- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Network Configuration
- 01-Access Public and Dedicated Networks Through Multiple WAN Interfaces (CLI)
- 02-Basic Network Access (DHCP-Based IP Address Acquisition) Configuration Examples (CLI)
- 03-ER G3 Routers PPPoE Configuration Examples (Web)
- 04-ER G3 Routers Basic Network Access (DHCP-Based IP Address Acquisition) (Web)
- 05-ER G3 Routers Basic Internet Access (Static IP) Web-Based Configuration Examples
- 06-MER Routers Basic Network Access (DHCP-Based IP Address Acquisition) (Web)
- 07-MER Routers Primary and Backup Network Accesses Through Multiple WAN Interfaces (Web)
- 08-MER Routers PPPoE Configuration Examples (Web)
- 09-MER Routers Access Public and Dedicated Networks Through Multiple WAN Interfaces (Web)
- 10-MER Routers Basic Internet Access (Static IP) Web-Based Configuration Examples
- 11-MSR Routers Basic Network Access (DHCP-Based IP Address Acquisition) (Web)
- 12-MSR Routers Basic Internet Access (Static IP) Web-Based Configuration Examples
- 13-MSR Routers Access Public and Dedicated Networks Through Multiple WAN Interfaces (Web)
- 14-MSR Routers PPPoE Configuration Examples (CLI)
- 15-Router Basic Internet Access (Static IP) CLI-Based Configuration Examples
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 11-MSR Routers Basic Network Access (DHCP-Based IP Address Acquisition) (Web) | 834.02 KB |
MSR Routers
Basic Network Access (DHCP-Based IP Address Acquisition) (Web)
Copyright © 2024 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written consent of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd.
Except for the trademarks of New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd., any trademarks that may be mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Introduction
This document provides an example of configuring basic network access (DHCP-based IP address acquisition) through the Web interface of an MSR router.
Prerequisites
This document is not restricted to specific software or hardware versions. Procedures and information in the examples might be slightly different depending on the software or hardware version of the device.
The configuration examples were created and verified in a lab environment, and all the devices were started with the factory default configuration. When you are working on a live network, make sure you understand the potential impact of every command on your network.
The following information is provided based on the assumption that you have basic knowledge of DHCP and NAT.
Example: Configuring basic network access
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 1, the device acts as the egress router on the enterprise network and uses a single DHCP-enabled WAN interface to provide the PC with access to the Internet.
Software version used
This example is applicable to the MSR router series of the H3C Comware 7 platform. This document takes version R6749P14 of the H3C MSR3610-X1-DP router as an example. The specific operations might differ by product model and software version.
Restrictions and guidelines
The address range in the address pool configured on the LAN interface cannot belong to the same network segment as the IP address of the WAN interface on the device.
Procedures
You can use either of the following methods to configure basic network access settings:
· Fast configuration: Configures the key settings used for fast network access in the single-WAN or dual-WAN scenario. This configuration method is simple and can satisfy common network access demands.
· Network configuration: Configures the network access settings used in the single-WAN, dual-WAN, or multi-WAN scenario. Compared with the fast configuration mode, this configuration mode provides more configurable parameters to meet requirements for higher network performance and custom network access.
Fast configuration
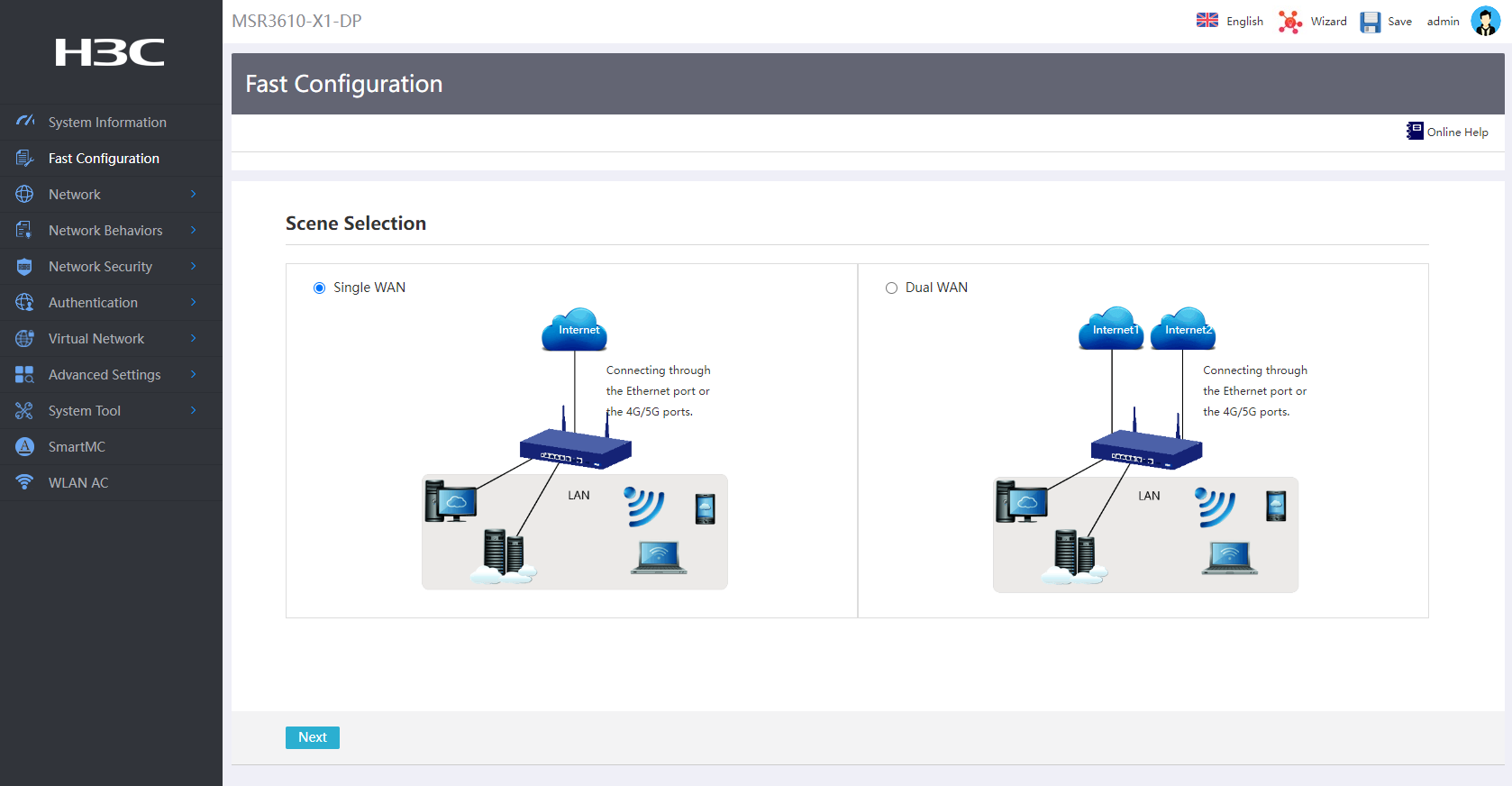
Configuring the WAN access scenario
# In this example, configure single-WAN as the access scenario for the router as follows:
1. Log into the Web interface of the router, and then select Fast Configuration from the left navigation pane.
2. On the Scene Selection page, select Single-WAN.
3. Click Next to open the single-WAN configuration page.
Figure 2 Selecting a WAN access scenario
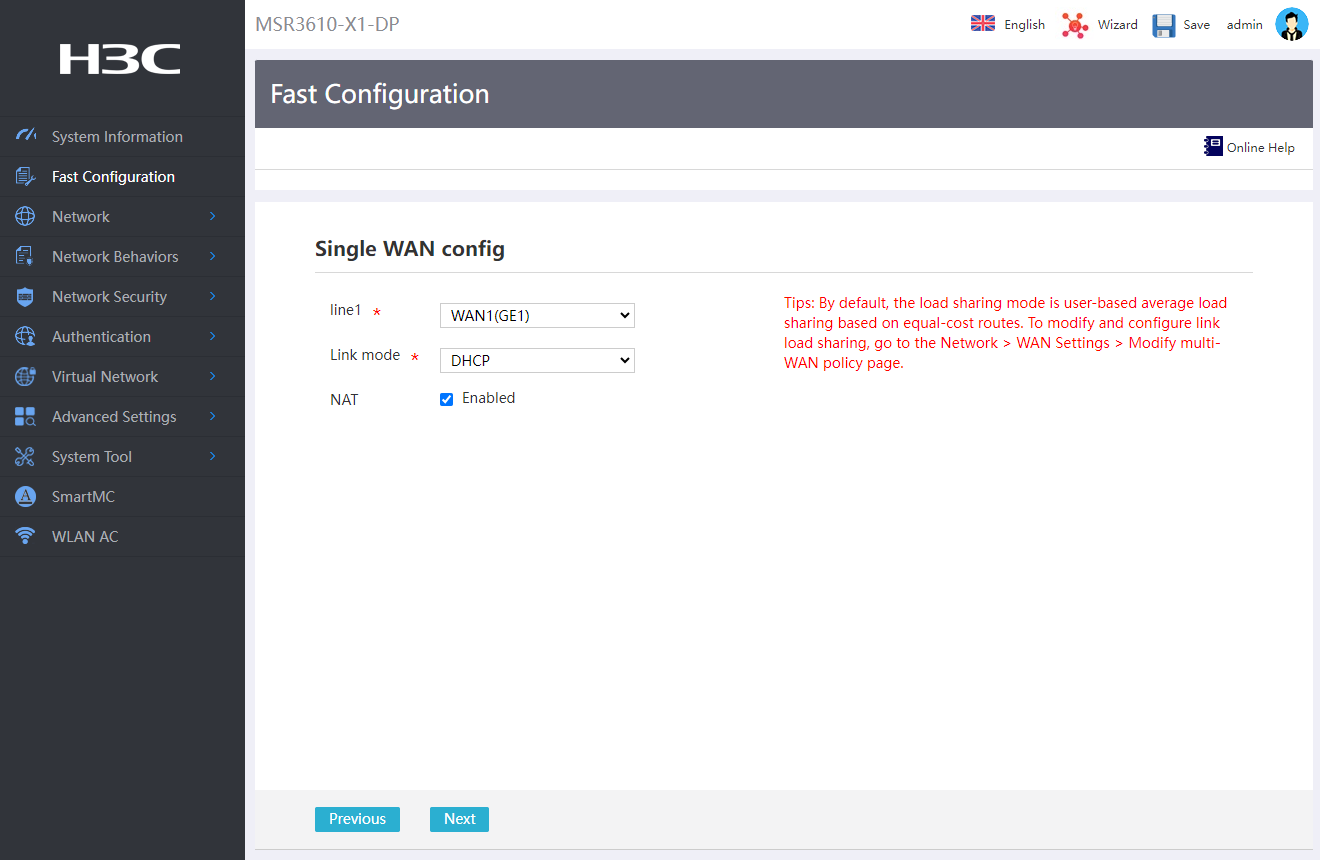
Configuring WAN interface settings
1. In the Line 1 field, select physical interface WAN1(GE1) for external network connectivity.
2. In the Link mode field, select DHCP.
3. In the NAT field, select Enable.
4. Click Next to open the LAN configuration page.
Figure 3 Configuring single-WAN settings
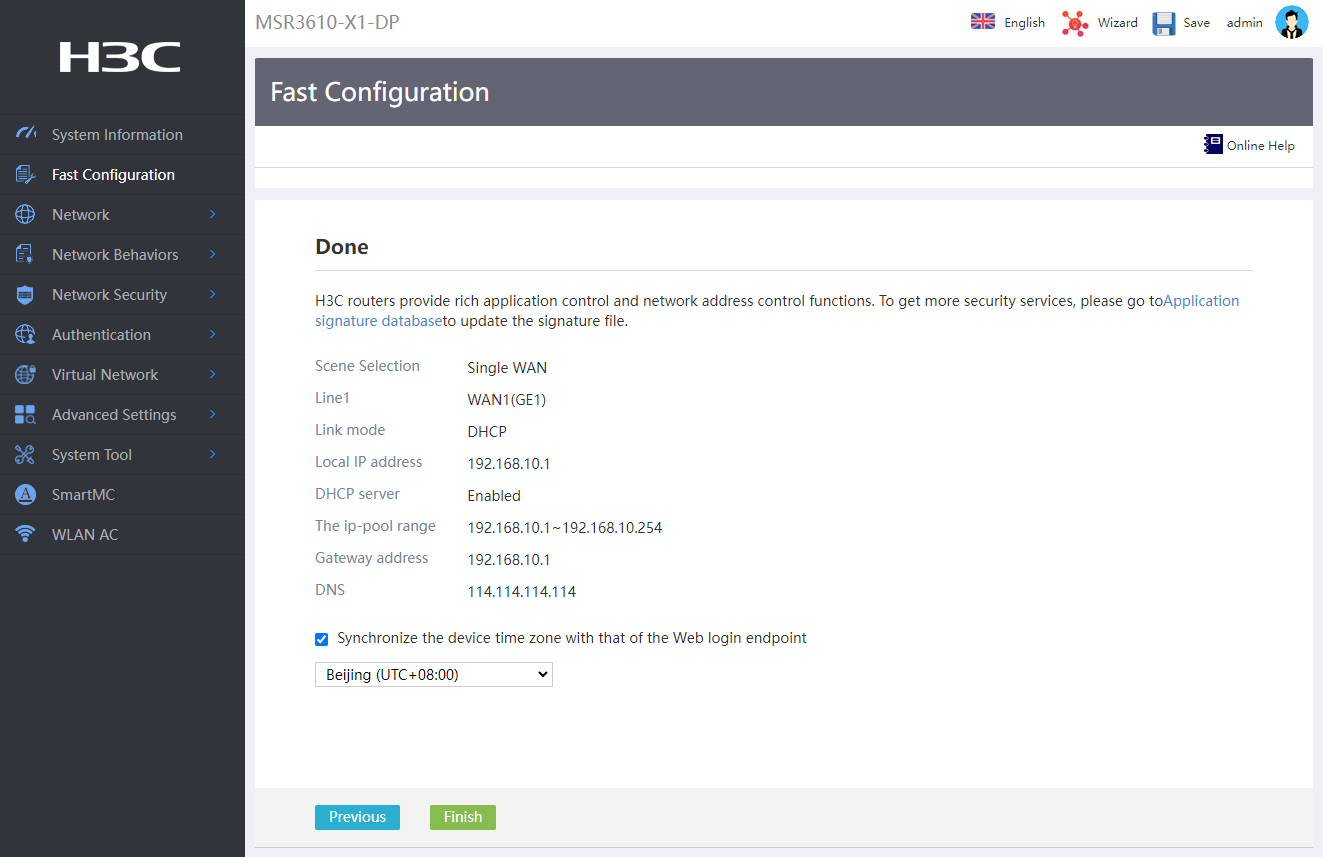
Configuring LAN interface settings
1. In the Local IP address field, enter 192.168.10.1. In the IP mask field, enter 255.255.255.0.
2. Enable the DHCP service.
3. In the IP distribution range field, enter IP address range 192.168.10.1 to 192.168.10.254. This IP address range is used for dynamic address assignment by DHCP.
4. In the Gateway address field, enter 192.168.10.1.
5. In the DNS field, enter DNS server IP address 114.114.114.114.
6. Click Next.
Figure 4 Configuring LAN interface settings
Saving the configuration
Click Finish to save the above configuration.
Figure 5 Saving the configuration
Network configuration
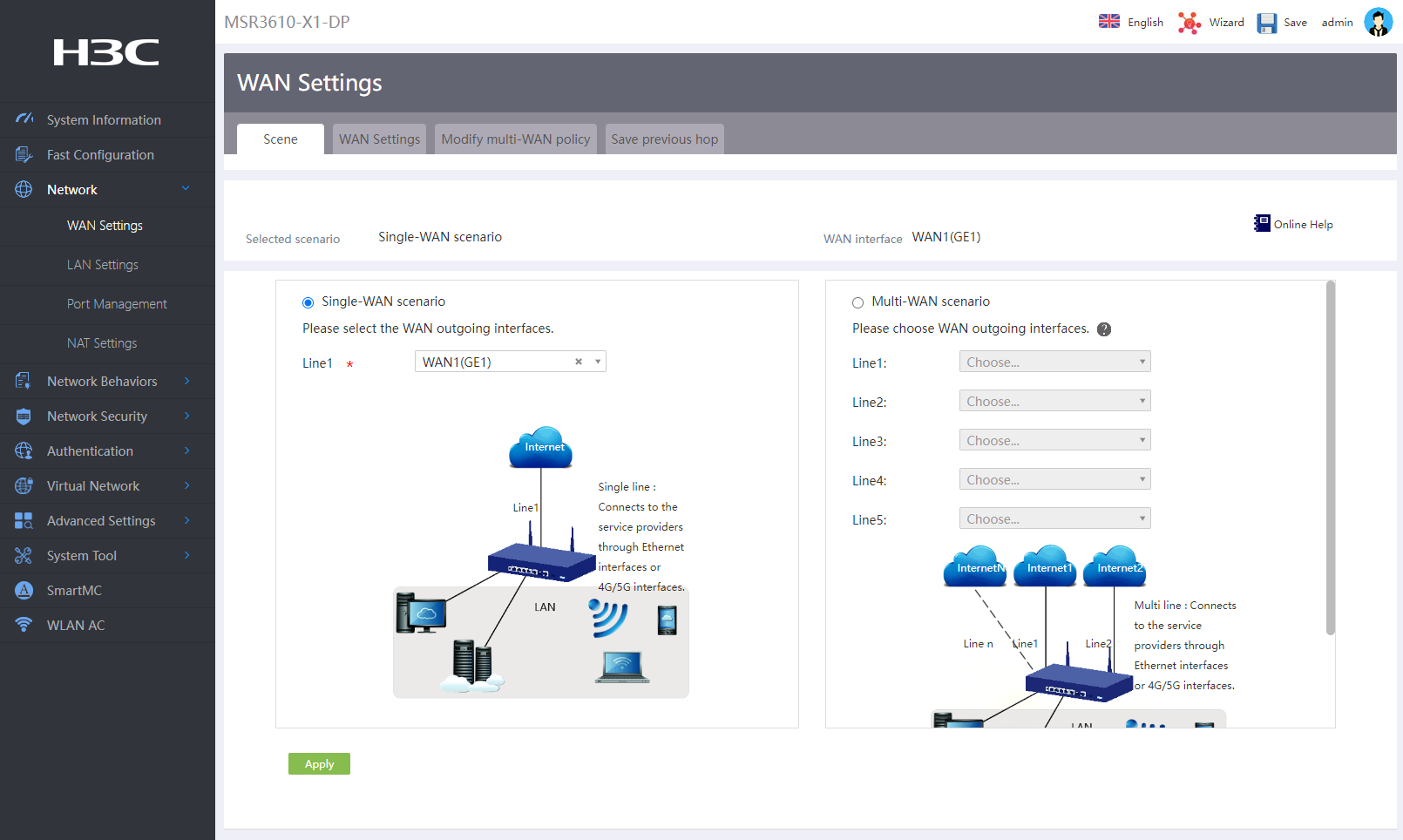
Configuring the WAN access scenario
# In this example, configure single-WAN as the interface mode for the router as follows:
1. Log in to the Web interface of the router, and then navigate to the Network > WAN Settings page.
2. On the Scene tab, select Single-WAN scenario.
3. In the Line 1 field, select physical interface WAN1(GE1) for external network connectivity.
4. Click Apply.
Figure 6 Configuring the WAN access scenario
Configuring WAN interface settings
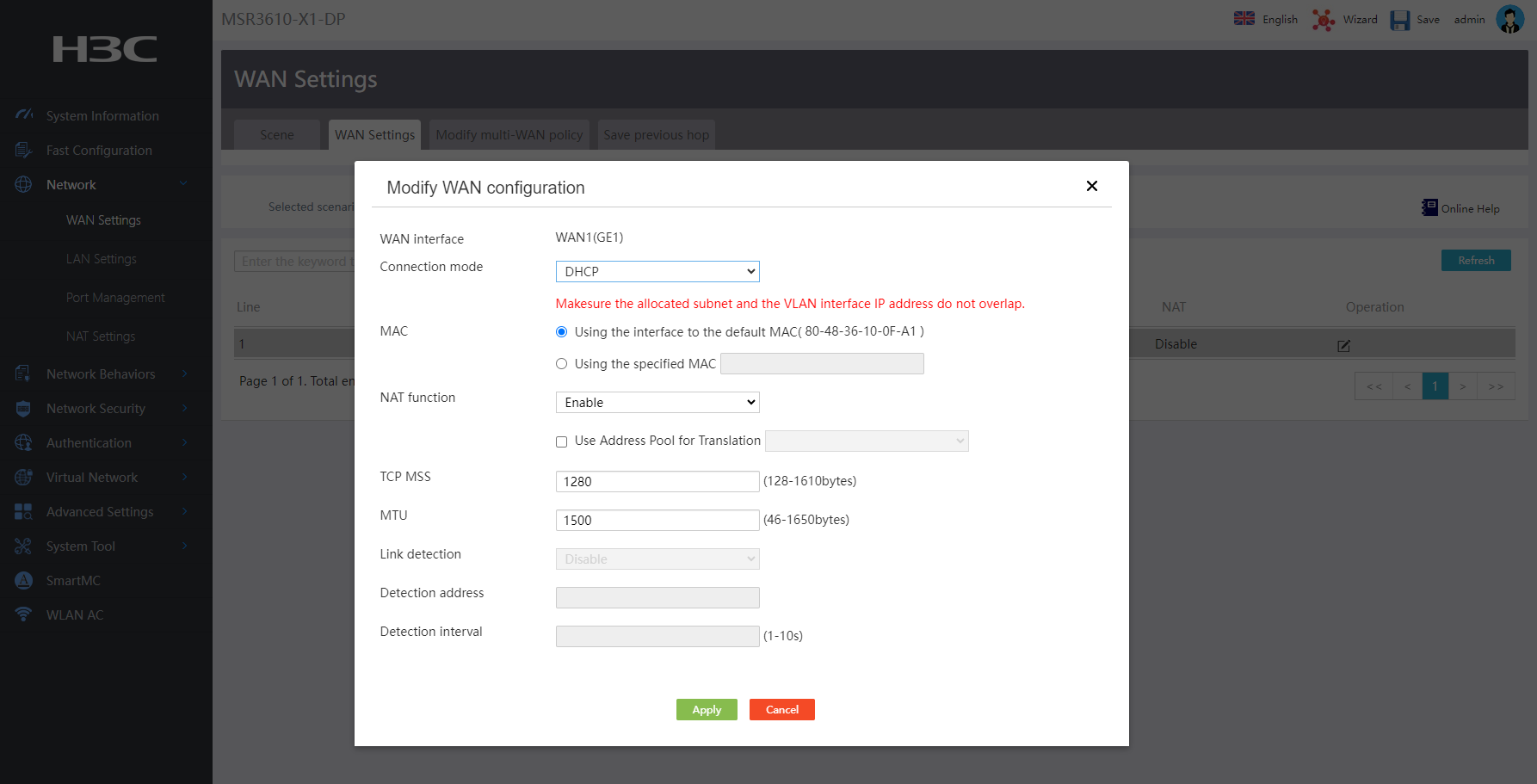
1. Click the WAN Settings tab.
2. Click the Edit icon in the Actions column for interface WAN1(GE1).
3. In the Connection mode field, select DHCP.
¡ In the MAC field, use the default MAC address, because the service provider does not specify a MAC address.
¡ In the NAT function field, select Enable.
¡ In the TCP MSS and MTU fields, configure the maximum segment size (MSS) of TCP packets and the MTU for the interface. In this example, the default settings are used.
4. Click Apply.
Figure 7 Edit WAN interface settings
Configuring LAN interface settings
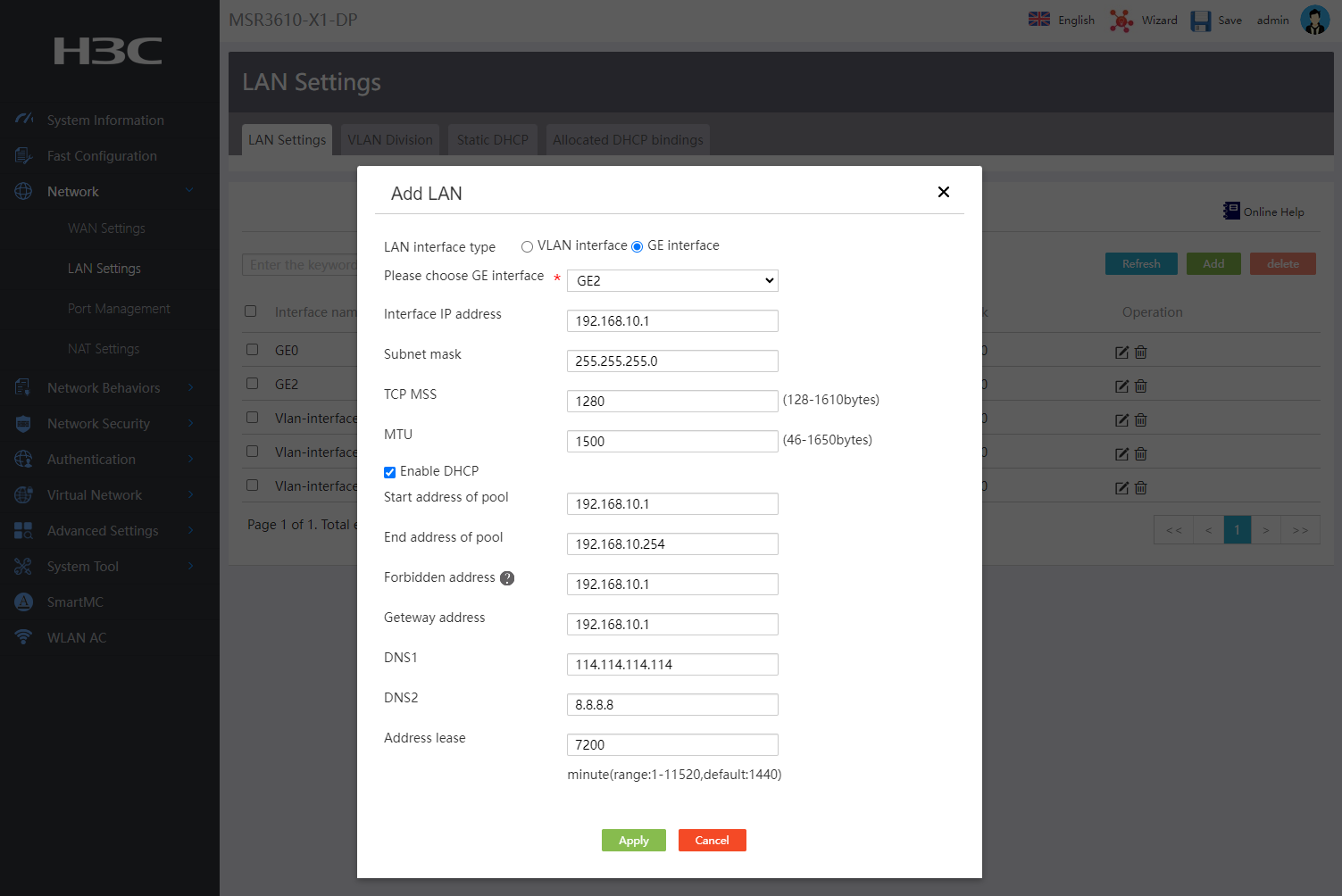
1. From the left navigation pane, select Network > LAN Settings.
2. Click the LAN Settings tab
3. Click Add to add a LAN.
4. In the LAN interface type field, select GE interface. In the Please choose GE interface field, select GE2 for internal network connectivity.
5. In the Interface IP address field, enter 192.168.10.1.
6. In the Subnet mask field, enter 255.255.255.0 or 24.
7. In the TCP MSS field, enter 1280.
8. In the MTU field, enter 1500.
9. To have the device assign IP addresses to clients attached to interface GE2, enable the DHCP service, and then configure the following parameters:
¡ In the Start IP Address and End IP Address fields, specify IP address range 192.168.10.0 to 192.168.10.254. This IP address range is used for dynamic IP address assignment to clients.
¡ In the Forbidden address field, exclude certain IP addresses in the specified IP address range from dynamic address assignment. In this example, gateway address 192.168.10.1 is excluded.
¡ In the Gateway address field, enter 192.168.10.1.
¡ In the DNS1 and DNS2 fields, enter DNS server IP addresses 114.114.114.114 and 8.8.8.8.
¡ In the Address lease field, enter the lease duration (in minutes) of IP addresses to be allocated. For example, to specify the lease of IP addresses as five days, enter 7200.
10. Click Apply.
Figure 8 Adding a LAN
Verifying the configuration
The PC can access the Internet.