- Table of Contents
-
- 09-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-802.1X configuration
- 03-MAC authentication configuration
- 04-Portal configuration
- 05-Web authentication configuration
- 06-Triple authentication configuration
- 07-Port security configuration
- 08-User profile configuration
- 09-Password control configuration
- 10-Keychain configuration
- 11-Public key management
- 12-PKI configuration
- 13-IPsec configuration
- 14-SSH configuration
- 15-SSL configuration
- 16-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 17-TCP attack prevention configuration
- 18-IP source guard configuration
- 19-ARP attack protection configuration
- 20-ND attack defense configuration
- 21-uRPF configuration
- 22-SAVI configuration
- 23-SAVA configuration
- 24-MFF configuration
- 25-Crypto engine configuration
- 26-FIPS configuration
- 27-MACsec configuration
- 28-802.1X client configuration
- 29-Microsegmentation configuration
- 30-IP-SGT mapping configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 30-IP-SGT mapping configuration | 164.53 KB |
Contents
IP-SGT mapping operating mechanism
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with IP-SGT mapping
Restrictions and guidelines: IP-SGT mapping configuration
IP-SGT mapping tasks at a glance
Prerequisites for IP-SGT mapping configuration
Configuring on-demand IP-SGT mapping
Display and maintenance commands for IP-SGT mapping
Configuring IP-SGT mapping
About IP-SGT mapping
Overview
In a traditional network, only the authenticator can receive access policies deployed by the EIA server and control user access based on the policies. Traditional networks manage user permissions based on geographical location attributes, such as VLAN or IP subnet. If the IP address of a user changes, the user might not obtain the same network access permissions as before.
IP address-Security Group Tag (IP-SGT) mapping binds user roles to security groups and decouples users and IP addresses for users to come online from different isolation domains with the same permissions. The feature realizes role-based policy assignment and enables user policy enforcement.
Network structure
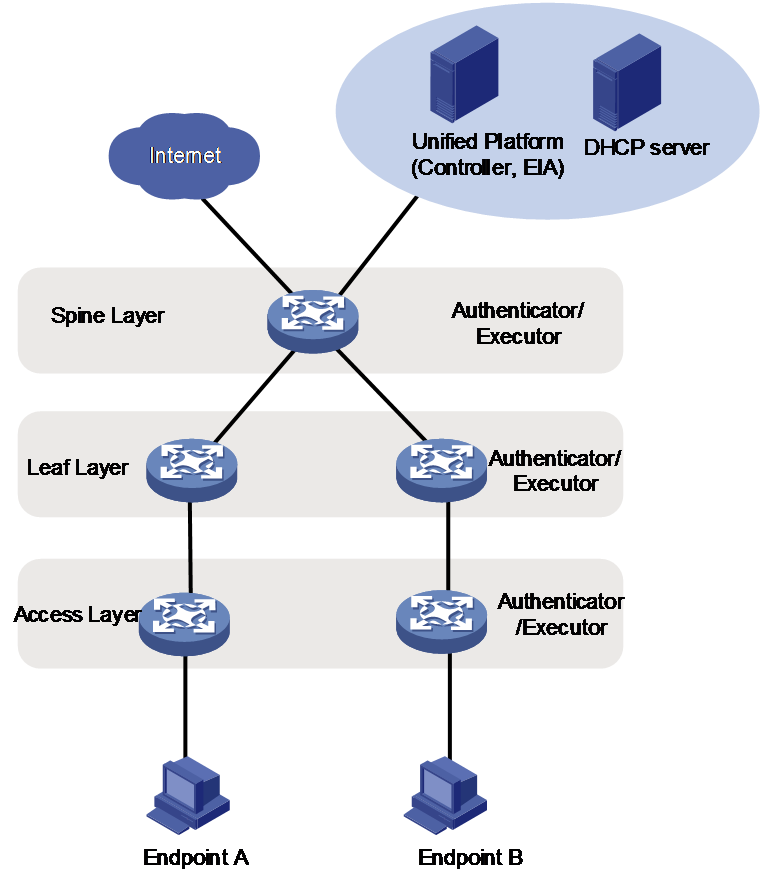
As shown in Figure 1, an IP-SGT mapping network includes the following devices:
· Unified Platform—Digital management platform installed on a physical server. You can deploy components such as controller and EIA server on Unified Platform to perform client authentication and policy deployment.
¡ Controller—Incorporates devices, creates security groups, and configures inter-group policies.
¡ EIA server—Performs user authentication, licensing, and network accounting, and sends IP-SGT mappings to subscribed devices (incorporated devices).
· DHCP server—Assigns IP addresses to users, and can be configured as one of Unified Platform components.
· Authenticator—Authenticates access clients.
· Executor—Subscribed device by the EIA server. An executor receives IP-SGT policies deployed by the EIA server and controls user access based on the policies. You can use the same device for authentication and execution.
· Endpoint—User device requesting to access the LAN. Endpoints are authenticated by the authenticator.
Figure 1 IP-SGT mapping architecture
Security group
Security group provides local group-based security isolation. You can add communication objects (such as personal endpoints, printers, or servers) in an area that have the same security isolation requirements to a security group and configure inter-group policies. This ensures that users in the same group can obtain the same access permissions regardless of their locations.
IP-SGT mapping provides security group-based policy enforcement cross isolation domains. Compared with traditional access control that uses VLAN and ACL, IP-SGT mapping significantly reduces inter-group configurations as well as administrator workload because IP address-based policy configuration is no longer required.
|
|
NOTE: · A security group can be identified as a microsegment whose microsegment ID is the label ID configured at security group creation. For more information about microsegmentation, see "Configuring microsegmentation." · Microsegmentation enables the system to bind users to security groups (microsegments) and decouple users from IP addresses. When a user comes online from different isolation domains by using the same account, the EIA server assigns the same microsegment ID to the user. |
IP-SGT mapping operating mechanism
Unless otherwise specified, authenticators mentioned in this document only authenticate users, and IP-SGT mapping is enabled on the executors.
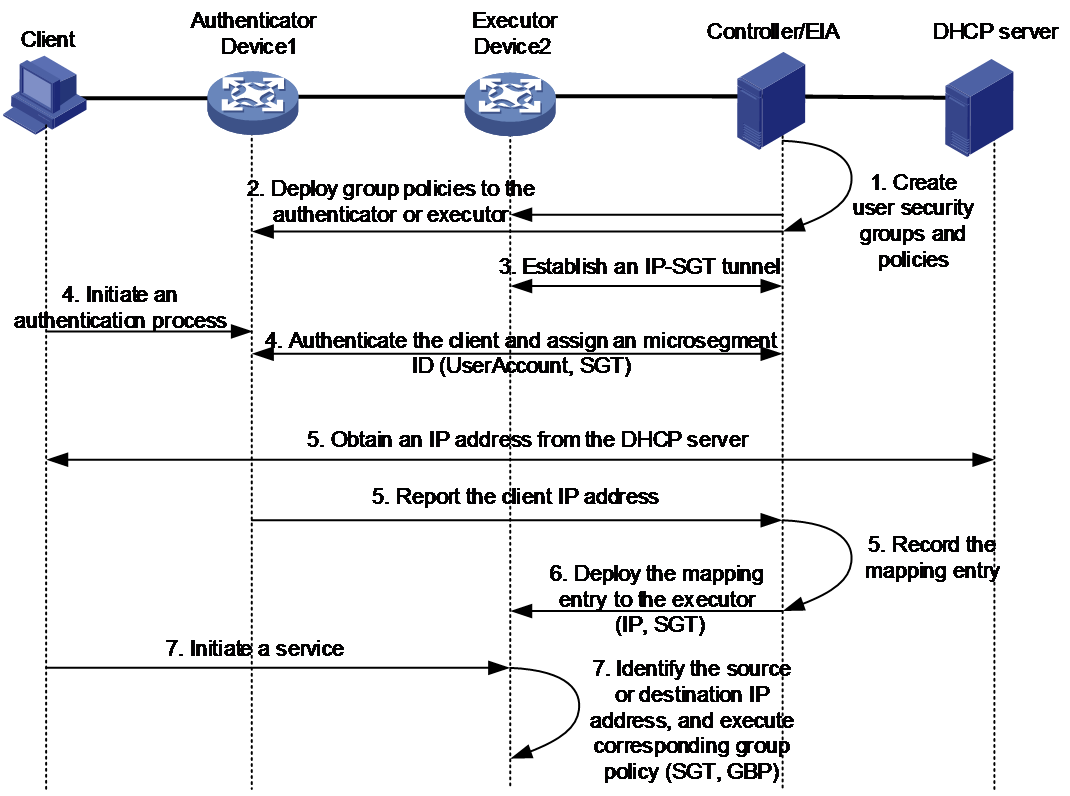
As shown in Figure 2, IP-SGT mapping works as follows:
1. The administrator creates security groups and Group Based Policies (GBP) on the controller, and then synchronizes security group and GBP information to the EIA server. For more information about GBP, see "Configuring Segmentation."
2. The controller deploys the configured GBP settings to the authenticator and executor.
3. The EIA server establishes an IP-SGT tunnel with the executor.
4. The client initiates an authentication process.
5. After a successful authentication, the EIA server adds the client into a security group based on the login information. The client now is assigned with a microsegment ID.
6. After the client obtains an IP address from the DHCP server (portal users obtain IP addresses before authentication),
7. The authenticator reports the client IP address to the EIA server through accounting packets.
|
CAUTION: · For portal users, the IP addresses have been obtained from the DHCP server before authentication and therefore the authenticator reports the client IP addresses to the EIA server during authentication. · For 802.1X, MAC, and Web authentication users, after they have obtained the IP addresses, the authenticator reports the client IP addresses to the EIA server through accounting packets. |
8. The EIA server then records the mapping relationship between the client IP address and microsegment ID.
9. The EIA server deploys the mapping entries to the executor through the IP-SGT tunnel. The executor then reports the entries to route management module for FIB deployment. According the FIB, drivers store the IP-SGT mapping entries in hardware resources. Once the client goes offline, the EIA server informs the executor to delete the corresponding IP-SGT entry.
10. After receiving service traffic from the client, the executor operates as follows:
a. Identifies the source or destination IP address of the packet.
b. Obtains the microsegment ID from the FIB.
c. Processes the traffic based on the corresponding group policy specified by the microsegment ID.
Figure 2 IP-SGT mapping workflow
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with IP-SGT mapping
Only S5560X-HI and S6520X-HI switch series support IP-SGT mapping.
Restrictions and guidelines: IP-SGT mapping configuration
To use IP-SGT, make sure an H3C IMC EIA server and an H3C SeerEngine-Campus controller are used, and the DHCP server must be a vDHCP server or a Microsoft DHCP server that supports tight coupling.
IP-SGT mapping tasks at a glance
To configure IP-SGT mapping, perform the following tasks:
· (Optional.) Configuring on-demand IP-SGT mapping
Prerequisites for IP-SGT mapping configuration
· Establish a cloud connection between the executor and Unified Platform. For more information, see cloud connection in Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
· Configure user authentication settings on the authenticator and the EIA server. IP-SGT mapping supports 802.1X, MAC address, Web, and portal authentications. For more information about configuring authentication, see the corresponding section in this document.
|
|
NOTE: · The administrator can directly deploy basic network configuration, 802.1X authentication, and IP-SGT mapping settings to devices through controller automated deployment or manually configure those features on devices. · For more information about the controller and the EIA server, see AD-Campus Configuration Guide. |
Enabling IP-SGT mapping
About this task
With IP-SGT mapping enabled, the executor identifies the source or destination IP address of a received packet, and searches the IP-SGT mapping entries in FIB deployed by the EIA server to obtain the microsegment ID. If a match is found, the executor processes the packet based on the action defined in the group policy.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable IP-SGT mapping.
ipsgt enable
By default, IP-SGT mapping is disabled.
Configuring on-demand IP-SGT mapping
About this task
By default, the device stores all the IP-SGT mapping entries deployed by the EIA server in hardware resources. This enables the device to fast obtain the microsegment ID from FIB and carry out group policy for packet processing and improves the forwarding efficiency. However, if the device is on a link that has few packet exchanges (such as an east-west link), storing all IP-SGT mappings wastes hardware resources.
To avoid the waste, configure on-demand IP-SGT mapping for the server to deploy the IP-SGT mapping entry only when the client IP address is in the specified subnet.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify a subnet for on-demand IP-SGT mapping.
ipsgt on-demand { ip ipv4-address { mask-length | mask } | ipv6 ipv6-address prefix-length } [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ]
By default, no subnet is specified for on-demand IP-SGT mapping.
Display and maintenance commands for IP-SGT mapping
Execute the display commands in any view, and execute the reset command in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display the operating status of IP-SGT mapping. |
display ipsgt state |
|
Display IP-SGT mapping statistics. |
display ipsgt statistics |
|
Display configured subnet information for on-demand IP-SGT mapping on the device. |
display ipsgt on-demand [ ip [ ipv4-address { mask-length | mask } ] | ipv6 [ ipv6-address prefix-length ] ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] |
|
Display the IP-SGT mapping entries on the device. |
display ipsgt map [ ip [ ipv4-address ] | ipv6 [ ipv6-address ] | microsegment microsegment-id ] [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] |
|
Clear IP-SGT mapping statistics. |
reset ipsgt statistics |
IP-SGT mapping configuration examples
Examples: Configuring IP-SGT mapping
Network configuration
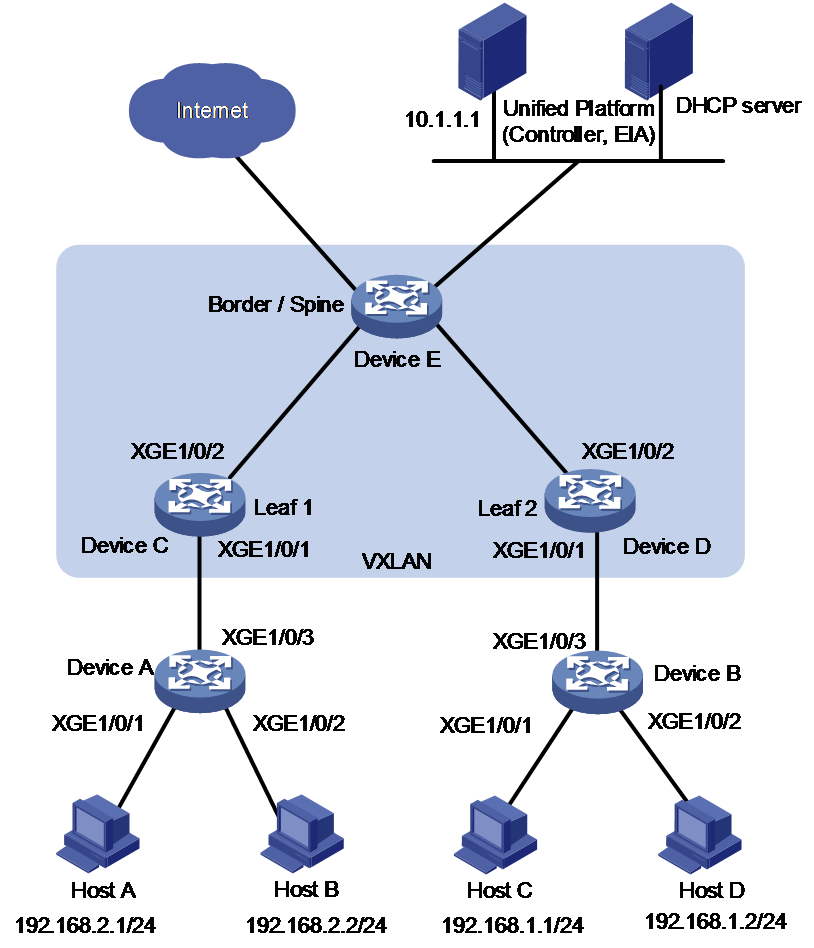
As shown in Figure 3, configure IP-SGT mapping to meet the following requirements:
· The network contains Access, Leaf, and Spine layers. The Leaf and Spine layers are connected through VXLAN, and the Leaf and Access layers are connected through VLAN. Overlay is used at Layer 2 and distributed gateways are used to decouple endpoint IP addresses and endpoint locations.
· Device A and device B act as authenticators to perform client authentication. Device C, Device D, and Device E at the Spine and Leaf layers act as executors to receive IP-SGT mappings sent by the EIA server and carry out the deployed IP-SGT policies.
· The endpoints (hosts) access the network through wired connections and are 802.1X authenticated.
· Subnet 192.168.1.0/24 in which Host C and Host D reside are specified for on-demand IP-SGT mapping.
Procedure
1. Configure basic network settings and incorporate devices for the controller and the EIA server. For more information, see AD-Campus Configuration Guide.
2. Configure Device A and Device B.
For more information about 802.1X authentication, see "Configuring 802.1X.".
3. Configure IP-SGT mapping on the executor. This section takes Device C as an example.
# Specify the northbound interface address of Unified Platform for the device to establish a cloud connection with the server.
<DeviceC> system-view
[DeviceC] cloud-management server domain 10.1.1.1
# Enable IP-SGT mapping.
[DeviceC] ipsgt enable
# Specify on-demand IP-SGT mapping to use subnet 192.168.1.0/24.
[DeviceC] ipsgt on-demand 192.168.1.0 24
4. Configure the EIA server. (Details not shown.)
a. Add devices to the server.
b. Add user accounts, and make sure the user authentication, authorization, and accounting features can operate correctly.
c. Configure security groups and define microsegment IDs.
Verifying the configuration
1. Execute the display cloud-management state command to view the cloud connection state. Make sure the device has established a cloud connection with Unified Platform and is in Established state. For more information, see the cloud connection in Network Management and Configuration Guide.
# View the current cloud connection status.
<DeviceC> display cloud-management state
Cloud connection state : Established
Device state : Request_success
Cloud server address : 10.1.1.1
Cloud server domain name : 10.1.1.1
Cloud server port : 443
Connected at : Mon Jan 24 07:47:24 2022
Duration : 00d 03h 38m 17s
Process state : Message received
Failure reason : N/A
2. Execute the display ipsgt state command to view the operating status for the IP-SGT mapping.
# View the current operating status of IP-SGT mapping.
<DeviceB> display ipsgt state
Global IP-SGT parameters:
IP-SGT: Enabled
Connection status with:
EIA server: Connected
IPv4 routing management: Connected
IPv6 routing management: Connected
IP-SGT URL:
http://10.1.1.1/ipsgtmgr/vim active
3. Execute the display ipsgt map command to view the mapping relationship between the current user IP address and microsegment ID.
<DeviceB> display ipsgt map
Total IPv4 IP-SGT entries: 1
Microsegment ID:1
IPv4 address Vpn-instance
192.168.2.1 N/A
Total IPv6 IP-SGT entries: 0
The device will use the group policy specified by the microsegment ID to control the service traffic of the user.