- Table of Contents
-
- 09-High Availability Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Hot backup configuration
- 02-RBM configuration
- 03-VRRP configuration
- 04-BFD configuration
- 05-Track configuration
- 06-Reth interface and redundancy group configuration
- 07-Failover group configuration
- 08-Interface collaboration configuration
- 09-Interface backup configuration
- 10-Monitor Link configuration
- 11-Smart Link configuration
- 12-Process placement configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 11-Smart Link configuration | 104.64 KB |
Contents
Collaboration between Smart Link and Monitor Link for port status detection
Restrictions and guidelines: Smart Link configuration
Configuring a Smart Link device
Prerequisites for Smart Link device configuration
Configuring protected VLANs for a smart link group
Configuring member ports for a smart link group
Configuring a preemption mode for a smart link group
Enabling the sending of flush messages
Configuring Smart Link
About Smart Link
Application scenario
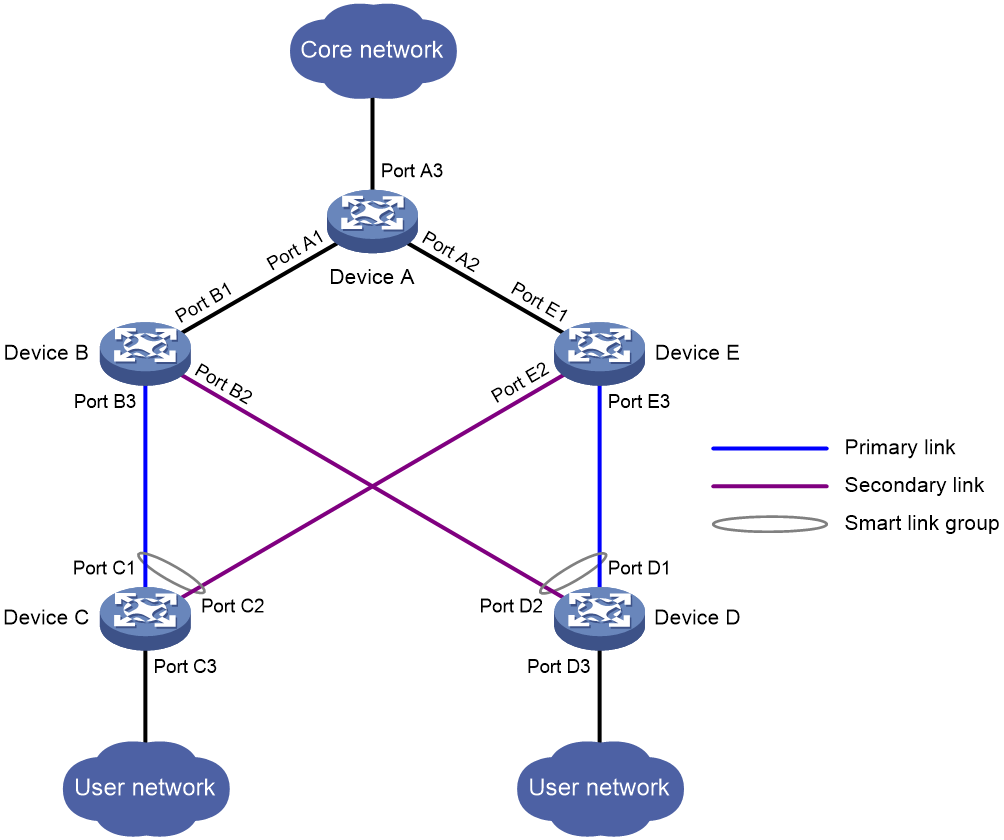
Smart Link provides link redundancy and subsecond convergence time in a dual uplink network. As shown in Figure 1, Smart Link is configured on Device C and Device D. The secondary link takes over quickly when the primary link fails.
Figure 1 Dual uplink network diagram
A Smart Link network has the following devices:
· Smart Link devices—A Smart Link device has two uplinks. A Smart Link device must be configured with a smart link group and a transmit control VLAN to transmit flush messages. Device C and Device D in Figure 1 are Smart Link devices.
· Associated devices—An associated device is an uplink device to which Smart Link devices are connected. An associated device supports Smart Link, and receives flush messages sent from the specified control VLAN. When a primary/secondary link switchover occurs, the associated device updates the MAC address entries and ARP/ND entries according to received flush messages. Device A, Device B, and Device E in Figure 1 are associated devices.
Terminology
Smart link group
A smart link group consists of only two member ports: the primary and the secondary ports. Only one port is active for forwarding at a time, and the other port is blocked and in standby state. When link failure occurs on the active portdue to port shutdown, the standby port becomes active and takes over. The original active port transits to the blocked state.
As shown in Figure 1, Port C1 and Port C2 of Device C form a smart link group. Port C1 is active, and Port C2 is standby. Port D1 and Port D2 of Device D form another smart link group. Port D1 is active, and Port D2 is standby.
Primary/secondary port
Primary port and secondary port are two port types in a smart link group. When both ports in a smart link group are up, the primary port preferentially transits to the forwarding state. The secondary port stays in standby state. When the primary port fails, the secondary port takes over to forward traffic.
As shown in Figure 1, Port C1 of Device C and Port D1 of Device D are primary ports. Port C2 of Device C and Port D2 of Device D are secondary ports.
Primary/secondary link
Flush message
When link switchover occurs, the smart link group uses flush messages to notify other devices to refresh their MAC address entries and ARP/ND entries. Flush messages are common multicast data packets, and will be dropped by a blocked receiving port.
Protected VLAN
A smart link group controls the forwarding state of protected VLANs. Each smart link group on a port controls a different protected VLAN. The state of the port in a protected VLAN is determined by the state of the port in the smart link group.
Transmit control VLAN
The transmit control VLAN is used for transmitting flush messages. When link switchover occurs, the devices (such as Device C and Device D in Figure 1) send flush messages within the transmit control VLAN.
Receive control VLAN
The receive control VLAN is used for receiving and processing flush messages. When link switchover occurs, the devices (such as Device A, Device B, and Device E in Figure 1) receive and process flush messages in the receive control VLAN. In addition, they refresh their MAC address entries and ARP/ND entries.
How Smart Link works
Link backup
As shown in Figure 1, the link on Port C1 of Device C is the primary link. The link on Port C2 of Device C is the secondary link. Port C1 is in forwarding state, and Port C2 is in standby state. When the primary link fails, Port C2 takes over to forward traffic and Port C1 is blocked and placed in standby state.
When a port switches to the forwarding state, the system outputs log information to notify the user of the port state change.
Topology change
Link switchover might outdate the MAC address entries and ARP/ND entries on all devices. A flush update mechanism is provided to ensure correct packet transmission. With this mechanism, a Smart Link-enabled device updates its information by transmitting flush messages over the backup link to its upstream devices. This mechanism requires the upstream devices to be capable of recognizing Smart Link flush messages to update their MAC address forwarding entries and ARP/ND entries.
Preemption mode
As shown in Figure 1, the link on Port C1 of Device C is the primary link. The link on Port C2 of Device C is the secondary link. When the primary link fails, Port C1 is automatically blocked and placed in standby state, and Port C2 takes over to forward traffic. When the primary link recovers, one of the following actions occurs:
· If the smart link group is not configured with a preemption mode, Port C1 stays blocked to keep traffic forwarding stable. Port C1 does not take over to forward traffic until the next link switchover.
· If the smart link group is configured with a preemption mode and the preemption conditions are met, Port C1 takes over to forward traffic as soon as its link recovers. Port C2 is automatically blocked and placed in standby state.
Load sharing
A ring network might carry traffic of multiple VLANs. Smart Link can forward traffic from different VLANs in different smart link groups for load sharing.
To implement load sharing, you can assign a port to multiple smart link groups. Configure each group with a different protected VLAN. Make sure the state of the port is different in these smart link groups, so traffic from different VLANs can be forwarded along different paths.
You can configure protected VLANs for a smart link group by referencing Multiple Spanning Tree Instances (MSTIs). For more information about MSTIs, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide.
Collaboration between Smart Link and Monitor Link for port status detection
Smart Link cannot detect when faults occur on the uplink of the upstream devices or when faults are cleared. You can configure the Monitor Link function to monitor the status of the uplink ports of the upstream devices. Monitor Link adapts the up/down state of downlink ports to uplink ports, and triggers Smart Link to perform link switchover on the downstream device. For more information about Monitor Link, see "Configuring Monitor Link."
Restrictions and guidelines: Smart Link configuration
If you configure a port as both an aggregation group member and a smart link group member, only the aggregation group configuration takes effect. The port is not shown in the output from the display smart-link group command. The smart link group configuration takes effect after the port leaves the aggregation group.
Smart Link tasks at a glance
To configure Smart Link, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring a Smart Link device
a. Configuring protected VLANs for a smart link group
b. Configuring member ports for a smart link group
c. (Optional.) Configuring a preemption mode for a smart link group
d. (Optional.) Enabling the sending of flush messages
2. Enabling an associated device to receive flush messages
Configuring a Smart Link device
Prerequisites for Smart Link device configuration
Before configuring a Smart Link device, complete the following tasks:
· To prevent loops, shut down a port before configuring it as a smart link group member. You can bring up the port only after completing the smart link group configuration.
· Disable the spanning tree feature on the ports you want to add to the smart link group.
Configuring protected VLANs for a smart link group
Prerequisites
Before you configure protected VLANs, you must configure an MST region and the VLAN-to-instance mapping table. For more information about MST regions, see spanning tree configuration in Layer 2—LAN Switching Configration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a smart link group and enter smart link group view.
smart-link group group-id
3. Configure protected VLANs for the smart link group.
protected-vlan reference-instance instance-id-list
Configuring member ports for a smart link group
Restrictions and guidelines
You can configure member ports for a smart link group either in smart link group view or in interface view. The configurations made in these two views have the same effect.
In smart link group view
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a smart link group and enter smart link group view.
smart-link group group-id
3. Configure member ports for a smart link group.
port interface-type interface-number { primary | secondary }
By default, no member port is configured for a smart link group.
In interface view
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure member ports for a smart link group.
port smart-link group group-id { primary | secondary }
By default, an interface is not a smart link group member.
Configuring a preemption mode for a smart link group
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter smart link group view.
smart-link group group-id
3. Configure a preemption mode for the smart link group.
preemption mode { role | speed [ threshold threshold-value ] }
By default, preemption is disabled.
4. Configure the preemption delay.
preemption delay delay
By default, the preemption delay is 1 second.
The preemption delay configuration takes effect only after a preemption mode is configured.
Enabling the sending of flush messages
Restrictions and guidelines
· The control VLAN configured for a smart link group must be different from the control VLAN configured for any other smart link group.
· Make sure the configured control VLAN already exists, and assign the smart link group member ports to the control VLAN.
· The control VLAN of a smart link group must also be one of its protected VLANs. Do not remove the control VLAN. Otherwise, flush messages cannot be sent correctly.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter smart link group view.
smart-link group group-id
3. Enable flush update.
flush enable [ control-vlan vlan-id ]
By default, flush update is enabled, and VLAN 1 is the control VLAN.
Enabling an associated device to receive flush messages
Restrictions and guidelines
· You do not need to enable all ports on the associated devices to receive flush messages. Enable the feature only on all control VLANs of ports on the primary and secondary links between the Smart Link device and the destination device.
· If no control VLAN is specified for processing flush messages, the device forwards the received flush messages without any processing.
· Make sure the receive control VLAN is the same as the transmit control VLAN configured on the Smart Link device. If they are not the same, the associated device will forward the received flush messages directly without any processing.
· Do not remove the control VLANs. Otherwise, flush messages cannot be sent correctly.
· Make sure the control VLANs are existing VLANs, and assign the ports capable of receiving flush messages to the control VLANs.
Prerequisites
Disable the spanning tree feature on the associated device's ports that connect to the member ports of the smart link group. Otherwise, the ports will discard flush messages when they are not in forwarding state if a topology change occurs.
Procedure
system-view
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Configure the control VLANs for receiving flush messages.
smart-link flush enable [ control-vlan vlan-id-list ]
By default, no control VLAN receives flush messages.
Display and maintenance commands for Smart Link
Execute display commands in any view and the reset command in user view:
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about the received flush messages. |
display smart-link flush |
|
Display smart link group information. |
display smart-link group { group-id | all } |
|
Clear the statistics about flush messages. |
reset smart-link statistics |