- Table of Contents
-
- 05-Network Connectivity Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-MAC address table configuration
- 02-Ethernet link aggregation configuration
- 03-VLAN configuration
- 04-Loop detection configuration
- 05-Spanning tree configuration
- 06-LLDP configuration
- 07-Layer 2 forwarding configuration
- 08-VLAN termination configuration
- 09-PPP configuration
- 10-L2TP configuration
- 11-ARP configuration
- 12-IP addressing configuration
- 13-DHCP configuration
- 14-DHCPv6 configuration
- 15-DNS configuration
- 16-NAT configuration
- 17-IP performance optimization configuration
- 18-IPv6 basics configuration
- 19-GRE configuration
- 20-Tunneling configuration
- 21-Basic IP routing configuration
- 22-IP forwarding basics configuration
- 23-Static routing configuration
- 24-IPv6 static routing configuration
- 25-Policy-based routing configuration
- 26-IPv6 policy-based routing configuration
- 27-RIP configuration
- 28-RIPng configuration
- 29-Multicast overview
- 30-IGMP snooping configuration
- 31-MLD snooping configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 08-VLAN termination configuration | 123.38 KB |
VLAN termination application scenarios
Restrictions and guidelines: VLAN termination configuration
VLAN termination tasks at a glance
Configuring ambiguous Dot1q termination
Configuring unambiguous Dot1q termination
Configuring ambiguous QinQ termination
About ambiguous QinQ termination
Configuring ambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the outermost two layers of VLAN IDs
Configuring ambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the Layer 2 VLAN IDs
Configuring unambiguous QinQ termination
About unambiguous QinQ termination
Configuring unambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the outermost two layers of VLAN IDs
Configuring unambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the Layer 2 VLAN ID
Configuring untagged termination
Configuring default termination
Enabling a VLAN termination-enabled interface to transmit broadcasts and multicasts
Configuring VLAN termination
About VLAN termination
VLAN termination typically processes packets that include VLAN tags. A VLAN termination-enabled interface performs the following tasks when receiving a VLAN-tagged packet:
1. Assigns the packet to an interface according to its VLAN tags.
2. Removes the VLAN tags of the packet.
3. Delivers the packet to Layer 3 forwarding or other processing pipelines.
Before sending the packet, the VLAN termination-enabled interface determines whether to add new VLAN tags to the packet, based on the VLAN termination type.
VLAN termination can also process packets that do not include any VLAN tags.
This document uses the following VLAN tag concepts for a packet that has two or more layers of VLAN tags:
· Layer 1 VLAN tag—Specifies the outermost layer of VLAN tags.
· Layer 2 VLAN tag—Specifies the second outermost layer of VLAN tags.
The VLAN IDs of the packets are numbered in the same manner as the VLAN tags.
VLAN termination types
|
Types of packets to be terminated on the interface |
Tags of outgoing packets on the interface |
|
|
Dot1q termination |
The packets must meet both of the following requirements: · The packets include one or more layers of VLAN tags. · The outermost VLAN ID matches the configured value. |
Single-tagged |
|
QinQ termination |
The packets must meet both of the following requirements: · The packets include two or more layers of VLAN tags. · The outermost two layers of tags match the configured values. |
Double-tagged |
|
Untagged termination |
Untagged packets. |
Untagged |
|
Default termination |
Packets that cannot be processed on any other subinterfaces of the same main interface. |
Untagged |
VLAN termination mechanism
VLAN interfaces and subinterfaces, such as Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces and Layer 3 aggregate subinterfaces, can terminate the following packets:
· Packets whose outermost VLAN IDs match the configured values.
· Packets whose outermost two layers of VLAN IDs match the configured values.
A VLAN interface terminates only the packets whose outermost VLAN ID is the same as the VLAN interface number. For example, VLAN-interface 10 terminates only the packets with the outermost VLAN tag 10.
A main interface does not terminate VLAN-tagged packets (for example, Layer 3 Ethernet interface or Layer 3 aggregate interface). To terminate VLAN-tagged packets, create subinterfaces for the main interface.
Subinterfaces of the same main interface can use different types of VLAN termination. To process received packets, the system selects a subinterface based on the following VLAN termination types in descending order of priority:
· QinQ termination.
· Dot1q termination or support for Dot1q termination by default.
· Untagged termination.
· Default termination.
If none of these VLAN termination types applies, the main interface processes the packets.
If untagged termination is enabled on a subinterface of an interface, untagged packets are processed by the subinterface instead of the main interface.
If default termination is enabled on a subinterface of an interface, packets are processed by the subinterface instead of the main interface.
When a main interface is bound to a VLAN interface, the main interface processes VLAN-tagged packets according to the VLAN termination configuration of the VLAN interface.
VLAN termination application scenarios
Inter-VLAN communication
Hosts in different VLANs cannot directly communicate with each other. You can use Layer 3 routing to allow all VLANs to communicate. To restrict communication to the specified VLANs, configure VLAN termination on subinterfaces or VLAN interfaces.
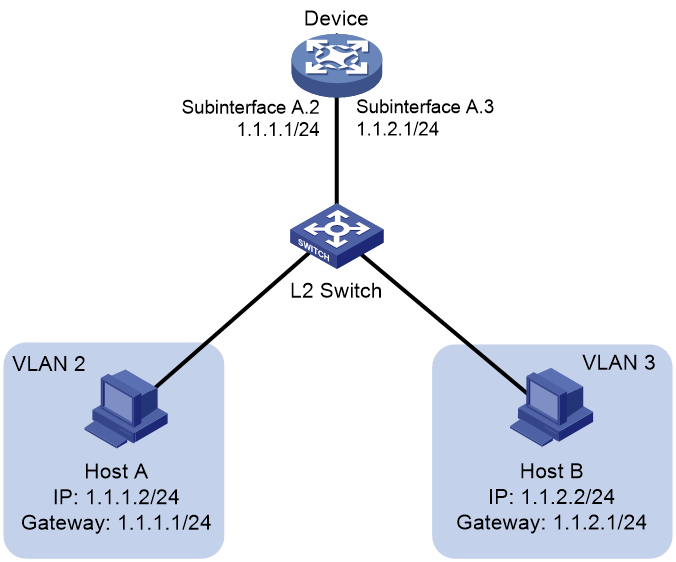
As shown in Figure 1, Host A and Host B are in different VLANs. For the two hosts to communicate with each other, perform the following tasks:
1. Specify 1.1.1.1/24 and 1.1.2.1/24 as the gateway IP address for Host A and Host B, respectively.
2. On the device, configure Dot1q termination on Layer 3 Ethernet subinterfaces Subinterface A.2 and Subinterface A.3.
Figure 1 Inter-VLAN communication through Layer 3 subinterfaces
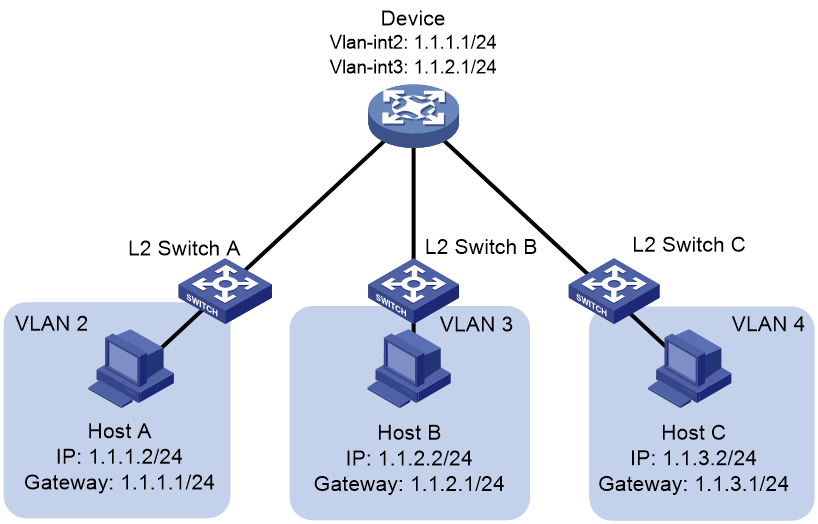
As shown in Figure 2, Host A is in VLAN 2, Host B is in VLAN 3, and Host C is in VLAN 4. For Host A and Host B to communicate with each other, perform the following tasks:
1. Specify 1.1.1.1/24 and 1.1.2.1/24 as the gateway IP address for Host A and Host B, respectively.
2. On the device, create VLAN-interface 2 and configure the IP address as 1.1.1.1/24, which is the same as the gateway address of Host A. Create VLAN-interface 3 and configure the IP address as 1.1.2.1/24, which is the same as the gateway address of Host B.
VLAN termination by the outermost VLAN ID of packets is automatically performed on VLAN interfaces. For example, when Host A sends a packet to Host B, VLAN-interface 2 removes the VLAN tag from the packet and forwards it to VLAN-interface 3. Then, VLAN-interface 3 tags the packet with VLAN 3 and Host B can receive the packet.
Because the device does not have a VLAN interface to terminate packets from VLAN 4, Host C cannot communicate with Host A or Host B.
Figure 2 Inter-VLAN communication through VLAN interfaces
Restrictions and guidelines: VLAN termination configuration
When you configure VLAN termination, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· On a portal-enabled interface, log off all portal users before you change the VLAN termination type, for example, from Dot1q termination to QinQ termination. Any portal users who remain online after the change cannot be logged off or reauthenticated. For more information about portal authentication, see User Access and Authentication Configuration Guide.
· After you modify the VLAN termination configuration for a subinterface, the subinterface automatically restarts. All dynamic ARP table entries for the subinterface are deleted.
VLAN termination tasks at a glance
To configure VLAN termination, perform the following tasks:
1. (Required.) Configuring VLAN termination
Choose one of the following tasks:
¡ Configuring ambiguous Dot1q termination
¡ Configuring unambiguous Dot1q termination
¡ Configuring ambiguous QinQ termination
¡ Configuring unambiguous QinQ termination
¡ Configuring untagged termination
¡ Configuring default termination
2. (Optional.) Enabling a VLAN termination-enabled interface to transmit broadcasts and multicasts
Perform this task to enable VLAN termination-enabled interfaces to transmit broadcasts and multicasts.
Configuring ambiguous Dot1q termination
About this task
Use this feature to terminate VLAN-tagged packets whose outermost VLAN IDs are in the specified range. Other VLAN-tagged packets are not allowed to pass.
When an interface receives a packet, it removes the outermost VLAN ID from the packet. When the interface sends a packet, it tags the packet with a VLAN ID as follows:
· For a PPPoE packet, the VLAN ID is from the matching PPPoE session entry.
· For a DHCP relay packet, the VLAN ID is from the matching DHCP session entry.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface view.
interface interface-type interface-number.subnumber
3. Configure ambiguous Dot1q termination.
vlan-type dot1q vid vlan-id-list
By default, Dot1q termination is disabled on a subinterface.
Configuring unambiguous Dot1q termination
About this task
Use this feature to terminate only VLAN-tagged packets whose outermost VLAN ID matches the specified VLAN ID. Other VLAN-tagged packets are not allowed to pass.
When an interface receives a packet, it removes the outermost VLAN ID from the packet. When the interface sends a packet, it tags the packet with the specified VLAN ID.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface view.
interface interface-type interface-number.subnumber
3. Configure unambiguous Dot1q termination.
vlan-type dot1q vid vlan-id
By default, Dot1q termination is disabled on a subinterface.
Configuring ambiguous QinQ termination
About ambiguous QinQ termination
Use this feature to terminate QinQ packets whose outermost two layers of VLAN IDs are in the specified range.
When an interface receives a packet, it removes the outermost two layers of VLAN tags from the packet. When the interface sends a packet, it tags the packet with the outermost two layers of VLAN IDs, which are determined as follows:
· For a PPPoE packet, VLAN IDs are from the matching PPPoE session entry.
· For a DHCP relay packet, VLAN IDs are from the matching DHCP relay entry.
Configuring ambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the outermost two layers of VLAN IDs
Restrictions and guidelines
· If you specify the same Layer 1 VLAN ID for multiple subinterfaces of the same main interface, specify different Layer 2 VLAN IDs for them. However, if you specify different Layer 1 VLAN IDs for the subinterfaces, the Layer 2 VLAN IDs specified for the subinterfaces are not required to be different.
· Subinterfaces of different main interfaces can terminate VLAN-tagged packets with the same Layer 1 and Layer 2 VLAN IDs.
· If you execute the vlan-type dot1q vid second-dot1q command multiple times, all specified pairs of Layer 1 IDs and Layer 2 IDs in each execution take effect.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface view.
interface interface-type interface-number.subnumber
3. Configure ambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the outermost two layers of VLAN IDs.
vlan-type dot1q vid vlan-id-list second-dot1q { vlan-id-list | any }
By default, QinQ termination is disabled on a subinterface.
Configuring ambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the Layer 2 VLAN IDs
Restrictions and guidelines
After you enable ambiguous QinQ termination on a VLAN interface, Layer 2 Ethernet interfaces bound to the VLAN interface operate as follows:
· Process only packets that match the ambiguous QinQ termination configuration of the VLAN interface.
· Drop any other packets sent to the VLAN interface.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter VLAN interface view.
interface vlan-interface interface-number
3. Configure ambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the Layer 2 VLAN IDs.
second-dot1q { vlan-id-list | any }
The Layer 1 VLAN ID of the VLAN-tagged packets that can be terminated by the subinterface or VLAN interface is the number of the subinterface or VLAN interface. This Layer 1 VLAN ID is not configurable.
Configuring unambiguous QinQ termination
About unambiguous QinQ termination
Use this feature to terminate QinQ packets whose outermost two layers of VLAN IDs match the specified values.
When an interface receives a packet, it removes the two layers of VLAN tags from the packet. When the interface sends a packet, it tags the packet with two layers of VLAN tags as specified.
Configuring unambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the outermost two layers of VLAN IDs
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface view.
interface interface-type interface-number.subnumber
3. Configure unambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the outermost two layers of VLAN IDs.
vlan-type dot1q vid vlan-id second-dot1q vlan-id
By default, QinQ termination is disabled on a subinterface.
Configuring unambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the Layer 2 VLAN ID
Restrictions and guidelines
After you enable unambiguous QinQ termination on a VLAN interface, Layer 2 Ethernet interfaces bound to the VLAN interface operate as follows:
· Process only packets that match the unambiguous QinQ termination configuration of the VLAN interface.
· Drop any other packets sent to the VLAN interface.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter VLAN interface view.
interface vlan-interface interface-number
3. Configure unambiguous QinQ termination by specifying the Layer 2 VLAN ID.
second-dot1q vlan-id
By default, QinQ termination is disabled on an interface.
The Layer 1 VLAN ID of the VLAN-tagged packets that can be terminated by the subinterface or VLAN interface is the number of the subinterface or VLAN interface. This Layer 1 VLAN ID is not configurable.
Configuring untagged termination
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface view.
interface interface-type interface-number.subnumber
3. Configure untagged termination.
vlan-type dot1q untagged
By default, untagged termination is disabled on a subinterface.
Configuring default termination
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface view.
interface interface-type interface-number.subnumber
3. Configure default termination.
vlan-type dot1q default
By default, default termination is disabled on a subinterface.
Enabling a VLAN termination-enabled interface to transmit broadcasts and multicasts
About this task
This function enables ambiguous Dot1q or QinQ termination-enabled interfaces to transmit broadcasts and multicasts.
To transmit a broadcast or multicast packet, the interface starts a traversal over the VLAN IDs specified for ambiguous termination. It copies the packet and tags each copy with a VLAN ID, until all VLAN IDs in the specified range are traversed. For example, when ambiguous QinQ termination is configured, both layers of VLAN ID ranges are traversed.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, use the vlan-termination broadcast ra command to enable an ambiguous Dot1q or QinQ termination-enabled interface to transmit RA multicast packets on an IPv6 network. This command prohibits transmission of broadcast packets and other types of multicast packets, and consumes less CPU resources than the vlan-termination broadcast enable command.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
¡ Enter Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface view.
interface interface-type interface-number.subnumber
¡ Enter VLAN interface view.
interface vlan-interface interface-number
3. Enable the interface to transmit broadcasts and multicasts.
¡ Enable the interface to transmit broadcasts and multicasts.
vlan-termination broadcast enable
¡ Enable the interface to transmit only RA multicasts on an IPv6 network.
vlan-termination broadcast ra
By default, an ambiguous Dot1q or QinQ termination-enabled interface does not transmit broadcasts and multicasts.