- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 04-EPON VoIP configuration | 114.69 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: EPON VoIP configuration
Configuring the IAD module on an ONU
Configuring the voice VLAN operation mode on an ONU
Bringing up a VoIP port on an ONU
Setting the heartbeat parameters for the voice service on an ONU
Configuring the negotiation and transmission modes for the fax and modem services on an ONU
Specifying SIP registrar servers for an ONU
Specifying SIP proxy servers for an ONU
Configuring SIP digit maps for an ONU
Specifying the port number of the SIP media gateway for an ONU
Specifying the outbound SIP server for an ONU
Display and maintenance commands for EPON VoIP
EPON VoIP configuration examples
Example: Configuring SIP voice for ONUs attached to an OLT
Configuring EPON VoIP
Restrictions and guidelines: EPON VoIP configuration
Support for EPON VoIP features depends on the ONU model.
EPON is supported only on the default MDC. For more information about the default MDC, see MDC configuration in Virtual Technologies Configuration Guide.
Configuring basic EPON VoIP
EPON VoIP tasks at a glance
To configure basic EPON VoIP, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring the IAD module on an ONU
2. Configuring the voice VLAN operation mode on an ONU
3. Bringing up a VoIP port on an ONU
4. (Optional.) Setting the heartbeat parameters for the voice service on an ONU
5. (Optional.) Configuring the negotiation and transmission modes for the fax and modem services on an ONU
Configuring the IAD module on an ONU
About this task
The Integrated Access Device (IAD) module acts as the gateway of the VoIP or FoIP media. Under the control of the SIP server or the Media Gateway Controller (MGC), IAD converts the analog voice data to IP data, transmits the IP data over the IP network, and completes call exchange between the calling and called parties.
You can configure the IP address of the IAD module on an ONU remotely.
You can issue the following operations to the IAD module on an ONU.
· cancel—Cancels the registration of the IAD module from the SIP registrar server or MGC.
· re-register—Registers the IAD module with the SIP registrar or MGC.
· reset—Restores the factory defaults to the IAD module.
Configuration procedure
To configure the IAD module on an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the IP address of the IAD module on the ONU. |
· Manually assign an IP address. · Obtain an IP address through DHCP. · Obtain an IP address through PPPoE. |
By default, no IP address is configured for the IAD module of an ONU. |
|
4. (Optional.) Issue an operation to the IAD module of the ONU. |
iad operation { cancel | re-register | reset } |
N/A |
Configuring the voice VLAN operation mode on an ONU
About this task
The voice VLAN feature enables the device to transmit voice packets on an ONU in a dedicated VLAN. Use this feature to guarantee the transmission of voice packets when a network congestion occurs.
The device supports the following voice VLAN modes:
· Transparent mode—The ONU directly sends voice packets to the OLT without tagging the packets. As a best practice, do not use this mode.
· VLAN tagging mode—The ONU tags voice packets with a VLAN ID.
· QinQ mode—The ONU tags voice packets with an inner VLAN ID and an outer VLAN ID. The outer VLAN ID is used as the voice VLAN in the network layer for the service provider to manage voice services in a centralized way.
Configuration procedure
To configure the voice VLAN operation mode on an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the operation mode for the voice VLAN feature. |
· Configure transparent mode. · Configure VLAN tagging mode. · Configure QinQ mode. |
By default, the voice VLAN feature operates in transparent mode. |
Bringing up a VoIP port on an ONU
About this task
You can remotely bring up a VoIP port on an ONU from an OLT.
An ONU might identify physical VoIP ports as POTS or FXS interfaces. Support for POTS and FXS interfaces depends on ONU model.
Configuration procedure
To bring up a VoIP port on an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Bring up a VoIP port on the ONU. |
undo voip-port port-number shutdown |
By default, VoIP ports on an ONU are shut down. |
Setting the heartbeat parameters for the voice service on an ONU
About this task
An ONU sends a keepalive message to the SIP server or MGC at the heartbeat cycle. If no reply message from the server or MGC is received after the specified heartbeat count, the ONU determines that the connection with the server is down.
Configuration procedure
To set the heartbeat parameters for the voice service on an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Set the heartbeat parameters for the voice service on the ONU. |
voip heartbeat { cycle interval | count count }* |
By default, the heartbeat cycle is 60 seconds and the heartbeat count is 3. |
Configuring the negotiation and transmission modes for the fax and modem services on an ONU
About this task
An ONU supports the following negotiation modes for the fax and modem services:
· Auto-Voice Band Data (auto-VBD) mode—The ONU automatically changes the codecs for the fax and modem services without negotiating with the SIP server or MGC.
· Auto-negotiation mode—The ONU negotiates the codecs for the fax and modem services with the SIP server or MGC.
An ONU supports the following transmission modes for the fax and modem services:
· T.38—Fax-dedicated transmission mode. The ONU encodes the fax signals into data and then sends the data to the peer device over an IP network. The peer fax machine decodes the data into fax signals upon receiving the data. This mode features in low bandwidth usage and high transmission efficiency.
· Transparent—Pass-through transmission mode, also called T30 mode. The ONU directly sends the fax signals to the peer fax machine over a PSTN network. This mode features in simple implementation and low transmission latency. However, it might suffer from packet loss and network jitter.
Configuration procedure
To configure the negotiation and transmission modes for the fax and modem services on an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Configure the negotiation mode for the fax and modem services on the ONU. |
voip fax-modem negotiation-mode { auto-vbd | negotiate } |
By default, the auto-negotiation mode is used for the fax and modem services on an ONU. |
|
4. Configure the transmission mode for the fax and modem services on the ONU. |
voip fax-modem transmission-mode { t38 | transparent } |
By default, the transparent mode is used for the fax and modem services on an ONU. |
Configuring EPON SIP
EPON SIP tasks at a glance
To configure EPON SIP, perform the following tasks:
1. Specifying SIP registrar servers for an ONU
2. Specifying SIP proxy servers for an ONU
3. Configuring SIP digit maps for an ONU
5. (Optional.) Specifying the port number of the SIP media gateway for an ONU
6. (Optional.) Specifying the outbound SIP server for an ONU
Specifying SIP registrar servers for an ONU
About this task
A SIP registrar server receives and manages registration from SIP users on Onus.
Configuration procedure
To specify SIP registrar servers for an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Specify SIP registrar servers for the ONU. |
· Specify the primary SIP registrar
server. · Specify the backup SIP registrar server. |
By default, no SIP registrar servers are specified for an ONU. |
|
4. (Optional.) Set the SIP user registration interval for the ONU. |
voip sip registration-interval interval |
By default, an ONU registers SIP users with the SIP registrar server at the interval of 3600 seconds. As a best practice, use the default setting. |
Specifying SIP proxy servers for an ONU
About this task
A SIP proxy server forwards requests and responses from SIP users, performs AAA on SIP users, and provides call control.
Configuration procedure
To specify SIP proxy servers for an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Specify SIP proxy servers for the ONU. |
· Specify the primary SIP proxy server. · Specify the backup SIP proxy server. |
By default, no SIP proxy servers are specified for an ONU. |
Configuring SIP digit maps for an ONU
About this task
A digit map is a dial plane used to restrict outgoing calls that can be placed on an ONU. If the dialed number does not meet the requirements of a digit map, the call cannot be placed.
A digit map can include the following characters:
· Digits 0 to 9.
· DTMF signs—Pound sign (#), asterisk sign (*), A, B, C, and D. These are functional keys on telephones.
· Wildcard character—X. It is used to match any digit.
· Range characters—Includes left square bracket ([), right square bracket (]), and hyphen (-). For example, range [*#] indicates asterisk sign (*) or pound sign (#) and range [0-9] indicates any digit in the range of 0 to 9.
· Position character—Dot (.). If a dot is included in a digit map, it indicates that the preceding digit appears one or more times.
· Digit map delimiter—Vertical bar (|). A digit map can include multiple dial plans separated by the delimiter, for example, 1xxx|3xxx.
· Timer—T, S, or L.
Restrictions and guidelines
The device issues the configured digit maps to ONUs. Support for digit maps depends on the ONU model. Interpretation of digit maps varies by ONU model.
To allow an ONU to place any call number, configure only one digit map [0-9*#]..
If you configure the content multiples times for the same digit map, the most recent configuration takes effect.
You can configure a maximum of 64 digit maps.
Configuration procedure
To configure SIP digit maps for an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Configure a digit map for the ONU. |
voip digit-map map-name map-content |
By default, no digit maps are configured for an ONU. Default digit maps exist on some ONUs. Calls can be directly placed on these ONUs and no digit maps are required to be configured. Support for default digit maps depends on ONU model. |
Adding SIP users to an ONU
Restrictions and guidelines
The SIP users to be added to an ONU must use phone numbers as well as username and password that have already been registered with the SIP registrar server.
Only one SIP user can be added to a VoIP port and a SIP user can be added to only one VoIP port.
Configuration procedure
To add SIP users to an ONU:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Add a SIP user to a VoIP port on the ONU. |
voip-port port-number sip account phone-number username username password { cipher | simple } password |
By default, no SIP user is added to any VoIP ports on an ONU. |
Specifying the port number of the SIP media gateway for an ONU
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Specify the port number of the SIP media gateway for the ONU. |
voip sip mg-port port |
By default, the port number is 5060 for the SIP media gateway on an ONU. |
Specifying the outbound SIP server for an ONU
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter interface view. |
· Enter ONU interface view. · Enter RONU interface view. |
N/A |
|
3. Specify the outbound SIP server for the ONU. |
voip sip outbound-server ip ip-address [ port port ] |
By default, no outbound SIP server is specified for an ONU. |
Display and maintenance commands for EPON VoIP
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about the IAD module on an ONU. |
display epon iad interface interface-type interface-number |
|
Display the status of a VoIP port on an ONU. |
display epon interface interface-type interface-number voip-port port-number status |
|
Display the SIP configuration on an ONU. |
display epon voip sip interface interface-type interface-number |
EPON VoIP configuration examples
Example: Configuring SIP voice for ONUs attached to an OLT
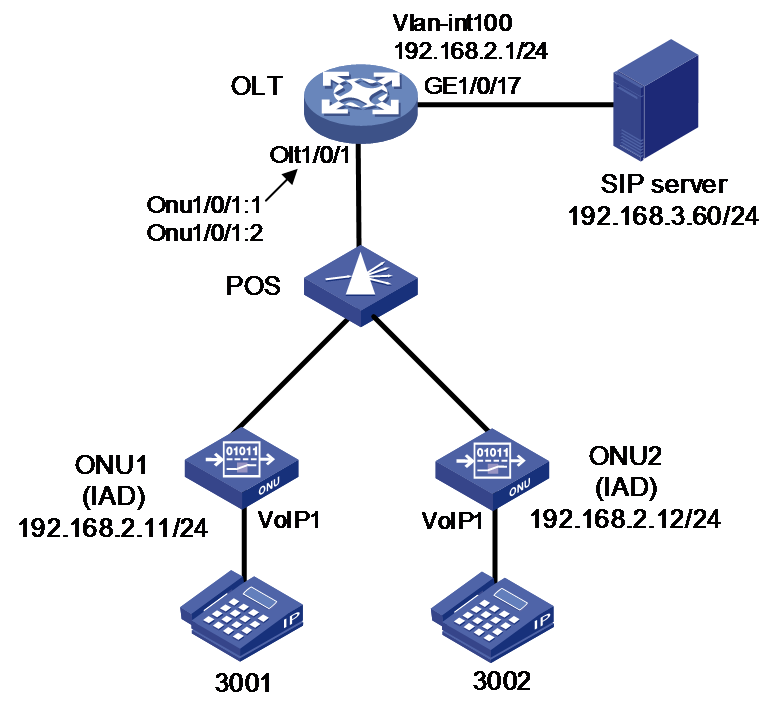
Network configuration
Configure SIP on the OLT so telephones attached to ONU 1 and ONU 2 can register with the SIP registrar server and then can call each other.
The OLT uses VLAN 100 to transmit voice data.
Configuration procedure
# Create VLAN 100 and its VLAN interface. Then, assign IP addresses to the interfaces on the OLT and make sure the OLT and the SIP server can reach each other. (Details not shown.)
# Enable auto ONU binding on slot 1. Then, the OLT will automatically create ONU interfaces ONU 1/0/1:1 and ONU 1/0/1:2.
<OLT> system-view
[OLT] ftth
[OLT-ftth] onu bind auto slot 1
[OLT-ftth] quit
# Assign OLT 1/0/1 to VLAN 100 as a tagged member.
[OLT] interface olt 1/0/1
[OLT-Olt1/0/1] port hybrid vlan 100 tag
[OLT-Olt1/0/1] quit
# Configure ONU 1/0/1:1 and ONU 1/0/1:2 as trunk ports, and assign them to all VLANs.
[OLT] interface range onu 1/0/1:1 to onu 1/0/1:2
[OLT-if-range] port link-type trunk
[OLT-if-range] port trunk permit vlan all
# Configure the VLAN tagging operation mode for the voice VLAN feature on ONU 1 and ONU 2.
[OLT-if-range] voice vlan 100
# Bring up VoIP port 1 on ONU 1 and ONU 2.
[OLT-if-range] undo voip-port 1 shutdown
# Specify the SIP registrar server at 192.168.3.60 for ONU 1 and ONU 2.
[OLT-if-range] voip sip registrar-server ip 192.168.3.60
# Specify the SIP proxy server at 192.168.3.60 for ONU 1 and ONU 2.
[OLT-if-range] voip sip proxy-server ip 192.168.3.60
# Configure digit map map1 for ONU 1 and ONU 2 to allow four-digit call numbers starting with 3 to be dialed out.
[OLT-if-range] voip digit-map map1 3xxx
[OLT-if-range] quit
# Configure the IP address and gateway address of the IAD module on ONU 1 as 192.168.2.11/24 and 192.168.2.1, respectively.
[OLT] interface onu 1/0/1:1
[OLT-Onu1/0/1:1] iad address 192.168.2.11 24 gateway 192.168.2.1
# Add SIP user with phone number 3001 as well as username 3001 and password 3001 in plaintext form to ONU 1.
[OLT-Onu1/0/1:1] voip-port 1 sip account 3001 username 3001 password simple 3001
[OLT-Onu1/0/1:1] quit
# Configure the IP address and gateway address of the IAD module on ONU 1 as 192.168.2.12/24 and 192.168.2.1, respectively.
[OLT] interface onu 1/0/1:2
[OLT-Onu1/0/1:2] iad address 192.168.2.12 24 gateway 192.168.2.1
# Add SIP user with phone number 3002 as well as username 3002 and password 3002 in plaintext form to ONU 1.
[OLT-Onu1/0/1:2] voip-port 1 sip account 3002 username 3002 password simple 3002
[OLT-Onu1/0/1:2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Register SIP users on ONU 1 and ONU 2 with the SIP registrar server and then place a call from 3001 to 3002. The call can be established. (Details not shown.)