- Table of Contents
-
- 02-IP Services Volume
- 00-IP Services Volume Organization
- 01-IP Addressing Configuration
- 02-ARP Configuration.doc
- 03-DHCP Configuration.doc
- 04-DNS Configuration
- 05-IP Performance Configuration
- 06-UDP Helper Configuration
- 07-URPF Configuration
- 08-IPv6 Basics Configuration
- 09-Dual Stack Configuration
- 10-Tunneling Configuration
- 11-sFlow Configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 09-Dual Stack Configuration | 33.37 KB |
When configuring dual stack, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
![]()
EA boards (such as LSQ1GP12EA and LSQ1TGX1EA) do not support IPv6 features.
Dual Stack Overview
Dual stack is the most direct approach to making IPv6 nodes compatible with IPv4 nodes. The best way for an IPv6 node to be compatible with an IPv4 node is to maintain a complete IPv4 stack. A network node that supports both IPv4 and IPv6 is called a dual stack node. A dual stack node configured with an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address can have both IPv4 and IPv6 packets transmitted.
For an upper layer application supporting both IPv4 and IPv6, either TCP or UDP can be selected at the transport layer, while IPv6 stack is preferred at the network layer.
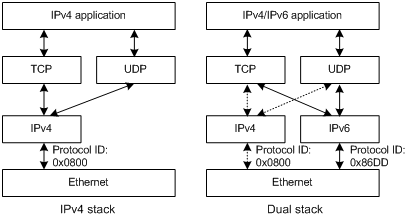
Figure 1-1 illustrates the IPv4/IPv6 dual stack in relation to the IPv4 stack.
Figure 1-1 IPv4/IPv6 dual stack in relation to IPv4 stack (on Ethernet)
Configuring Dual Stack
You must enable the IPv6 packet forwarding function before dual stack. Otherwise, the device cannot forward IPv6 packets even if IPv6 addresses are configured for interfaces.
Follow these steps to configure dual stack on a gateway:
|
To do… |
Use the command… |
Remarks |
||
|
system-view |
— |
|||
|
Enable the IPv6 packet forwarding function |
ipv6 |
Required Disabled by default. |
||
|
Enter interface view |
interface interface-type interface-number |
— |
||
|
Configure an IPv4 address for the interface |
ip address ip-address { mask | mask-length } [ sub ] |
Required By default, no IP address is configured. |
||
|
Configure an IPv6 address on the interface |
Configure an IPv6 global unicast address or site-local address |
Manually specify an IPv6 address |
ipv6 address { ipv6-address prefix-length | ipv6-address/prefix-length } |
Use either command. By default, no site-local address or global unicast address is configured on an interface. |
|
Configure an IPv6 address in the EUI-64 format |
ipv6 address ipv6-address/prefix-length eui-64 |
|||
|
Configure an IPv6 link-local address |
Automatically create an IPv6 link-local address |
ipv6 address auto link-local |
Optional By default, after you configured an IPv6 site-local address or global unicast address, a link local address is automatically created. |
|
|
Manually specify an IPv6 link-local address |
ipv6 address ipv6-address link-local |
|||
![]()
l For information about IPv4 addressing, refer to IP Addressing Configuration in the IP Services Volume.
l For more information about IPv6 address, refer to IPv6 Basics Configuration in the IP Services Volume.
l For how to enable IPv6 and configure an IPv6 address on an interface, refer to IPv6 Basics Commands in the IP Services Volume.

