- Table of Contents
-
- 17-High Availability Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Ethernet OAM configuration
- 02-CFD configuration
- 03-DLDP configuration
- 04-ERPS configuration
- 05-Smart Link configuration
- 06-Monitor Link configuration
- 07-S-Trunk configuration
- 08-Error code detection configuration
- 09-VRRP configuration
- 10-BFD configuration
- 11-Track configuration
- 12-Process placement configuration
- 13-Interface collaboration configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-ERPS configuration | 660.76 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: ERPS configuration
Configuring ERPS ring member ports
Enabling R-APS packets to carry the ring ID in the destination MAC address
Configuring R-APS packet levels
Setting the non-revertive mode
Associating a ring with a subring
Enabling flush packet transparent transmission
Associating an ERPS ring member port with a track entry
Removing the MS mode and FS mode settings for an ERPS ring
Verifying and maintaining ERPS
Verifying ERPS configuration and running status
Displaying and clearing ERPS packet statistics
Example: Configuring one subring
Example: Configuring one-ring multi-instance load balancing
The owner node cannot receive SF packets from a faulty node when the link state is normal
Configuring ERPS
About ERPS
Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) is a robust link layer protocol that ensures a loop-free topology and implements quick link recovery.
ERPS structure
Rings
ERPS rings can be divided into major rings and subrings. An ERPS network consists of one major ring or multiple major rings, and multiple subrings. By default, a ring is a major ring. You can configure a ring as a subring manually.
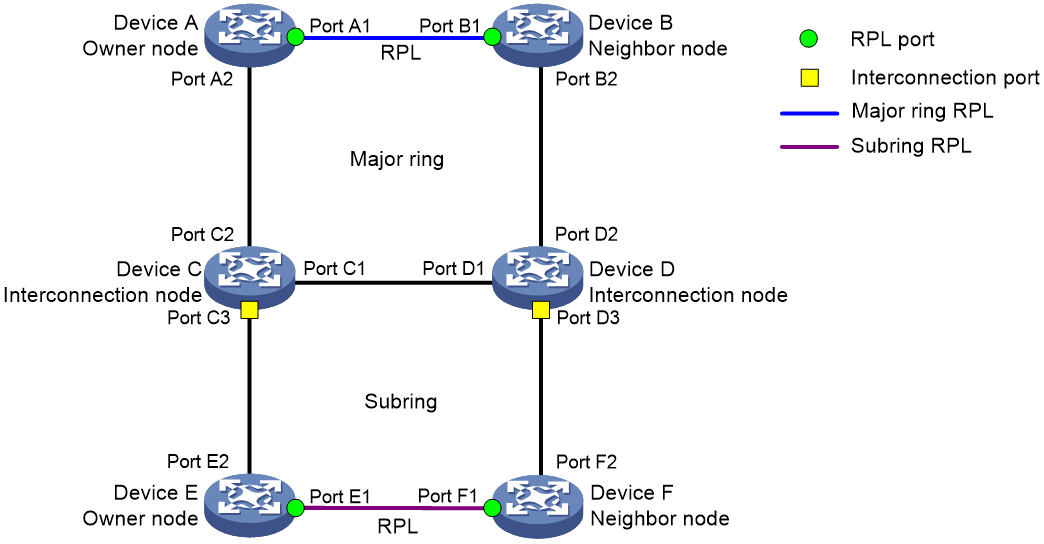
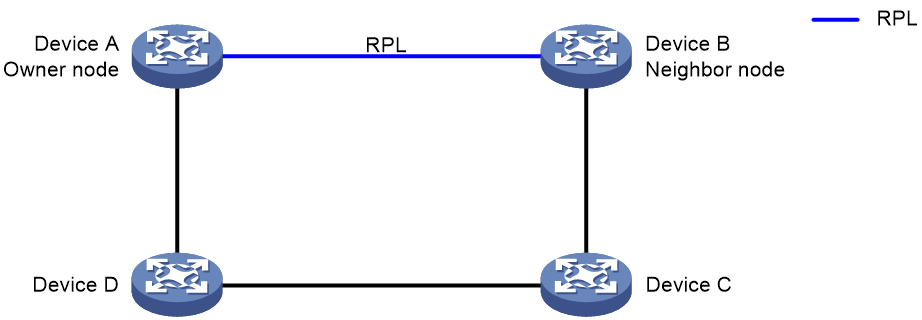
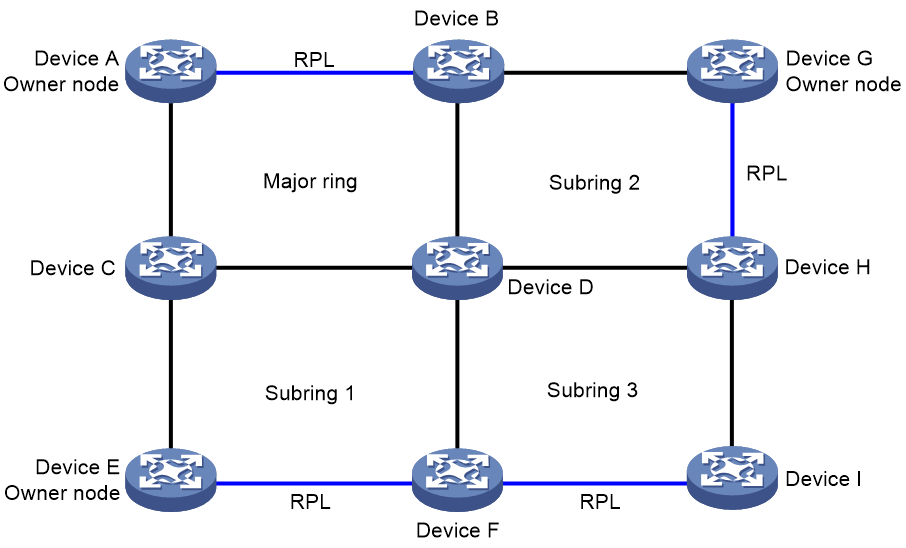
As shown in Figure 1, a major ring is a closed ring formed by Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D. A subring is an open ring formed by the link Device C<—>Device E<—>Device F<—>Device D.
RPL
An ERPS ring is composed of many nodes. Some nodes use ring protection links (RPLs) to prevent loops on the ERPS ring. As shown in Figure 1, the link between Device A and Device B and the link between Device E and Device F are RPLs.
Nodes
ERPS nodes include owner nodes, neighbor nodes, interconnection nodes, and normal nodes.
· The owner node and neighbor node block and unblock ports on the RPL to prevent loops and switch traffic. An RPL connects an owner node and a neighbor node.
· Interconnection nodes connect different rings. Interconnection nodes reside on subrings and forward service packets but not protocol packets.
· Normal nodes forward both service packets and protocol packets.
As shown in Figure 1, on the major ring, Device A is the owner node and Device B is the neighbor node. On the subring, Device E is the owner node and Device F is the neighbor node. Devices C and D are interconnection nodes.
Ports
Each node consists of two ERPS ring member ports: Port 0 and port 1. ERPS ring member ports have the following types:
· RPL port—Port on an RPL link.
· Interconnection port—Port that connects a subring to a major ring.
· Normal port—Default type of a port that forwards both service packets and protocol packets.
As shown in Figure 1, ports A1, B1, E1, and F1 are RPL ports. Ports C3 and D3 are interconnection ports. Other ports are normal ports.
Instances
An ERPS ring supports multiple ERPS instances. An ERPS instance is a logical ring to process service and protocol packets. Each ERPS instance has its own owner node and maintains its own state and data. An ERPS instance is uniquely identified by the ring ID and VLAN ID of ERPS packets. The ring ID indicates the ring of ERPS packets. It can be represented by the last byte in the destination MAC address of the packets. The VLAN ID indicates the ERPS instance of the packets.
ERPS protocol packets
ERPS protocol packets are Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) packets. You can configure the R-APS packet level. A node does not process R-APS packets whose levels are greater than the level of the packets sent by the node. On a ring, the levels of R-APS packets must be the same for all nodes in an ERPS instance.
Table 1 R-APS packet types and functions
|
Packet type |
Function |
|
No request, RPL block (NR-RB) |
When the link is stable, an owner node in idle state periodically sends NR-RB packets to inform other nodes that the RPL ports are blocked. The nodes that receive the NR-RB packets unblock available ports and update MAC address entries. |
|
No request (NR) |
After the link fault is cleared, the node that detects the recovery periodically sends NR packets. When the owner node receives the NR packets, it starts the WTR timer. The node stops sending NR packets after receiving NR-RB packets from the owner node. |
|
Signal fail (SF) |
When a link fails to send or receive signals, the node that detects the fault periodically sends SF packets. When the owner node and neighbor node receive the FS packets, they unblock the RPL ports. The node stops sending SF packets after the fault is cleared. |
|
Manual switch (MS) |
A port configured with the MS mode is blocked and periodically sends MS packets. When other nodes receive the MS packets, they unblock available ports and update MAC address entries. |
|
Forced switch (FS) |
A port configured with the FS mode is blocked and periodically sends FS packets. When other nodes receive the FS packets, they unblock all ports and update MAC address entries. |
|
Flush |
If the topology of a subring changes, the interconnection ports on the subring broadcasts flush packets. All nodes that receive the flush packets update MAC address entries. |
|
|
NOTE: · Typically R-APS packets are transmitted within a ring. The flush packets sourced from the subring can be forwarded to the major ring. · Service packets can be transmitted between different rings. |
ERPS node states
Table 2 ERPS states
|
State |
Description |
|
Init |
State for a non-interconnection node that has less than two ERPS ring member ports or for an interconnection node that does not have ERPS ring member ports. |
|
Idle |
Stable state when all non-RPL links are available. In this state, the owner node blocks the RPL port and periodically sends NR-RB packets. The neighbor node blocks the RPL port. All nodes enter the idle state after the owner node enters the idle state. |
|
Protection |
State when a non-RPL link is faulty. In this state, the RPL link is unblocked to forward traffic. All nodes enter the protection state after a node enters the protection state. |
|
MS |
State when traffic paths are manually switched. All nodes enter the MS state after a node is configured with the MS mode. |
|
FS |
State when traffic paths are forcibly switched. All nodes enter the FS state after a node is configured with the FS mode. |
|
Pending |
Transient state between the previous states. |
ERPS timers
Hold-off timer
The hold-off timer starts when the port detects a link fault. The port reports the link fault if the fault persists when the timer expires.
This timer delays the fault report time and affects the link switching performance.
Guard timer
The guard timer starts when the port detects a link recovery. The port does not process R-APS packets before the timer expires.
This timer prevents R-APS packets from impacting the network and affects the link switching performance when multiple points of failures exist.
WTR timer
In revertive mode, the WTR timer starts when the owner node in protection state receives NR packets. The RPL is unblocked and the recovered node is blocked before the timer expires. The owner node blocks the RPL and sends NR-RB packets when the timer expires. If the port receives SF packets before the timer expires, the timer stops and the RPL remains unblocked.
This timer prevents intermittent link failures from impacting the network.
WTB timer
In revertive mode, the WTB timer starts when the owner node in MS or FS state receives NR packets. The RPL is unblocked and the recovered node sends NR packets before the timer expires. The owner node blocks the RPL and sends NR-RB packets when the timer expires. If the port receives SF packets before the timer expires, the timer stops and the RPL remains unblocked.
This timer prevents the RPL ports from being blocked and unblocked frequently.
ERPS operation mechanism
ERPS uses the detection mechanism defined in ITU-T G.8032/Y.1344 to locate the point of failure and identify unidirectional or bidirectional faults.
ERPS uses the SF packets to report signal failures on a link and the NR packets to report link recovery. When a node detects a link status change, the node sends three packets first and then sends subsequent packets every five seconds.
Link-down report mechanism
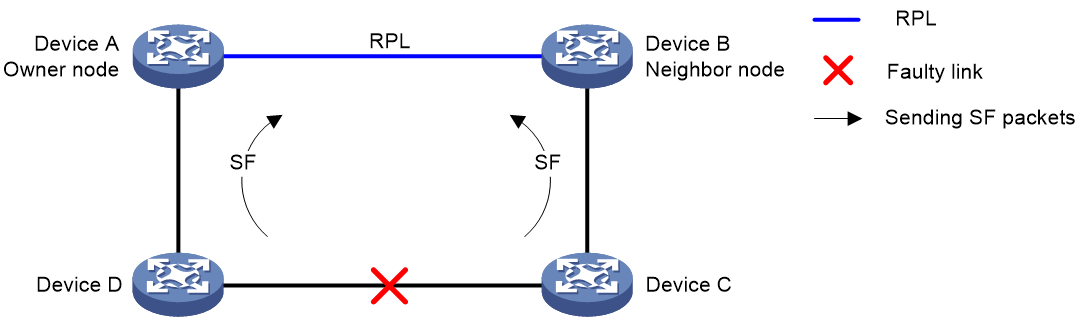
Figure 2 Link-down report mechanism
As shown in Figure 2, the link-down report mechanism uses the following process:
1. Device C and Device D detect the link failure and perform the following operations:
a. Block the ports on both side of the faulty link.
b. Periodically send SF packets to other nodes.
2. Device A and Device B receive the SF packets and perform the following operations:
a. Unblock RPL ports.
b. Update the MAC address entries.
Service packets are switched to the RPL link.
Link recovery mechanism
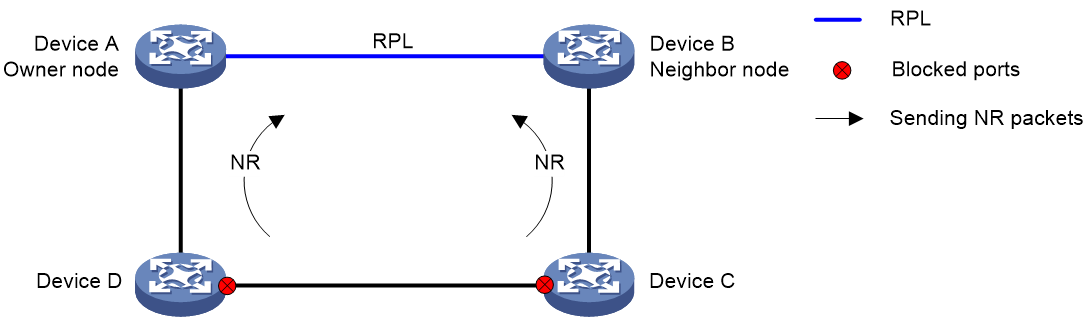
Figure 3 Link recovery mechanism
As shown in Figure 3, the link recovery mechanism uses the following process:
1. Device C and Device D detect the link recovery and perform the following operations:
a. Block the recovered ports.
b. Start the guard timer.
c. Send NR packets.
2. When Device A (owner node) receives the NR packets, it does not perform any operations if it is in non-revertive mode. If Device A is in revertive mode, it performs the following operations:
a. Starts the WTR timer.
b. Blocks the RPL port and periodically sends NR-RB packets when the WTR timer expires.
3. When other nodes receive the NR-RB packets, they perform the following operations:
a. Device B (neighbor port) blocks the RPL port.
b. Device C and Device D unblock the recovered ports.
Service packets are switched to the recovered link.
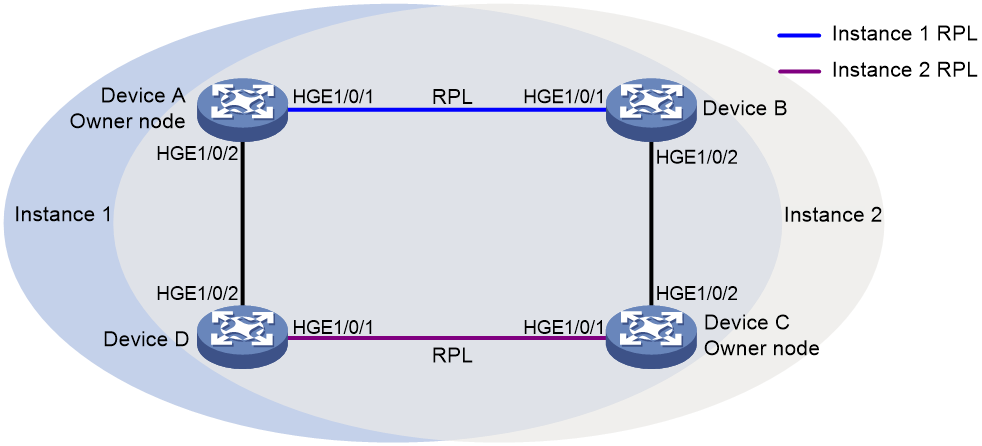
Multi-instance load balancing mechanism
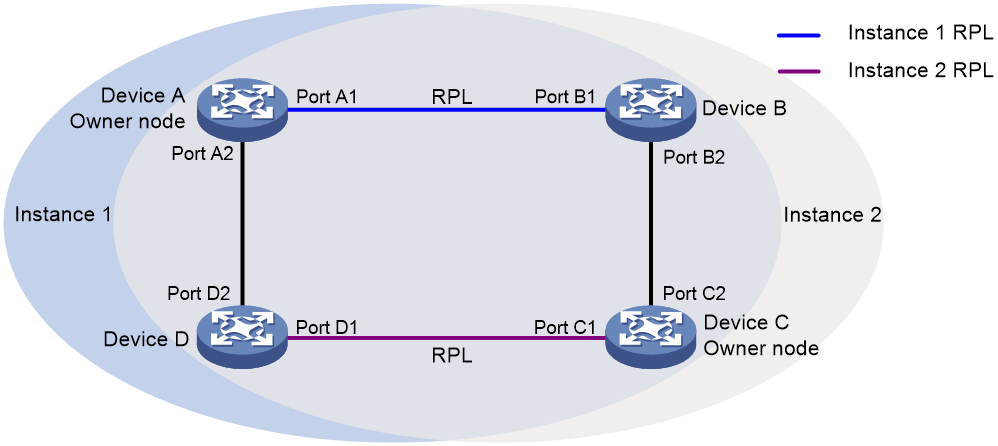
Figure 4 Multi-instance load balancing mechanism
An ERPS ring topology might carry traffic from multiple VLANs. Traffic from different VLANs can be load balanced among different ERPS instances.
ERPS uses the following types of VLANs:
· Control VLAN—Carries ERPS protocol packets. Each ERPS instance has its own control VLAN.
· Protected VLAN—Carries data packets. Each ERPS instance has its own protected VLAN. Protected VLANs are configured by using the mappings between VLANs and MSTIs.
As shown in Figure 4, the ERPS ring is configured with instance 1 and instance 2. For instance 1, the owner node is Device A, and the RPL is the link between Device A and Device B. For instance 2, the owner node is Device C, and the RPL is the link between Device C and Device D. Traffic from different VLANs can be load balanced among different links.
Manual configuration mechanism
ERPS supports the following manual configuration modes:
· MS—Use the erps switch manual command to block an ERPS ring member port. A port in MS mode is blocked and sends MS packets. The nodes that receive the MS packets unblock available ports. If the nodes in MS mode receive an SF packet, they unblock the blocked ports.
· FS—Use the erps switch force ring command to block an ERPS ring member port. A port in FS mode is blocked and sends FS packets. The nodes that receive the FS packets unblock available ports. If the nodes in FS mode receive an SF packet, they do not unblock the blocked ports.
Collaboration mechanism
To detect and clear link faults typically for a fiber link, use ERPS with CFD and Track. You can associate ERPS ring member ports with the continuity check function of CFD through track entries. CFD reports link events only when the monitored VLAN is the control VLAN of the ERPS instance for the port. For more information about CFD and Track, see "Configuring CFD" and "Configuring Track."
ERPS network diagrams
One major ring
The network has one major ring.
Figure 5 Network diagram
One major ring connecting one subring
The network has one major ring and one subring.
Figure 6 Network diagram
One major ring connecting multiple subrings
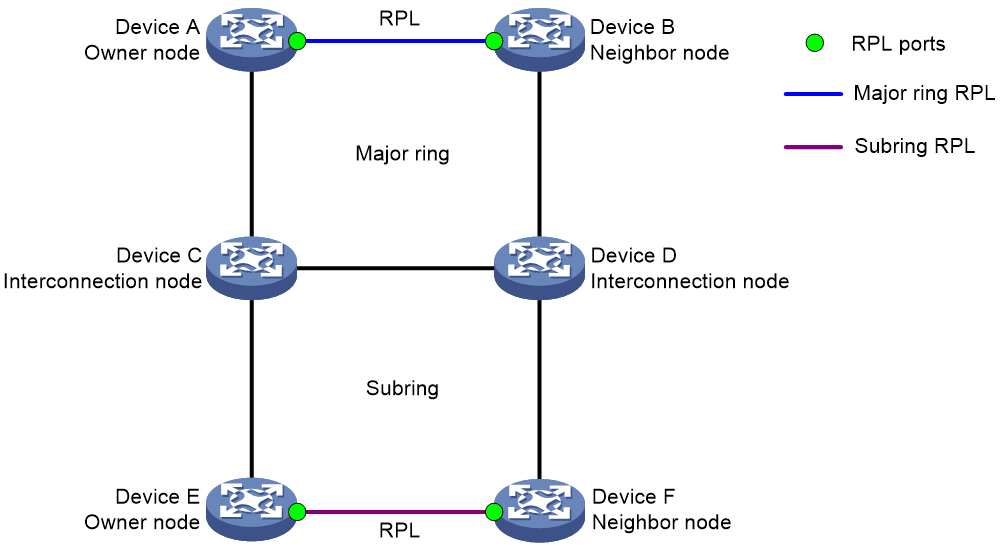
The network has three or more rings. Each subring is connected to the major ring by two interconnection nodes.
Figure 7 Network diagram
One subring connecting multiple subrings
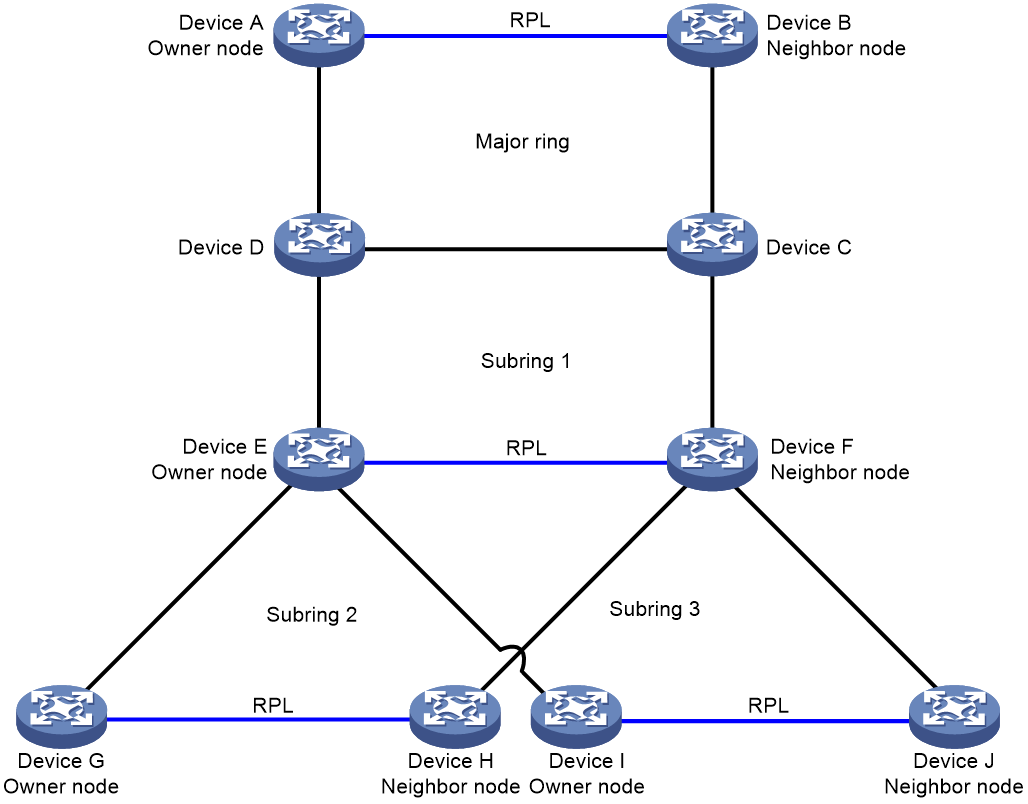
The network has three or more rings. As shown in Figure 8, subring 1 is connected to the major ring. Other subrings are connected to subring 1 by two interconnection nodes.
One subring connecting multiple rings
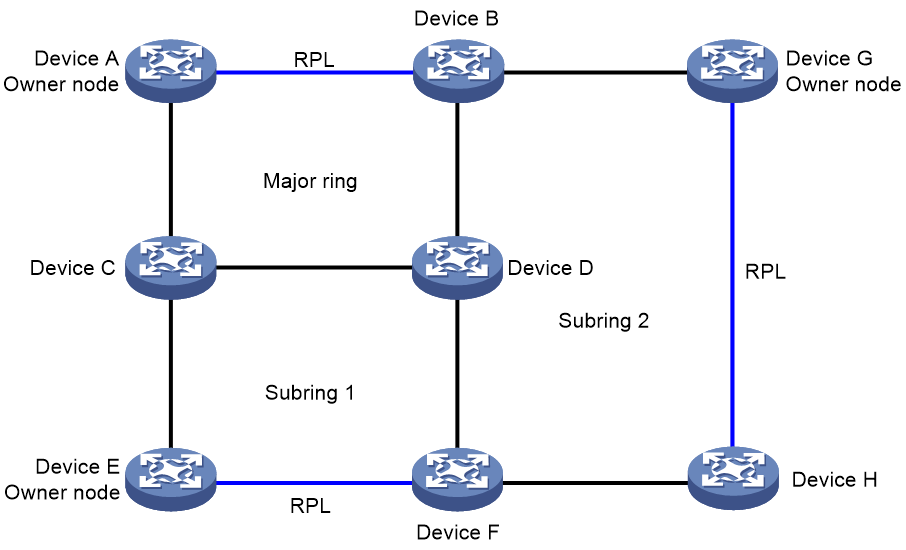
The network has three or more rings. A minimum of one subring is connected to two rings. As shown in Figure 9, one interconnection node on subring 2 is connected to the major ring; and another interconnection node is connected to subring 1. As shown in Figure 10, subring 3 is connected to subring 1 and subring 2.
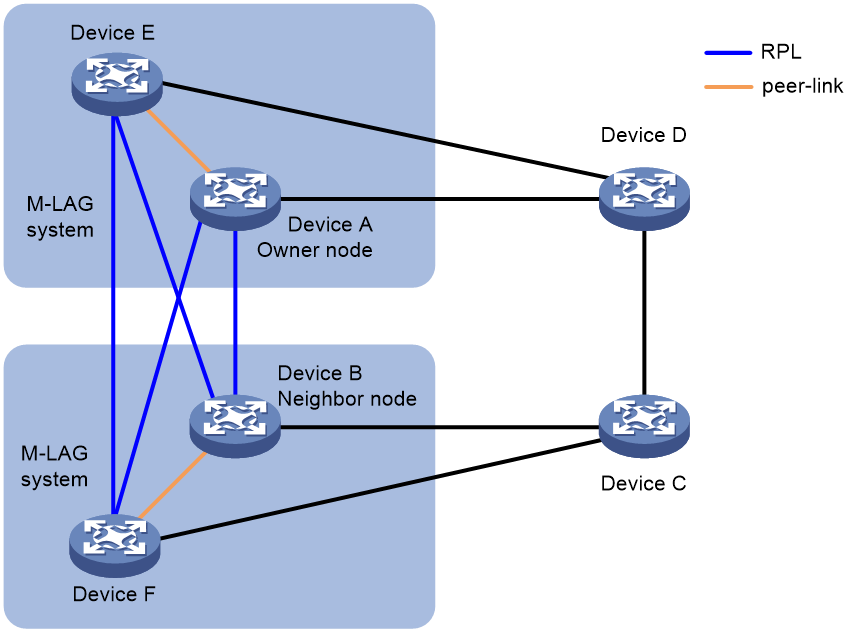
ERPS with M-LAG
M-LAG allows you to virtualize the devices in an ERPS ring into one system through multichassis link, thereby achieving device-level redundancy and load balancing.
You can use the display erps detail ring command to determine whether ERPS works correctly in an M-LAG network. For more information about M-LAG, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Figure 11 ERPS with M-LAG
Protocols and standards
· ITU-T G.8032, Recommendation ITU-T G.8032/Y.1344, Ethernet ring protection switching
· IEEE 802.1D, IEEE Std 802.1D™-2004, IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Media Access Control (MAC) Bridges
· IEEE 802.3, IEEE Std 802.3-2008, IEEE Standard for Information technology
Restrictions and guidelines: ERPS configuration
ERPS does not provide an election mechanism. To implement ring detection and protection, configure all nodes correctly.
ERPS tasks at a glance
To configure ERPS, perform the following tasks:
Perform this task on devices you want to configure as ERPS nodes.
Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
b. Configuring ERPS ring member ports
d. Configuring protected VLANs
3. Enabling ERPS for an instance
Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
4. (Optional.) Enabling R-APS packets to carry the ring ID in the destination MAC address
Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
5. (Optional.) Configuring R-APS packet levels
6. (Optional.) Setting ERPS timers
Perform this task on the owner node on an ERPS ring.
7. (Optional.) Setting the non-revertive mode
Perform this task on the owner node on an ERPS ring.
8. (Optional.) Setting a switchover mode
Perform this task on the nodes that you want to block their ports.
9. (Optional.) Associating a ring with a subring
Perform this task on the interconnection node on an ERPS ring.
10. (Optional.) Enabling flush packet transparent transmission
Perform this task on the interconnection node on an ERPS ring.
11. (Optional.) Associating an ERPS ring member port with a track entry
12. (Optional.) Removing the MS mode and FS mode settings for an ERPS ring
Prerequisites
Before you configure ERPS, complete the following tasks:
· Establish the Ethernet ring topology.
· Determine the ERPS rings, ERPS instances, control VLANs, protected VLANs, and node roles.
Enabling ERPS globally
Restrictions and guidelines
· Perform this task on devices you want to configure as ERPS nodes.
· For ERPS to take effect for an instance, enable it globally first.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable ERPS globally.
erps enable
By default, ERPS is disabled globally.
Configuring an ERPS ring
Creating an ERPS ring
Restrictions and guidelines
· Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
· A ring ID uniquely identifies an ERPS ring. All nodes on an ERPS ring must be configured with the same ring ID.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an ERPS ring.
erps ring ring-id
3. (Optional.) Configure the ring type.
ring-type sub-ring
By default, an ERPS ring is a major ring.
Configuring ERPS ring member ports
Restrictions and guidelines
· Perform this task on each node's ports intended for accessing ERPS rings.
· ERPS ring member ports automatically allow packets from the control VLAN to pass through.
· Do not enable Ethernet OAM remote loopback for ERPS ring member ports. This feature might cause a broadcast storm. For more information about Ethernet OAM, see "Configuring Ethernet OAM."
· For faster topology convergence, use the link-delay command on ERPS ring member ports to set the physical state change suppression interval to 0 seconds. For more information about the link-delay command, see Interface Command Reference.
· You must configure ERPS ring member ports as trunk ports.
· Do not assign an interface to both an aggregation group and an ERPS ring. If you do so, the interface does not take effect on the ERPS ring and cannot be displayed by using the display erps detail command.
· Do not assign an M-LAG peer-link interface to an ERPS ring. An M-LAG peer-link interface does not work for an ERPS ring and cannot be displayed by using the display erps detail command.
· Do not assign both an M-LAG interface and a non-M-LAG interface on a non-interconnection node to an ERPS ring. If you do so, the M-LAG interface does not take effect on the ERPS ring.
Configuring ERPS ring member port attributes
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the port as a trunk port.
port link-type trunk
By default, a port is an access port.
For more information about this command, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference.
4. Assign the trunk port to protected VLANs.
port trunk permit vlan { vlan-id-list | all }
By default, a trunk port is assigned only to VLAN 1.
For more information about this command, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference.
5. Disable the spanning tree feature.
undo stp enable
By default, the spanning tree feature is enabled.
For more information about this command, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference.
Configuring an ERPS ring member port
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Configure an ERPS ring member port.
{ port0 | port1 } interface interface-type interface-number
By default, an ERPS ring does not have ERPS ring member ports.
Configuring control VLANs
Restrictions and guidelines
· Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
· The control VLAN must be a VLAN that has not been created on the device.
· Configure the same control VLAN for all nodes in an ERPS instance.
· Do not configure the default VLAN of an ERPS ring member port as the control VLAN.
·
· Make sure the ERPS instance has been configured. After the ERPS instance is enabled, the control VLAN cannot be changed.
· For a device not configured with ERPS to transparently transmit ERPS packets, make sure only the two ports accessing the ERPS ring permit packets from the control VLAN. If other ports on the device permit packets from the control VLAN, the packets from other VLANs might enter the control VLAN and strike the ERPS ring.
· When configuring ERPS with M-LAG, make sure the peer-link interface is a trunk port. The peer-link interface will automatically join or leave a control VLAN as the control VLAN is created or deleted.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Enable ERPS instance view.
instance instance-id
4. Configure a control VLAN.
control-vlan vlan-id
Configuring protected VLANs
Restrictions and guidelines
· Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
· Configure the same protected VLAN for all nodes of an ERPS instance. To implement load balancing, configure different protected VLANs for different ERPS instances.
Prerequisites
Before you configure protected VLANs, you must configure an MST region and the VLAN-to-instance mapping table. For more information about MST regions, see spanning tree configuration in Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Enable ERPS instance view.
instance instance-id
4. Configure the protected VLANs.
protected-vlan reference-instance instance-id-list
Configuring the node role
Restrictions and guidelines
· Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
· For the owner node to work correctly, you must configure only one owner node for an ERPS ring.
· You can only configure the interconnection node for subrings.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Enter ERPS instance view.
instance instance-id
4. Configure the node role.
node-role { { owner | neighbor } rpl | interconnection } { port0 | port1 }
By default, a node is a normal node.
Enabling ERPS for an instance
Restrictions and guidelines
· Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
· You can enable ERPS for an instance only when it is configured with a control VLAN and a protected VLAN.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Enter ERPS instance view.
instance instance-id
4. Enable ERPS for the instance.
instance enable
By default, ERPS is disabled for an instance.
Enabling R-APS packets to carry the ring ID in the destination MAC address
About this task
Perform this task to configure the ring ID as the last byte of the destination MAC address for R-APS packets. The ring of R-APS packets can be identified by their destination MAC addresses.
Restrictions and guidelines
Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Enable R-APS packets to carry the ring ID in the destination MAC address.
r-aps ring-mac
By default, R-APS packets do not carry ring IDs in their destination MAC addresses. The last byte of the destination MAC address is 1.
Configuring R-APS packet levels
Restrictions and guidelines
Perform this task on all nodes on an ERPS ring.
On a ring, the levels of R-APS packets must be the same for all nodes in an ERPS instance.
A node does not process R-APS packets whose levels are greater than the level of R-APS packets sent by the node.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Enter ERPS instance view.
instance instance-id
4. Configure the R-APS packet level.
r-aps level level-value
By default, the level for R-APS packets is 7.
Setting ERPS timers
Restrictions and guidelines
Perform this task on the owner node on an ERPS ring.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Enter ERPS instance view.
instance instance-id
4. Set the guard timer.
timer guard guard-value
By default, the guard timer is 500 milliseconds.
5. Set the hold-off timer.
timer hold-off hold-off-value
By default, the hold-off timer is 0 milliseconds.
6. Set the WTR timer.
timer wtr wtr-value
By default, the WTR timer is 5 minutes.
Setting the non-revertive mode
About this task
Perform this task if you do not want to switch back to the recovered link after the link fault is cleared.
Restrictions and guidelines
Perform this task on the owner node on an ERPS ring.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Enter ERPS instance view.
instance instance-id
4. Set the non-revertive mode.
revertive-operation non-revertive
By default, revertive mode is used.
Setting a switchover mode
Restrictions and guidelines
Perform this task on the nodes that you want to block their ports.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set a switchover mode.
erps switch { force | manual } ring ring-id instance instance-id { port0 | port1 }
By default, no switchover mode is not set.
Associating a ring with a subring
About this task
On a multi-ring network, perform this task if you want to advertise topology changes in a subring to a ring.
Restrictions and guidelines
Perform this task on the interconnection node on an ERPS ring.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter ERPS ring view.
erps ring ring-id
3. Configure the ERPS ring as a subring.
ring-type sub-ring
By default, an ERPS ring is a major ring.
4. Enter ERPS instance view.
instance instance-id
5. Associate a ring with the subring.
sub-ring connect ring ring-id instance instance-id
By default, a subring is not associated with any rings.
Enabling flush packet transparent transmission
About this task
This feature enables the interconnection nodes to forward flush packets for topology changes in the subring to the ring associated with the subring. The associated ring can flush the MAC address table quickly to speed up convergence.
Restrictions and guidelines
Perform this task on the interconnection node on an ERPS ring.
To use this feature, you must also associate a subring on the interconnection node with the ring.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable flush packet transparent transmission.
erps tcn-propagation
By default, flush packet transparent transmission is disabled.
Associating an ERPS ring member port with a track entry
Restrictions and guidelines
Before you associate a port with a track entry, make sure the port has joined an ERPS instance.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Associate an ERPS ring member port with a track entry.
port erps ring ring-id instance instance-id track track-entry-index
By default, an ERPS ring member port is not associated with any track entries.
Removing the MS mode and FS mode settings for an ERPS ring
About this task
After you configure this task, the owner node can ignore the WTR timer and immediately switch traffic to the recovered link upon link recovery.
This task also switches an ERPS ring in non-revertive mode to revertive mode.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view.
erps clear ring ring-id instance instance-id
Verifying and maintaining ERPS
Verifying ERPS configuration and running status
Perform display tasks in any view.
· Display brief ERPS information.
display erps
· Display detailed ERPS information.
display erps detail ring ring-id [ instance instance-id ]
Displaying and clearing ERPS packet statistics
To display ERPS packet statistics, execute the following command in any view:
display erps statistics [ ring ring-id [ instance instance-id ] ]
To clear ERPS packet statistics, execute the following command in user view:
reset erps statistics ring ring-id [ instance instance-id ]
ERPS configuration examples
Example: Configuring one ring
Network configuration
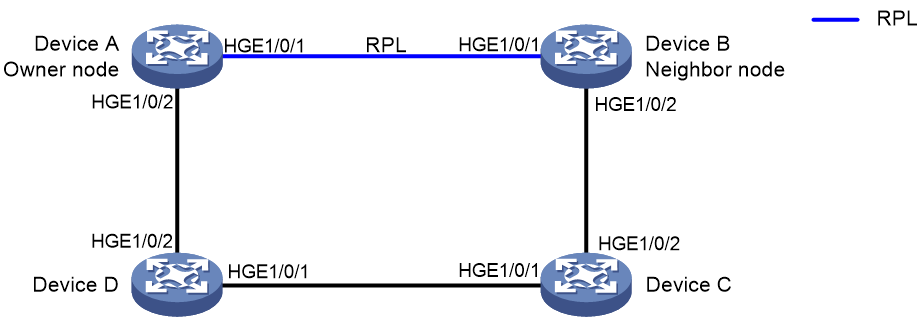
As shown in Figure 12, perform the following tasks to eliminate loops on the network:
· Configure the ring as ERPS ring 1.
· Configure VLAN 100 as the control VLAN for ERPS ring 1.
· Configure VLANs 1 to 30 as the protected VLANs for ERPS ring 1.
· Configure Device A as the owner node, HundredGigE 1/0/1 as ERPS ring member port 0 and the RPL port, and HundredGigE 1/0/2 as ERPS ring member port 1.
· Configure Device B as the neighbor node, HundredGigE 1/0/1 as ERPS ring member port 0 and the RPL port, and HundredGigE 1/0/2 as ERPS ring member port 1.
· Configure Device C and Device D as normal nodes, HundredGigE 1/0/1 as ERPS ring member port 0, and HundredGigE 1/0/2 as ERPS ring member port 1.
Prerequisites
By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA] stp region-configuration
[DeviceA-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceA-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceA] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Enable R-APS packets to carry ring ID in the destination MAC address.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] r-aps ring-mac
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] node-role owner rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceA] cfd enable
[DeviceA] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 1, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 1.
[DeviceA] cfd service-instance 1 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 1
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 1, create outward-facing MEP 1001 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceA] cfd meplist 1001 1002 service-instance 1
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 1001 service-instance 1 outbound
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1001 enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 2, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 2.
[DeviceA] cfd service-instance 2 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 2
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 2, create outward-facing MEP 2001 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceA] cfd meplist 2001 2002 service-instance 2
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 2001 service-instance 2 outbound
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2001 enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 1001 in Ethernet service instance 1.
[DeviceA] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 2001 in Ethernet service instance 2.
[DeviceA] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 2 and bring up the port.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceA] erps enable
2. Configure Device B.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB] stp region-configuration
[DeviceB-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceB-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceB] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Enable R-APS packets to carry ring ID in the destination MAC address.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] r-aps ring-mac
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] node-role neighbor rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceB] cfd enable
[DeviceB] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 1, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 1.
[DeviceB] cfd service-instance 1 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 1
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 1, create outward-facing MEP 1002 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceB] cfd meplist 1001 1002 service-instance 1
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 1002 service-instance 1 outbound
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1002 enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 3, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 3.
[DeviceB] cfd service-instance 3 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 3
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 3, create outward-facing MEP 3002 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceB] cfd meplist 3001 3002 service-instance 3
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 3002 service-instance 3 outbound
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3002 enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 1002 in Ethernet service instance 1.
[DeviceB] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 3 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 3002 in Ethernet service instance 3.
[DeviceB] track 3 cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 3 and bring up the port.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceB] erps enable
3. Configure Device C.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC] stp region-configuration
[DeviceC-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceC-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceC] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Enable R-APS packets to carry ring ID in the destination MAC address.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] r-aps ring-mac
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceC] cfd enable
[DeviceC] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 3, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 3.
[DeviceC] cfd service-instance 3 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 3
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 3, create outward-facing MEP 3001 in Ethernet service instance 3, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceC] cfd meplist 3001 3002 service-instance 3
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 3001 service-instance 3 outbound
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3001 enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 4, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 4.
[DeviceC] cfd service-instance 4 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 4
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 4, create outward-facing MEP 4001 in Ethernet service instance 4, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceC] cfd meplist 4001 4002 service-instance 4
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 4001 service-instance 4 outbound
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4001 enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 3001 in Ethernet service instance 3.
[DeviceC] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 4001 in Ethernet service instance 4.
[DeviceC] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 3 and bring up the port.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceC] erps enable
4. Configure Device D.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD] stp region-configuration
[DeviceD-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceD-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceD] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Enable R-APS packets to carry ring ID in the destination MAC address.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] r-aps ring-mac
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceD] cfd enable
[DeviceD] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 2, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 2.
[DeviceD] cfd service-instance 2 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 2
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 2, create outward-facing MEP 2002 in Ethernet service instance 2, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceD] cfd meplist 2001 2002 service-instance 2
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 2002 service-instance 2 outbound
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2002 enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 4, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 4.
[DeviceD] cfd service-instance 4 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 4
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 4, create outward-facing MEP 4002 in Ethernet service instance 4, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceD] cfd meplist 4001 4002 service-instance 4
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 4002 service-instance 4 outbound
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4002 enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 2002 in Ethernet service instance 2.
[DeviceD] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 4002 in Ethernet service instance 4.
[DeviceD] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 2 and bring up the port.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceD] erps enable
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about ERPS instance 1 for Device A.
[DeviceA] display erps detail ring 1
Ring ID : 1
Port0 : HundredGigE1/0/1
Port1 : HundredGigE1/0/2
Subring : No
Default MAC : No
Instance ID : 1
Node role : Owner
Node state : Idle
Connect(ring/instance): -
Control VLAN : 100
Protected VLAN : Reference-instance 1
Guard timer : 500 ms
Hold-off timer : 0 ms
WTR timer : 5 min
Revertive operation : Revertive
Enable status : Yes
Active status : Yes
R-APS level : 7
Port PortRole PortStatus
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port0 RPL Block
Port1 Non-RPL Up
The output shows the following information:
· Device A is the owner node.
· The ERPS ring is in idle state.
· The RPL port is blocked.
· The non-RPL port is unblocked.
Example: Configuring one subring
Network configuration
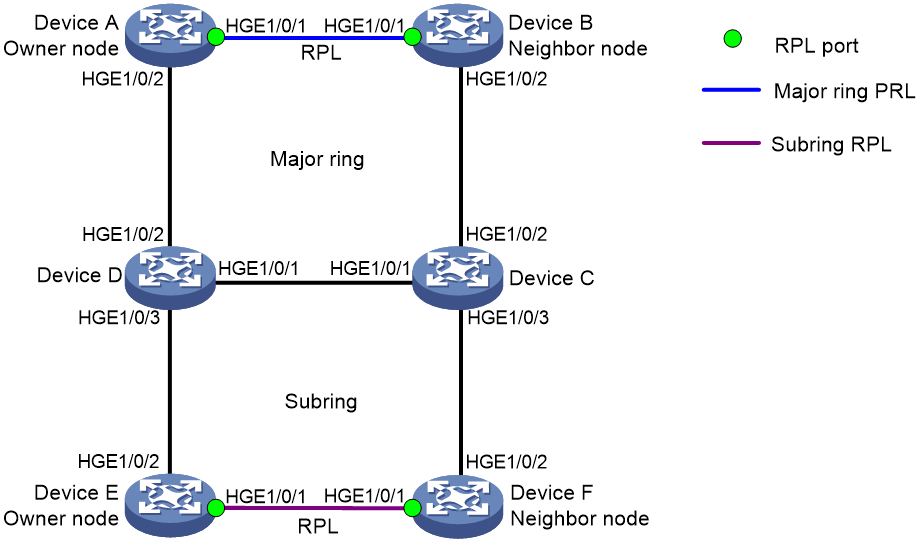
As shown in Figure 13, perform the following tasks to eliminate loops on the network:
· Configure VLAN 100 and VLAN 200 as the control VLANs for the major ring and the subring, respectively.
· Configure VLANs 1 to 30 as the protected VLANs for the major ring and subring.
· Configure Device A as the owner node for the major ring, HundredGigE 1/0/1 as ERPS ring member port 0 and the RPL port, and HundredGigE 1/0/2 as ERPS ring member port 1.
· Configure Device B as the neighbor node for the major ring, HundredGigE 1/0/1 as ERPS ring member port 0 and the RPL port, and HundredGigE 1/0/2 as ERPS ring member port 1.
· Configure Devices C and D as interconnection nodes, HundredGigE 1/0/1 as ERPS ring member port 0, HundredGigE 1/0/2 as ERPS ring member port 1, and GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 as the interconnection port.
· Configure Device E as the owner node for the subring, HundredGigE 1/0/1 as ERPS ring member port 0 and the RPL port, and HundredGigE 1/0/2 as ERPS ring member port 1.
· Configure Device F as the neighbor node for the subring, HundredGigE 1/0/1 as ERPS ring member port 0 and the RPL port, and HundredGigE 1/0/2 as ERPS ring member port 1.
Prerequisites
By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA] stp region-configuration
[DeviceA-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceA-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceA] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] node-role owner rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceA] cfd enable
[DeviceA] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 1, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 1.
[DeviceA] cfd service-instance 1 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 1
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 1, create outward-facing MEP 1001 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceA] cfd meplist 1001 1002 service-instance 1
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 1001 service-instance 1 outbound
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1001 enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 2, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 2.
[DeviceA] cfd service-instance 2 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 2
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 2, create outward-facing MEP 2001 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceA] cfd meplist 2001 2002 service-instance 2
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 2001 service-instance 2 outbound
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2001 enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 1001 in Ethernet service instance 1.
[DeviceA] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 2001 in Ethernet service instance 2.
[DeviceA] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 2 and bring up the port.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceA] erps enable
2. Configure Device B.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB] stp region-configuration
[DeviceB-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceB-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceB] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] node-role neighbor rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceB] cfd enable
[DeviceB] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 1, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 1.
[DeviceB] cfd service-instance 1 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 1
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 1, create outward-facing MEP 1002 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceB] cfd meplist 1001 1002 service-instance 1
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 1002 service-instance 1 outbound
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1002 enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 3, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 3.
[DeviceB] cfd service-instance 3 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 3
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 3, create outward-facing MEP 3002 in Ethernet service instance 2, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceB] cfd meplist 3001 3002 service-instance 3
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 3002 service-instance 3 outbound
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3002 enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 1002 in Ethernet service instance 1.
[DeviceB] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 3 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 3002 in Ethernet service instance 3.
[DeviceB] track 3 cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 3 and bring up the port.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceB] erps enable
3. Configure Device C.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC] stp region-configuration
[DeviceC-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceC-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/3 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] link-delay up 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] link-delay down 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] undo stp enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceC] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceC] cfd enable
[DeviceC] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 3, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 3.
[DeviceC] cfd service-instance 3 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 3
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 3, create outward-facing MEP 3001 in Ethernet service instance 3, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceC] cfd meplist 3001 3002 service-instance 3
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 3001 service-instance 3 outbound
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3001 enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 4, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 4.
[DeviceC] cfd service-instance 4 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 4
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 4, create outward-facing MEP 4001 in Ethernet service instance 4, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceC] cfd meplist 4001 4002 service-instance 4
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 4001 service-instance 4 outbound
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4001 enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 3001 in Ethernet service instance 3.
[DeviceC] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 4001 in Ethernet service instance 4.
[DeviceC] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 2 and bring up the port.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create ERPS ring 2.
[DeviceC] erps ring 2
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceC-erps-ring2] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/3
# Configure ERPS ring 2 as the subring.
[DeviceC-erps-ring2] ring-type sub-ring
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceC-erps-ring2] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceC-erps-ring2-inst1] node-role interconnection port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceC-erps-ring2-inst1] control-vlan 110
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceC-erps-ring2-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceC-erps-ring2-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceC-erps-ring2-inst1] quit
[DeviceC-erps-ring2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 5, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 5.
[DeviceC] cfd service-instance 5 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 5
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 5, create outward-facing MEP 5001 in Ethernet service instance 3, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/3.
[DeviceC] cfd meplist 5001 5002 service-instance 5
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] cfd mep 5001 service-instance 5 outbound
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] cfd cc service-instance 5 mep 5001 enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 5001 in Ethernet service instance 3.
[DeviceC] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 5 mep 5001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/3 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] port erps ring 2 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] undo shutdown
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceC] erps enable
4. Configure Device D.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD] stp region-configuration
[DeviceD-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceD-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/3 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] link-delay up 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] link-delay down 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] undo stp enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceD] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceD] cfd enable
[DeviceD] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 2, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 2.
[DeviceD] cfd service-instance 2 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 2
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 2, create outward-facing MEP 2002 in Ethernet service instance 2, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceD] cfd meplist 2001 2002 service-instance 2
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 2002 service-instance 2 outbound
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2002 enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 4, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 4.
[DeviceD] cfd service-instance 4 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 4
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 4, create outward-facing MEP 4002 in Ethernet service instance 4, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceD] cfd meplist 4001 4002 service-instance 4
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 4002 service-instance 4 outbound
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4002 enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 2002 in Ethernet service instance 2.
[DeviceD] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 4002 in Ethernet service instance 4.
[DeviceD] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 2 and bring up the port.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create ERPS ring 2.
[DeviceD] erps ring 2
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceD-erps-ring2] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/3
# Configure ERPS ring 2 as the subring.
[DeviceD-erps-ring2] ring-type sub-ring
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceD-erps-ring2] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceD-erps-ring2-inst1] node-role interconnection port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceD-erps-ring2-inst1] control-vlan 110
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceD-erps-ring2-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceD-erps-ring2-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceD-erps-ring2-inst1] quit
[DeviceD-erps-ring2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 6, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 6.
[DeviceD] cfd service-instance 6 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 6
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 6, create outward-facing MEP 6002 in Ethernet service instance 3, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/3.
[DeviceD] cfd meplist 6001 6002 service-instance 6
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] cfd mep 6002 service-instance 6 outbound
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] cfd cc service-instance 6 mep 6002 enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 6002 in Ethernet service instance 6.
[DeviceD] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 6 mep 6002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/3 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/3
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] port erps ring 2 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] undo shutdown
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/3] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceD] erps enable
5. Configure Device E.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceE> system-view
[DeviceE] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceE] stp region-configuration
[DeviceE-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceE-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceE-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceE] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceE] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 2.
[DeviceE] erps ring 2
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceE-erps-ring2] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceE-erps-ring2] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Configure ERPS ring 2 as the subring.
[DeviceE-erps-ring2] ring-type sub-ring
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceE-erps-ring2] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceE-erps-ring2] node-role owner rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceE-erps-ring2-inst1] control-vlan 110
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceE-erps-ring2-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceE-erps-ring2-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceE-erps-ring2-inst1] quit
[DeviceE-erps-ring2] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceE] cfd enable
[DeviceE] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 6, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 6.
[DeviceE] cfd service-instance 6 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 6
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 6, create outward-facing MEP 6001 in Ethernet service instance 6, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceE] cfd meplist 6001 6002 service-instance 6
[DeviceE] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 6001 service-instance 6 outbound
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 6 mep 6001 enable
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 7, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 7.
[DeviceE] cfd service-instance 7 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 7
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 7, create outward-facing MEP 7001 in Ethernet service instance 7, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceE] cfd meplist 7001 7002 service-instance 7
[DeviceE] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 7001 service-instance 7 outbound
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 7 mep 7001 enable
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 6001 in Ethernet service instance 6.
[DeviceE] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 6 mep 6001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceE] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 2 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 7001 in Ethernet service instance 7.
[DeviceE] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 7 mep 7001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 2 and bring up the port.
[DeviceE] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 2 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceE-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceE] erps enable
6. Configure Device F.
# Create VLANs 1 to 30, map these VLANs to MSTI 1, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceF> system-view
[DeviceF] vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceF] stp region-configuration
[DeviceF-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceF-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceF-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceF] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 30.
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceF] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 2.
[DeviceF] erps ring 2
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceF-erps-ring2] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceF-erps-ring2] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Configure ERPS ring 2 as the subring.
[DeviceF-erps-ring2] ring-type sub-ring
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceF-erps-ring2] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceF-erps-ring2] node-role neighbor rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceF-erps-ring2-inst1] control-vlan 110
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceF-erps-ring2-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceF-erps-ring2-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceF-erps-ring2-inst1] quit
[DeviceF-erps-ring2] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceF] cfd enable
[DeviceF] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 5, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 5.
[DeviceF] cfd service-instance 5 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 5
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 5, create outward-facing MEP 5002 in Ethernet service instance 5, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceF] cfd meplist 5001 5002 service-instance 5
[DeviceF] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 5002 service-instance 5 outbound
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 5 mep 5002 enable
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 7, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 7.
[DeviceF] cfd service-instance 7 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 7
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 7, create outward-facing MEP 7002 in Ethernet service instance 7, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceF] cfd meplist 7001 7002 service-instance 7
[DeviceF] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 7002 service-instance 7 outbound
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 7 mep 7002 enable
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 5001 in Ethernet service instance 5.
[DeviceF] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 5 mep 5002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 1 and bring up the port.
[DeviceF] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 2 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 7002 in Ethernet service instance 7.
[DeviceF] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 7 mep 7002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 2 and bring up the port.
[DeviceF] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 2 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceF-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceF] erps enable
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about ERPS instance 1 for Device A.
[Device A] display erps detail ring 1
Ring ID : 1
Port0 : HundredGigE1/0/1
Port1 : HundredGigE1/0/2
Subring : Yes
Default MAC : No
Instance ID : 1
Node role : Owner
Node state : Idle
Connect(ring/instance): -
Control VLAN : 100
Protected VLAN : Reference-instance 1
Guard timer : 500 ms
Hold-off timer : 0 ms
WTR timer : 5 min
Revertive operation : Revertive
Enable status : Yes
Active status : Yes
R-APS level : 7
Port PortRole PortStatus
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port0 RPL Block
Port1 Non-RPL Up
The output shows the following information:
· Device A is the owner node.
· The ERPS ring is in idle state.
· The RPL port is blocked.
· The non-RPL port is unblocked.
Example: Configuring one-ring multi-instance load balancing
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 14, perform the following tasks to improve network resource utilization and implement load balancing among links:
· Configure ERPS instances 1 and 2 on the ERPS ring.
· For ERPS instance 1, configure the following items:
¡ Configure Device A as the owner node.
¡ Configure the link between Devices A and Device B as the RPL.
¡ Configure VLAN 100 as the control VLAN.
¡ Configure VLANs 1 to 30 as the protected VLANs.
· For ERPS instance 2, configure the following items:
¡ Configure Device A as the owner node.
¡ Configure the link between Devices C and Device D as the RPL.
¡ Configure VLAN 100 as the control VLAN.
¡ Configure VLANs 31 to 60 as the protected VLANs.
Prerequisites
By default, interfaces on the device are disabled (in ADM or Administratively Down state). To have an interface operate, you must use the undo shutdown command to enable that interface.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A.
# Create VLANs 1 to 60, map VLANs 1 to 30 to MSTI 1, map VLANs 31 to 60 to MSTI 2, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceA] stp region-configuration
[DeviceA-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceA-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 31 to 60
[DeviceA-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceA-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 60.
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceA] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] node-role owner rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] quit
# Create ERPS instance 2.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] instance 2
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst2] control-vlan 110
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2
# Enable ERPS for instance 2.
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst2] instance enable
[DeviceA-erps-ring1-inst2] quit
[DeviceA-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceA] cfd enable
[DeviceA] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 1, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 1.
[DeviceA] cfd service-instance 1 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 1
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 1, create outward-facing MEP 1001 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceA] cfd meplist 1001 1002 service-instance 1
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 1001 service-instance 1 outbound
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1001 enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 2, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 2.
[DeviceA] cfd service-instance 2 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 2
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 2, create outward-facing MEP 2001 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceA] cfd meplist 2001 2002 service-instance 2
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 2001 service-instance 2 outbound
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2001 enable
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 1001 in Ethernet service instance 1.
[DeviceA] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 1 and bring up the port for ERPS instances 1 and 2.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 2 track 1
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 2001 in Ethernet service instance 2.
[DeviceA] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 2 and bring up the port for ERPS instances 1 and 2.
[DeviceA] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 2 track 2
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceA-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceA] erps enable
2. Configure Device B.
# Create VLANs 1 to 60, map VLANs 1 to 30 to MSTI 1, map VLANs 31 to 60 to MSTI 2, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceB] stp region-configuration
[DeviceB-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceB-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 31 to 60
[DeviceB-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceB-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 60.
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceB] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] node-role neighbor rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] quit
# Create ERPS instance 2.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] instance 2
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst2] control-vlan 110
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2
# Enable ERPS for instance 2.
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst2] instance enable
[DeviceB-erps-ring1-inst2] quit
[DeviceB-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceB] cfd enable
[DeviceB] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 1, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 1.
[DeviceB] cfd service-instance 1 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 1
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 1, create outward-facing MEP 1002 in Ethernet service instance 1, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceB] cfd meplist 1001 1002 service-instance 1
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 1002 service-instance 1 outbound
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1002 enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 3, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 3.
[DeviceB] cfd service-instance 3 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 3
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 3, create outward-facing MEP 3002 in Ethernet service instance 3, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceB] cfd meplist 3001 3002 service-instance 3
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 3002 service-instance 3 outbound
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3002 enable
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 1002 in Ethernet service instance 1.
[DeviceB] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 1 mep 1002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 1 and bring up the port for ERPS instances 1 and 2.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 2 track 1
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 3002 in Ethernet service instance 3.
[DeviceB] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 2 and bring up the port for ERPS instances 1 and 2.
[DeviceB] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 2 track 2
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceB-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceB] erps enable
3. Configure Device C.
# Create VLANs 1 to 60, map VLANs 1 to 30 to MSTI 1, map VLANs 31 to 60 to MSTI 2, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceC] stp region-configuration
[DeviceC-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceC-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 31 to 60
[DeviceC-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceC-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 60.
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceC] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst1] quit
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] quit
# Create ERPS instance 2.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] instance 2
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst2] node-role owner rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst2] control-vlan 110
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2
# Enable ERPS for instance 2.
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst2] instance enable
[DeviceC-erps-ring1-inst2] quit
[DeviceC-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceC] cfd enable
[DeviceC] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 3, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 3.
[DeviceC] cfd service-instance 3 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 3
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 3, create outward-facing MEP 3001 in Ethernet service instance 3, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceC] cfd meplist 3001 3002 service-instance 3
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 3001 service-instance 3 outbound
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3001 enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 4, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 4.
[DeviceC] cfd service-instance 4 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 4
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 4, create outward-facing MEP 4001 in Ethernet service instance 4, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceC] cfd meplist 4001 4002 service-instance 4
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 4001 service-instance 4 outbound
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4001 enable
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 3001 in Ethernet service instance 3.
[DeviceC] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 3 mep 3001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 1 and bring up the port for ERPS instances 1 and 2.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 2 track 1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 4001 in Ethernet service instance 4.
[DeviceC] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4001
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 2 and bring up the port for ERPS instances 1 and 2.
[DeviceC] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 2 track 2
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceC-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceC] erps enable
4. Configure Device D.
# Create VLANs 1 to 60, map VLANs 1 to 30 to MSTI 1, map VLANs 31 to 60 to MSTI 2, and activate the MST region configuration.
<DeviceD> system-view
[DeviceD] vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceD] stp region-configuration
[DeviceD-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 1 to 30
[DeviceD-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 31 to 60
[DeviceD-mst-region] active region-configuration
[DeviceD-mst-region] quit
# Set the link state change suppression interval to 0 seconds on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay up 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] link-delay down 0
# Disable the spanning tree feature on the port.
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo stp enable
# Configure the port as a trunk port and assign it to VLANs 1 to 60.
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Configure HundredGigE 1/0/2 in the same way HundredGigE 1/0/1 is configured.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay up 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] link-delay down 0
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo stp enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 1 to 60
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create ERPS ring 1.
[DeviceD] erps ring 1
# Configure ERPS ring member ports.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] port0 interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] port1 interface hundredgige 1/0/2
# Create ERPS instance 1.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] instance 1
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] control-vlan 100
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] protected-vlan reference-instance 1
# Enable ERPS for instance 1.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst1] instance enable
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] quit
# Create ERPS instance 2.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] instance 2
# Configure the node role.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst2] node-role neighbor rpl port0
# Configure the control VLAN.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst2] control-vlan 110
# Configure the protected VLANs.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst2] protected-vlan reference-instance 2
# Enable ERPS for instance 2.
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst2] instance enable
[DeviceD-erps-ring1-inst2] quit
[DeviceD-erps-ring1] quit
# Enable CFD, and create a level-5 MD named MD_A.
[DeviceD] cfd enable
[DeviceD] cfd md MD_A level 5
# Create Ethernet service instance 2, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 2.
[DeviceD] cfd service-instance 2 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 2
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 2, create outward-facing MEP 2002 in Ethernet service instance 2, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/2.
[DeviceD] cfd meplist 2001 2002 service-instance 2
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd mep 2002 service-instance 2 outbound
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2002 enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create Ethernet service instance 4, in which the MA is identified by a VLAN and serves VLAN 4.
[DeviceD] cfd service-instance 4 ma-id vlan-based md MD_A vlan 4
# Configure a MEP list in Ethernet service instance 4, create outward-facing MEP 4002 in Ethernet service instance 4, and enable CCM sending on HundredGigE 1/0/1.
[DeviceD] cfd meplist 4001 4002 service-instance 4
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd mep 4002 service-instance 4 outbound
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4002 enable
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Create track entry 1 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 2002 in Ethernet service instance 2.
[DeviceD] track 1 cfd cc service-instance 2 mep 2002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/2 with track entry 1 and bring up the port for ERPS instances 1 and 2.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] port erps ring 1 instance 2 track 1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] undo shutdown
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/2] quit
# Create track entry 2 and associate it with the CC function of CFD for MEP 4002 in Ethernet service instance 4.
[DeviceD] track 2 cfd cc service-instance 4 mep 4002
# Associate HundredGigE 1/0/1 with track entry 2 and bring up the port for ERPS instances 1 and 2.
[DeviceD] interface hundredgige 1/0/1
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 1 track 2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] port erps ring 1 instance 2 track 2
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] undo shutdown
[DeviceD-HundredGigE1/0/1] quit
# Enable ERPS.
[DeviceD] erps enable
Verifying the configuration
# Display information about ERPS instance 1 for Device A.
[Device A] display erps detail ring 1
Ring ID : 1
Port0 : HundredGigE1/0/1
Port1 : HundredGigE1/0/2
Subring : No
Default MAC : No
Instance ID : 1
Node role : Owner
Node state : Idle
Connect(ring/instance): -
Control VLAN : 100
Protected VLAN : Reference-instance 1
Guard timer : 500 ms
Hold-off timer : 0 ms
WTR timer : 5 min
Revertive operation : Revertive
Enable status : Yes
Active status : Yes
R-APS level : 7
Port PortRole PortStatus
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port0 RPL Block
Port1 Non-RPL Up
Instance ID : 2
Node role : Normal
Node state : Idle
Connect(ring/instance): -
Control VLAN : 100
Protected VLAN : Reference-instance 2
Guard timer : 500 ms
Hold-off timer : 0 ms
WTR timer : 5 min
Revertive operation : Revertive
Enable status : Yes
Active status : Yes
R-APS level : 7
Port PortRole PortStatus
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port0 Non-RPL Up
Port1 Non-RPL Up
The output shows the following information:
· For ERPS instance 1:
¡ Device A is the owner node.
¡ The ERPS ring is in idle state.
¡ The RPL port is blocked.
¡ The non-RPL port is unblocked.
· For ERPS instance 2:
¡ Device A is a normal node.
¡ The ERPS ring is in idle state.
¡ The non-RPL port is unblocked.
Troubleshooting ERPS
The owner node cannot receive SF packets from a faulty node when the link state is normal
Symptom
The link between the owner node and the faulty node is available, but the owner node cannot receive SF packets sent by the faulty node. The RPL port is blocked.
Analysis
Possible reasons include:
· ERPS is not enabled for some nodes on the ERPS ring.
· The ring IDs are different for the nodes on the same ERPS ring.
· The control VLAN IDs are different for the nodes in the same ERPS instance.
· A port on the ERPS ring is faulty.
Solutions
To resolve the problem:
· Use the display erps command to examine whether ERPS is enabled for all nodes on the ERPS ring. If ERPS is disabled for some nodes, use the erps enable command to enable ERPS for the nodes.
· Set the same ring ID for all nodes on a ERPS ring and configure the same control VLAN for all nodes in an ERPS instance.
· Use the display erps detail command to examine the port status for all nodes. Bring up the ports in down state.
· Use the debugging erps command on all nodes to view debugging information about packets and node status.