- Table of Contents
-
- 04-Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-MAC address table configuration
- 02-Ethernet link aggregation configuration
- 03-Port isolation configuration
- 04-Spanning tree configuration
- 05-Loop detection configuration
- 06-VLAN configuration
- 07-MVRP configuration
- 08-QinQ configuration
- 09-VLAN mapping configuration
- 10-LLDP configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 05-Loop detection configuration | 121.79 KB |
Contents
Loop detection configuration task list
Enabling loop detection globally
Enabling loop detection on a port
Setting the loop protection action
Setting the global loop protection action
Setting the loop protection action on a port
Setting the loop detection interval
Displaying and maintaining loop detection
Overview
Incorrect network connections or configurations can create Layer 2 loops, which results in repeated transmission of broadcasts, multicasts, or unknown unicasts. The repeated transmission can waste network resources and sometimes can paralyze networks. The loop detection mechanism immediately generates a log when a loop occurs so that you are promptly notified to adjust network connections and configurations. You can configure loop detection to shut down the looped port. Logs are maintained in the information center. For more information, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Loop detection mechanism
The device detects loops by sending detection frames and then checking whether these frames return to any port on the device. If they do, the device considers that the port is on a looped link.
Loop detection usually works within a VLAN. If a detection frame is returned with a different VLAN tag than it was sent out with, an inter-VLAN loop has occurred. To remove the loop, examine the QinQ configuration for incorrect settings. For more information about QinQ, see "Configuring QinQ."
Figure 1 Ethernet frame header for loop detection
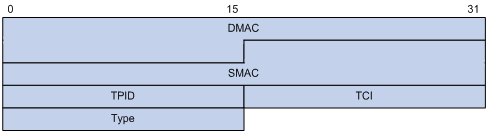
The Ethernet frame header for loop detection contains the following fields:
· DMAC—Destination MAC address of the frame, which is the multicast MAC address 010F-E200-0007. When a loop detection-enabled device receives a frame with this destination MAC address, the device performs the following tasks:
¡ Sends the frame to the CPU.
¡ Floods the frame in the VLAN from which the frame was originally received.
· SMAC—Source MAC address of the frame, which is the bridge MAC address of the sending device.
· TPID—Type of the VLAN tag, with the value of 0x8100.
· TCI—Information of the VLAN tag, including the priority and VLAN ID.
· Type—Protocol type, with the value of 0x8918.
Figure 2 Inner frame header for loop detection
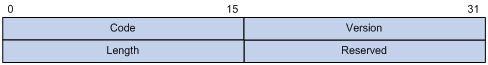
The inner frame header for loop detection contains the following fields:
· Code—Protocol sub-type, which is 0x0001, indicating the loop detection protocol.
· Version—Protocol version, which is always 0x0000.
· Length—Length of the frame. The value includes the inner header, but excludes the Ethernet header.
· Reserved—This field is reserved.
Frames for loop detection are encapsulated as TLV triplets.
Table 1 TLVs supported by loop detection
|
TLV |
Description |
Remarks |
|
End of PDU |
End of a PDU. |
Optional. |
|
Device ID |
Bridge MAC address of the sending device. |
Required. |
|
Port ID |
ID of the PDU sending port. |
Optional. |
|
Port Name |
Name of the PDU sending port. |
Optional. |
|
System Name |
Device name. |
Optional. |
|
Chassis ID |
Chassis ID of the sending port. |
Optional. |
|
Slot ID |
Slot ID of the sending port. |
Optional. |
|
Sub Slot ID |
Sub-slot ID of the sending port. |
Optional. |
Loop detection interval
Loop protection action
When the device detects a loop on a port, it generates a log but performs no action on the port by default. Alternatively, you can configure the device to shut down the port to disable it from receiving and sending any frames. The port is always in the down state until manually brought up with the undo shutdown command.
Loop detection configuration task list
|
Tasks at a glance |
|
(Required.) Enabling loop detection |
|
(Optional.) Setting the loop protection action |
|
(Optional.) Setting the loop detection interval |
Enabling loop detection
You can enable loop detection globally or on a per-port basis. The global configuration applies to all ports in the specified VLANs. The per-port configuration applies to the individual port only when the port belongs to the specified VLANs. Per-port configurations take precedence over global configurations.
After you enable loop detection for a VLAN, do not configure it as the source VLAN for remote port mirroring. Otherwise, loop detection might not operate correctly. For more information about remote port mirroring, see Network Management and Mirroring Configuration Guide.
Enabling loop detection globally
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Globally enable loop detection. |
loopback-detection global enable vlan { vlan-list | all } |
Disabled by default. |
Enabling loop detection on a port
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view. |
interface interface-type interface-number |
N/A |
|
3. Enable loop detection on the port. |
loopback-detection enable vlan { vlan-list | all } |
Disabled by default. |
Setting the loop protection action
You can configure the loop protection action globally or on a per-port basis. The global setting applies to all ports. The per-port setting applies to the individual ports. The per-port setting takes precedence over the global setting.
Setting the global loop protection action
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Configure the global loop protection action. |
loopback-detection global action shutdown |
By default, the device generates a log but performs no action on the port on which a loop is detected. |
Setting the loop protection action on a port
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enter Layer 2 Ethernet interface view or Layer 2 aggregate interface view. |
· Enter Layer 2 Ethernet
interface view: · Enter Layer 2 aggregate interface view: |
Use either command. |
|
3. Configure the loop protection action on the interface. |
loopback-detection action shutdown |
By default, the device generates a log but performs no action on the port on which a loop is detected. |
Setting the loop detection interval
With loop detection enabled, the device sends loop detection frames at a specified interval. A shorter interval offers more sensitive detection but consumes more resources. Consider the system performance and loop detection speed when you set the loop detection interval.
To set the loop detection interval:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Set the loop detection interval. |
loopback-detection interval-time interval |
The default setting is 30 seconds. |
Displaying and maintaining loop detection
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the loop detection configuration and status. |
display loopback-detection |
Loop detection configuration example
By default, Ethernet, VLAN, and aggregate interfaces are shut down. You must use the undo shutdown command to bring them up. The examples assume that all these interfaces are already up.
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 3, configure loop detection on Device A, so that Device A generates a log as a notification and automatically shuts down the port on which a loop is detected.
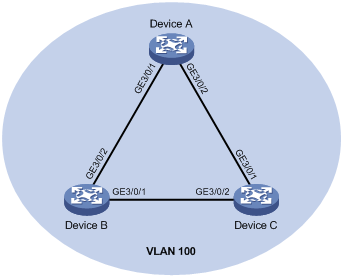
Configuration procedure
1. Configure Device A:
# Create VLAN 100, and globally enable loop detection for the VLAN.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] vlan 100
[DeviceA-vlan100] quit
[DeviceA] loopback-detection global enable vlan 100
# Configure GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 as trunk ports, and assign them to VLAN 100.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/2
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
# Configure the global loop protection action as shutdown.
[DeviceA] loopback-detection global action shutdown
# Set the loop detection interval to 35 seconds.
[DeviceA] loopback-detection interval-time 35
2. Configure Device B:
# Create VLAN 100.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] vlan 100
[DeviceB–vlan100] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 as trunk ports, and assign them to VLAN 100.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/2
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
3. Configure Device C:
# Create VLAN 100.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] vlan 100
[DeviceC–vlan100] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 as trunk ports, and assign them to VLAN 100.
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/1
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet3/0/1] quit
[DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 3/0/2
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port link-type trunk
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 100
[DeviceC-GigabitEthernet3/0/2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# View the system logs on devices, for example, Device A.
[DeviceA]
%Feb 24 15:04:29:663 2011 DeviceA LPDT/4/LOOPED:Slot=1;
Loopback exists on GigabitEthernet3/0/1.
%Feb 24 15:04:29:667 2011 DeviceA LPDT/4/LOOPED:Slot=1;
Loopback exists on GigabitEthernet3/0/2.
%Feb 24 15:04:44:243 2011 DeviceA LPDT/4/RECOVERED:Slot=1;
Loopback on GigabitEthernet3/0/1 recovered.
%Feb 24 15:04:44:248 2011 DeviceA LPDT/4/RECOVERED:Slot=1;
Loopback on GigabitEthernet3/0/2 recovered.
The output shows the following information:
· Device A detected loops on ports GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 within a loop detection interval.
· Loops on ports GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 were removed..
# Display the loop detection configuration and status on devices, for example, Device A.
[DeviceA] display loopback-detection
Loop detection is enabled.
Loop detection interval is 35 second(s).
No loopback is detected.
The output shows that the device has removed the loops from GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 according to the shutdown action.
# Display the status of GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 on Device A.
[DeviceA] display interface gigabitethernet 3/0/1
GigabitEthernet3/0/1 current state: DOWN (Loop detection down)
...
The output shows that GigabitEthernet 3/0/1 is already shut down by the loop detection module.
# Display the status of GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 on Device A.
[DeviceA] display interface gigabitethernet 3/0/2
GigabitEthernet3/0/2 current state: DOWN (Loop detection down)
...
The output shows that GigabitEthernet 3/0/2 is already shut down by the loop detection module.

