mode or port authorization state. The port security automatically modifies these settings in different security modes.
You cannot disable port security when online users are present.
|
|
NOTE: · For more information about 802.1X configuration, see the chapter “802.1X configuration.” · For more information about MAC authentication configuration, see the chapter “MAC authentication configuration.” |
Setting port security’s limit on the number of MAC addresses on a port
You can set the maximum number of MAC addresses that port security allows on a port for the following purposes:
· Controlling the number of concurrent users on the port. The maximum number of concurrent users on the port equals this limit or the limit of the authentication mode (802.1X for example) in use, whichever is smaller.
· Controlling the number of secure MAC addresses on the port in autoLearn mode.
Follow these steps to set the maximum number of secure MAC addresses allowed on a port:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Set the limit of port security on the number of MAC addresses |
port-security max-mac-count count-value |
Required Not limited by default |
|
|
NOTE: The port security’s limit on the number of MAC addresses on a port is independent of the MAC learning limit described in MAC address table configuration in the Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide. |
Setting the port security mode
Configuration prerequisites
Before you set a port security mode for a port, complete the following tasks:
· Disable 802.1X and MAC authentication.
· Check that the port does not belong to any aggregation group.
· If you are configuring the autoLearn mode, set port security’s limit on the number of MAC addresses. You cannot change the setting when the port is operating in autoLearn mode.
|
|
NOTE: · You can specify a port security mode when port security is disabled, but your configuration cannot take effect. · You cannot change the port security mode of a port when online users are present. |
Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to enable a port security mode:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Set an OUI value for user authentication |
port-security oui oui-value index index-value |
Optional Not configured by default. The command is required for the userlogin-withoui mode. |
|
Enter interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Set the port security mode |
port-security port-mode { autolearn | mac-authentication | mac-else-userlogin-secure | mac-else-userlogin-secure-ext | secure | userlogin | userlogin-secure | userlogin-secure-or-mac | userlogin-secure-or-mac-ext | userlogin-withoui } |
Required By default, a port operates in noRestrictions mode. |
|
|
NOTE: · An OUI, as defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), is the first 24 bits of the MAC address, which uniquely identifies a device vendor. · A port in userLoginWithOUI mode allows only one 802.1X user and one user whose MAC address contains any specified OUI to pass authentication concurrently. · After enabling port security, you can change the port security mode of a port only when the port is operating in noRestrictions (the default) mode. To change the port security mode for a port in any other mode, use the undo port-security port-mode command to restore the default port security mode first. |
Configuring port security features
Configuring NTK
The NTK feature checks the destination MAC addresses in outbound frames to make sure that frames are forwarded only to authenticated devices. Any unicast frame with an unknown destination MAC address is discarded.
The NTK feature supports the following modes:
· ntkonly—Forwards only unicast frames with authenticated destination MAC addresses.
· ntk-withbroadcasts—Forwards only broadcast frames and unicast frames with authenticated destination MAC addresses.
· ntk-withmulticasts—Forwards only broadcast frames, multicast frames, and unicast frames with authenticated destination MAC addresses.
Follow these steps to configure the NTK feature:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Configure the NTK feature |
port-security ntk-mode { ntk-withbroadcasts | ntk-withmulticasts | ntkonly } |
Required By default, NTK is disabled on a port and all frames are allowed to be sent. The device supports only the ntk-withmulticast mode. |
|
|
NOTE: Whether the NTK feature can be triggered depends on the port security mode. For more information, see Table 1. |
Configuring intrusion protection
The intrusion protection enables a device to take one of the following actions in response to illegal frames:
· blockmac—Adds the source MAC addresses of illegal frames to the blocked MAC addresses list and discards the frames. All subsequent frames sourced from a blocked MAC address will be dropped. A blocked MAC address is restored to normal state after being blocked for three minutes. The interval is fixed and cannot be changed.
· disableport—Disables the port until you bring it up manually.
· disableport-temporarily—Disables the port for a specified period of time. The period can be configured with the port-security timer disableport command.
Follow these steps to configure the intrusion protection feature:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Configure the intrusion protection feature |
port-security intrusion-mode { blockmac | disableport | disableport-temporarily } |
Required By default, intrusion protection is disabled. |
|
Return to system view |
quit |
— |
|
Set the silence timeout period during which a port remains disabled |
port-security timer disableport time-value |
Optional 20 seconds by default |
|
|
NOTE: On a port operating in either the macAddressElseUserLoginSecure mode or the macAddressElseUserLoginSecureExt mode, intrusion protection is triggered only after both MAC authentication and 802.1X authentication for the same frame fail. |
Enabling port security traps
You can configure the port security module to send traps for the following categories of events:
· addresslearned—Learning of new MAC addresses.
· dot1xlogfailure/dot1xlogon/dot1xlogoff—802.1X authentication failure, success, and 802.1X user logoff.
· ralmlogfailure/ralmlogon/ralmlogoff—MAC authentication failure, MAC authentication user logon, and MAC authentication user logoff.
· intrusion—Detection of illegal frames.
Follow these steps to enable port security traps:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enable port security traps |
port-security trap { addresslearned | dot1xlogfailure | dot1xlogoff | dot1xlogon | intrusion | ralmlogfailure | ralmlogoff | ralmlogon } |
Required By default, port security traps are disabled. |
Configuring secure MAC addresses
Secure MAC addresses are MAC addresses configured or learned in autoLearn mode. They can survive link down/up events, and once saved, can survive a device reboot. You can bind a MAC address to only one port in a VLAN.
Static secure MAC addresses are manually configured at the command line or in the MIB in autoLearn mode. No aging mechanism is available for this type of MAC address. They never age out unless you manually remove them, change the port security mode, or disable the port security feature.
When the maximum number of secure MAC address entries is reached, the port changes to secure mode, and no more secure MAC addresses can be added or learned. The port allows only frames sourced from a secure MAC address or a MAC address configured with the mac-address dynamic or mac-address static command to pass through.
Configuration prerequisites
· Enable port security.
· Set port security’s limit on the number of MAC addresses on the port. Perform this task before you enable autoLearn mode.
· Set the port security mode to autoLearn.
Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to configure a secure MAC address:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
|
Configure a secure MAC address |
In system view |
port-security mac-address security mac-address interface interface-type interface-number vlan vlan-id |
Required Use either approach No secure MAC address is configured by default. |
|
In interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
||
|
port-security mac-address security mac-address vlan vlan-id |
|||
Ignoring authorization information from the server
The authorization information is delivered by the RADIUS server to the device after an 802.1X user or MAC authenticated user passes RADIUS authentication. You can configure a port to ignore the authorization information from the RADIUS server.
Follow these steps to configure a port to ignore the authorization information from the RADIUS server:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Enter system view |
system-view |
— |
|
Enter interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
|
Ignore the authorization information from the RADIUS server |
port-security authorization ignore |
Required By default, a port uses the authorization information from the RADIUS server. |
Displaying and maintaining port security
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
|
Display port security configuration information, operation information, and statistics about one or more ports or all ports |
display port-security [ interface interface-list ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display information about secure MAC addresses |
display port-security mac-address security [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
|
Display information about blocked MAC addresses |
display port-security mac-address block [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ vlan vlan-id ] [ count ] [ | { begin | exclude | include } regular-expression ] |
Available in any view |
Port security configuration examples
Configuring the autoLearn mode
Network requirements
See Figure 1. Configure port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 on the Switch, as follows:
· Accept up to 64 users on the port without authentication.
· Permit the port to learn and add MAC addresses as MAC addresses, and set the MAC aging timer to 30 minutes.
· After the number of secure MAC addresses reaches 64, the port stops learning MAC addresses. If any frame with an unknown MAC address arrives, intrusion protection starts, and the port shuts down and stays silent for 30 seconds.
Figure 1 Network diagram for configuring the autoLearn mode
Configuration procedure
1. Configure port security
# Enable port security.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] port-security enable
# Enable intrusion protection traps on port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Switch] port-security trap intrusion
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
# Set the port security mode to autoLearn.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security port-mode autolearn
# Configure the port to be silent for 30 seconds after the intrusion protection feature is triggered.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security intrusion-mode disableport-temporarily
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[Switch] port-security timer disableport 30
2. Verify the configuration
After completing the configurations, you can use the following command to view the port security configuration information:
<Switch> display port-security interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
Equipment port-security is enabled
Intrusion trap is enabled
Disableport Timeout: 30s
OUI value:
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is link-up
Port mode is autoLearn
NeedToKnow mode is disabled
Intrusion Protection mode is DisablePortTemporarily
Max MAC address number is 64
Stored MAC address number is 0
Authorization is permitted
The output shows that the port security's limit on the number of secure MAC addresses on the port is 64, the port security mode is autoLearn, intrusion protection traps are enabled, and the intrusion protection action is disabling the port (DisablePortTemporarily) for 30 seconds.
You can also use the command repeatedly to track the number of MAC addresses learned by the port, or use the display this command in interface view to display the secure MAC addresses learned:
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] display this
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
port-security max-mac-count 64
port-security port-mode autolearn
port-security mac-address security 0002-0000-0015 vlan 1
port-security mac-address security 0002-0000-0014 vlan 1
port-security mac-address security 0002-0000-0013 vlan 1
port-security mac-address security 0002-0000-0012 vlan 1
port-security mac-address security 0002-0000-0011 vlan 1
#
Issuing the display port-security interface command after the number of MAC addresses learned by the port reaches 64, you will see that the port security mode has changed to secure. When any frame with a new MAC address arrives, intrusion protection is triggered and you will see the following traps:
#Jul 14 10:39:47:135 2009 Switch PORTSEC/4/VIOLATION:Traph3cSecureViolation
An intrusion occurs!
IfIndex: 9437185
Port: 9437185
MAC Addr: 00:02:00:00:00:32
VLAN ID: 1
IfAdminStatus: 1
In addition, you will see that the port security feature has disabled the port if you issue the following command:
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] display interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 current state: Port Security Disabled
IP Packet Frame Type: PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware Address: 000f-cb00-5558
Description: GigabitEthernet1/0/1 Interface
......
The port should be re-enabled 30 seconds later.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] display interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 current state: UP
IP Packet Frame Type: PKTFMT_ETHNT_2, Hardware Address: 000f-cb00-5558
Description: GigabitEthernet1/0/1 Interface
......
If you manually delete several secure MAC addresses, the port security mode of the port will be restored to autoLearn, and the port will be able to learn MAC addresses again.
Configuring the userLoginWithOUI mode
Network requirements
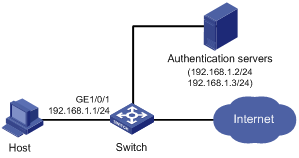
As shown in Figure 2, a client is connected to the Switch through port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. The Switch authenticates the client with a RADIUS server. If the authentication succeeds, the client is authorized to access the Internet.
· The RADIUS server at 192.168.1.2 functions as the primary authentication server and the secondary accounting server, and the RADIUS server at 192.168.1.3 functions as the secondary authentication server and the primary accounting server. The shared key for authentication is name, and that for accounting is money.
· All users use the default authentication, authorization, and accounting methods of ISP domain sun, which can accommodate up to 30 users.
· The RADIUS server response timeout time is five seconds and the maximum number of RADIUS packet retransmission attempts is five. The Switch sends real-time accounting packets to the RADIUS server at an interval of 15 minutes, and sends user names without domain names to the RADIUS server.
Configure port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of the Switch to:
· Allow only one 802.1X user to be authenticated.
· Allow up to 16 OUI values to be configured and allow one terminal that uses any of the OUI values to access the port in addition to an 802.1X user.
Figure 2 Network diagram for configuring the userLoginWithOUI mode
Configuration procedure
|
|
NOTE: · The following configuration steps cover some AAA/RADIUS configuration commands. For more information about the commands, see the chapter “AAA configuration.” · Configurations on the host and RADIUS servers are omitted. |
1. Configure the RADIUS protocol
# Configure a RADIUS scheme named radsun.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] radius scheme radsun
[Switch-radius-radsun] primary authentication 192.168.1.2
[Switch-radius-radsun] primary accounting 192.168.1.3
[Switch-radius-radsun] secondary authentication 192.168.1.3
[Switch-radius-radsun] secondary accounting 192.168.1.2
[Switch-radius-radsun] key authentication name
[Switch-radius-radsun] key accounting money
[Switch-radius-radsun] timer response-timeout 5
[Switch-radius-radsun] retry 5
[Switch-radius-radsun] timer realtime-accounting 15
[Switch-radius-radsun] user-name-format without-domain
[Switch-radius-radsun] quit
# Configure ISP domain sun to use RADIUS scheme radsun for authentication, authorization, and accounting of all types of users. Specify that the ISP domain can contain up to 30 users.
[Switch] domain sun
[Switch-isp-sun] authentication default radius-scheme radsun
[Switch-isp-sun] authorization default radius-scheme radsun
[Switch-isp-sun] accounting default radius-scheme radsun
[Switch-isp-sun] access-limit enable 30
[Switch-isp-sun] quit
2. Configure 802.1X
# Set the 802.1X authentication method to CHAP. (This configuration is optional. By default, the authentication method is CHAP for 802.1X.)
[Switch] dot1x authentication-method chap
3. Configure port security
# Enable port security.
[Switch] port-security enable
# Add five OUI values.
[Switch] port-security oui 1234-0100-1111 index 1
[Switch] port-security oui 1234-0200-1111 index 2
[Switch] port-security oui 1234-0300-1111 index 3
[Switch] port-security oui 1234-0400-1111 index 4
[Switch] port-security oui 1234-0500-1111 index 5
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
# Set the port security mode to userLoginWithOUI.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security port-mode userlogin-withoui
4. Verify the configuration
After completing the configurations, you can use the following command to view the configuration information of the RADIUS scheme named radsun:
<Switch> display radius scheme radsun
SchemeName : radsun
Index : 1 Type : standard
Primary Auth Server:
IP: 192.168.1.2 Port: 1812 State: active
Encryption Key : N/A
Primary Acct Server:
IP: 192.168.1.3 Port: 1813 State: active
Encryption Key : N/A
Second Auth Server:
IP: 192.168.1.3 Port: 1812 State: active
Encryption Key : N/A
Second Acct Server:
IP: 192.168.1.2 Port: 1813 State: active
Encryption Key : N/A
Auth Server Encryption Key : name
Acct Server Encryption Key : money
Accounting-On packet disable, send times : 5 , interval : 3s
Interval for timeout(second) : 5
Retransmission times for timeout : 5
Interval for realtime accounting(minute) : 15
Retransmission times of realtime-accounting packet : 5
Retransmission times of stop-accounting packet : 500
Quiet-interval(min) : 5
Username format : without-domain
Data flow unit : Byte
Packet unit : one
Use the following command to view the configuration information of the ISP domain named sun:
<Switch> display domain sun
Domain : sun
State : Active
Access-limit : 30
Accounting method : Required
Default authentication scheme : radius:radsun
Default authorization scheme : radius:radsun
Default accounting scheme : radius:radsun
Domain User Template:
Idle-cut : Disabled
Self-service : Disabled
Authorization attributes:
Use the following command to view the port security configuration information:
<Switch> display port-security interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
Equipment port-security is enabled
Trap is disabled
Disableport Timeout: 20s
OUI value:
Index is 1, OUI value is 123401
Index is 2, OUI value is 123402
Index is 3, OUI value is 123403
Index is 4, OUI value is 123404
Index is 5, OUI value is 123405
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is link-up
Port mode is userLoginWithOUI
NeedToKnow mode is disabled
Intrusion Protection mode is NoAction
Max MAC address number is not configured
Stored MAC address number is 0
Authorization is permitted
After an 802.1X user gets online, you can see that the number of secure MAC addresses stored is 1. You can also use the following command to view information about 802.1X:
<Switch> display dot1x interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
Equipment 802.1X protocol is enabled
CHAP authentication is enabled
EAD quick deploy is disabled
Configuration: Transmit Period 30 s, Handshake Period 15 s
Quiet Period 60 s, Quiet Period Timer is disabled
Supp Timeout 30 s, Server Timeout 100 s
Reauth Period 3600 s
The maximal retransmitting times 2
EAD quick deploy configuration:
EAD timeout: 30m
The maximum 802.1X user resource number is 1024 per slot
Total current used 802.1X resource number is 1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is link-up
802.1X protocol is enabled
Handshake is enabled
Handshake secure is disabled
802.1X unicast-trigger is enabled
Periodic reauthentication is disabled
The port is an authenticator
Authentication Mode is Auto
Port Control Type is Mac-based
802.1X Multicast-trigger is enabled
Mandatory authentication domain: NOT configured
Guest VLAN: NOT configured
Auth-Fail VLAN: NOT configured
Max number of on-line users is 256
EAPOL Packet: Tx 16331, Rx 102
Sent EAP Request/Identity Packets : 16316
EAP Request/Challenge Packets: 6
EAP Success Packets: 4, Fail Packets: 5
Received EAPOL Start Packets : 6
EAPOL LogOff Packets: 2
EAP Response/Identity Packets : 80
EAP Response/Challenge Packets: 6
Error Packets: 0
1. Authenticated user : MAC address: 0002-0000-0011
Controlled User(s) amount to 1
In addition, the port allows an additional user whose MAC address has an OUI among the specified OUIs to access the port. You can use the following command to view the related information:
<Switch> display mac-address interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
MAC ADDR VLAN ID STATE PORT INDEX AGING TIME(s)
1234-0300-0011 1 Learned GigabitEthernet1/0/1 AGING
--- 1 mac address(es) found ---
Configuring the macAddressElseUserLoginSecure mode
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, a client is connected to the Switch through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. The Switch authenticates the client by a RADIUS server. If the authentication succeeds, the client is authorized to access the Internet.
Restrict port GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of the Switch:
· Allow more than one MAC authenticated user to log on.
· For 802.1X users, perform MAC authentication first and then, if MAC authentication fails, 802.1X authentication. Allow only one 802.1X user to log on.
· Set fixed username and password for MAC authentication. Set the total number of MAC authenticated users and 802.1X authenticated users to 64.
· Enable NTK to prevent frames from being sent to unknown MAC addresses.
Configuration procedure
|
|
NOTE: Configurations on the host and RADIUS servers are omitted. |
1. Configure the RADIUS protocol
Configure the RADIUS authentication/accounting and ISP domain settings the same as in Configuring the userLoginWithOUI mode.
2. Configure port security
# Enable port security.
<Switch> system-view
[Switch] port-security enable
# Configure a MAC authentication user, setting the username and password to aaa and 123456 respectively.
[Switch] mac-authentication user-name-format fixed account aaa password simple 123456
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
# Specify ISP domain sun for MAC authentication.
[Switch] mac-authentication domain sun
# Set the 802.1X authentication method to CHAP. (This configuration is optional. By default, the authentication method is CHAP for 802.1X.)
[Switch] dot1x authentication-method chap
# Set port security’s limit on the number of MAC addresses to 64 on the port.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security max-mac-count 64
# Set the port security mode to macAddressElseUserLoginSecure.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security port-mode mac-else-userlogin-secure
# Set the NTK mode of the port to ntkonly.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security ntk-mode ntkonly
3. Verify the configuration
After completing the configurations, you can use the following command to view the port security configuration information:
<Switch> display port-security interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
Equipment port-security is enabled
Trap is disabled
Disableport Timeout: 20s
OUI value:
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is link-up
Port mode is macAddressElseUserLoginSecure
NeedToKnow mode is NeedToKnowOnly
Intrusion Protection mode is NoAction
Max MAC address number is 64
Stored MAC address number is 0
Authorization is permitted
Use the following command to view MAC authentication information:
<Switch> display mac-authentication interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
MAC address authentication is enabled.
User name format is fixed account
Fixed username:aaa
Fixed password:123456
Offline detect period is 60s
Quiet period is 5s
Server response timeout value is 100s
The max allowed user number is 1024 per slot
Current user number amounts to 3
Current domain is mac
Silent MAC User info:
MAC Addr From Port Port Index
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is link-up
MAC address authentication is enabled
Authenticate success: 3, failed: 7
Max number of on-line users is 256
Current online user number is 3
MAC ADDR Authenticate state Auth Index
1234-0300-0011 MAC_AUTHENTICATOR_SUCCESS 13
1234-0300-0012 MAC_AUTHENTICATOR_SUCCESS 14
1234-0300-0013 MAC_AUTHENTICATOR_SUCCESS 15
Use the following command to view 802.1X authentication information:
<Switch> display dot1x interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
Equipment 802.1X protocol is enabled
CHAP authentication is enabled
EAD quick deploy is disabled
Configuration: Transmit Period 30 s, Handshake Period 15 s
Quiet Period 60 s, Quiet Period Timer is disabled
Supp Timeout 30 s, Server Timeout 100 s
The maximal retransmitting times 2
EAD quick deploy configuration:
EAD timeout: 30m
Total maximum 802.1X user resource number is 1024 per slot
Total current used 802.1X resource number is 1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 is link-up
802.1X protocol is enabled
Handshake is enabled
Handshake secure is disabled
802.1X unicast-trigger is enabled
Periodic reauthentication is disabled
The port is an authenticator
Authentication Mode is Auto
Port Control Type is Mac-based
802.1X Multicast-trigger is enabled
Mandatory authentication domain: NOT configured
Guest VLAN: NOT configured
Auth-Fail VLAN: NOT configured
Max number of on-line users is 256
EAPOL Packet: Tx 16331, Rx 102
Sent EAP Request/Identity Packets : 16316
EAP Request/Challenge Packets: 6
EAP Success Packets: 4, Fail Packets: 5
Received EAPOL Start Packets : 6
EAPOL LogOff Packets: 2
EAP Response/Identity Packets : 80
EAP Response/Challenge Packets: 6
Error Packets: 0
1. Authenticated user : MAC address: 0002-0000-0011
Controlled User(s) amount to 1
Troubleshooting port security
Cannot set the port security mode
Symptom
Cannot set the port security mode.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security port-mode autolearn
Error:When we change port-mode, we should first change it to noRestrictions, then change it to the other.
Analysis
For a port operating in a port security mode other than noRestrictions, you cannot change the port security mode by using the port-security port-mode command directly.
Solution
Set the port security mode to noRestrictions first.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo port-security port-mode
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security port-mode autolearn
Cannot configure secure MAC addresses
Symptom
Cannot configure secure MAC addresses.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security mac-address security 1-1-2 vlan 1
Error: Security MAC address configuration failed.
Error:Can not operate security MAC address for current port mode is not autoLearn!
Analysis
No secure MAC address can be configured on a port operating in a port security mode other than autoLearn.
Solution
Set the port security mode to autoLearn.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo port-security port-mode
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security max-mac-count 64
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security port-mode autolearn
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] port-security mac-address security 1-1-2 vlan 1
Cannot change port security mode when a user is online
Symptom
Port security mode cannot be changed when an 802.1X authenticated or MAC authenticated user is online.
[SwitchGigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo port-security port-mode
Error:Cannot configure port-security for there is 802.1X user(s) on line on port GigabitEthernet1/0/1.
Analysis
Changing port security mode is not allowed when an 802.1X authenticated or MAC authenticated user is online.
Solution
Use the cut command to forcibly disconnect the user from the port before changing the port security mode.
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[Switch] cut connection interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Switch-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] undo port-security port-mode

