- Table of Contents
-
- 11-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 02-NQA configuration
- 03-NTP configuration
- 04-PoE configuration
- 05-SNMP configuration
- 06-RMON configuration
- 07-Event MIB configuration
- 08-NETCONF configuration
- 09-SmartMC configuration
- 10-EPA configuration
- 11-CWMP configuration
- 11-EAA configuration
- 12-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 13-Mirroring configuration
- 14-sFlow configuration
- 15-Information center configuration
- 16-Packet capture configuration
- 17-VCF fabric configuration
- 18-Cloud connection configuration
- 19-Ansible configuration
- 20-Chef configuration
- 21-Puppet configuration
- 22-EPS agent configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 22-EPS agent configuration | 158.64 KB |
Contents
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with EPS agent
Display and maintenance commands for EPS agent
EPS agent configuration examples
Example: Configuring EPS agent
Contents
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with EPS agent
Display and maintenance commands for EPS agent
EPS agent configuration examples
Example: Configuring EPS agent
Configuring EPS agent
About EPS and EPS agent
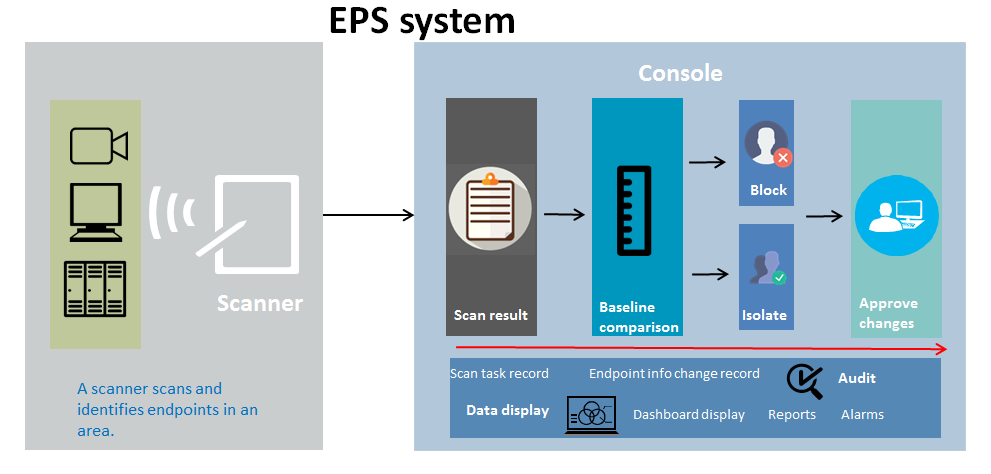
H3C iMC Endpoints Profiling System (EPS) detects, identifies, and monitors network-wide endpoints, including cameras, PCs, servers, switches, routers, firewalls, APs, printers, and ATMs. New endpoints and abnormal endpoints can be timely discovered and identified.
As shown in Figure 1, an EPS system contains the EPS server, scanners, and endpoints.
Figure 1 EPS network architecture
EPS server
The EPS server is a server installed with the iMC EPS component. It acts as the console to assign instructions to scanners, receive scan results, compare scan results with baselines, and support change auditing.
Scanner
A scanner is a device installed with iMC EScan and enabled with EPS agent. The scanner scans and manages endpoints by following the instruction of the EPS server and reports scan results to the EPS server.
EPS agent is based on the Comware platform and integrates the EPS scanner function. This chapter describes how to configure EPS agent.
Endpoint
An endpoint refers to a device scanned by a scanner. EPS supports user-defined endpoint types and the following system-defined endpoint types: camera, PC, server, switch, router, firewall, AP, printer, ATM, unknown, and other.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with EPS agent
The device does not support scanning endpoints connected to the gateway. If the console assigns a gateway-based scan task, no endpoints will be scanned.
Configuring EPS agent
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Configure EPS server parameters
eps server ip-address port port-number [ key { cipher | simple } key-value ] [ log-level level-value ] [ use-server-setting ]
By default, EPS server parameters are not configured.
3. Enable EPS agent.
eps agent enable
By default, EPS agent is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for EPS agent
Execute display commands in any view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display scanned endpoint information. |
display eps agent discovery |
EPS agent configuration examples
Example: Configuring EPS agent
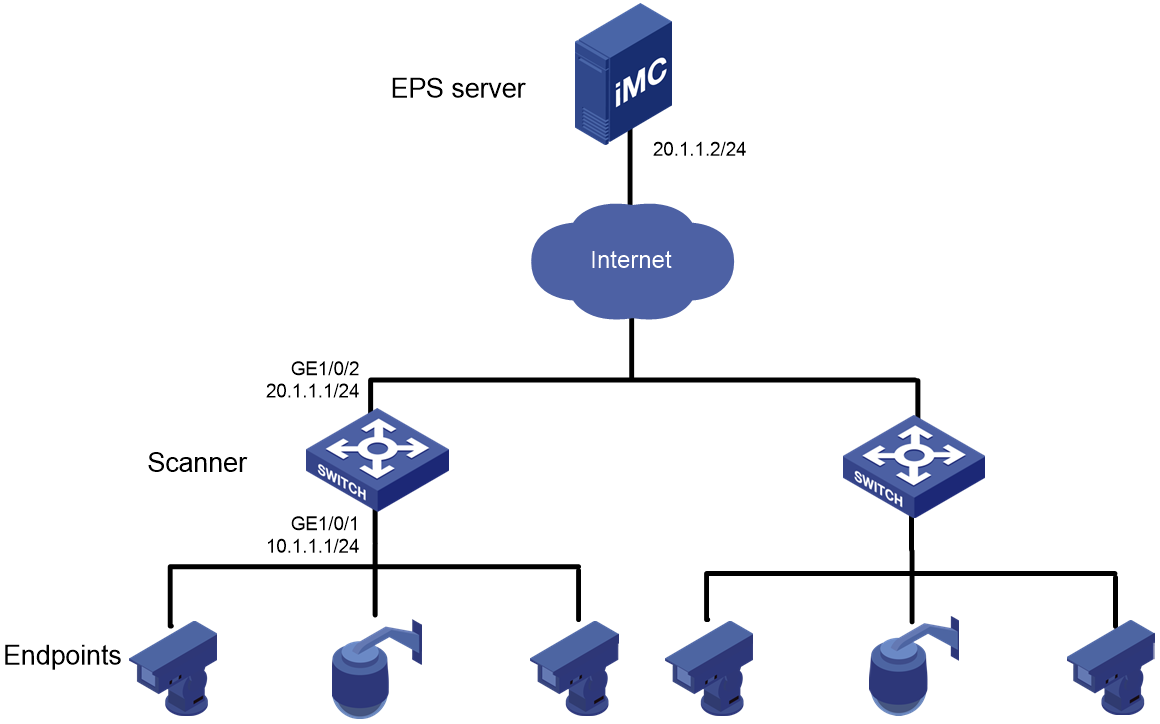
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, configure the scanner to enable it to scan endpoints based on the instruction of the EPS server.
Procedure
# Specify 20.1.1.2 and 4500 as the IP address and port number of the EPS server, respectively.
<Device> system-view
[Device] eps server 20.1.1.2 port 4500
# Enable EPS agent.
[Device] eps agent enable
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the scanned information is displayed after the EPS server issues a scan instruction.
[Device] display eps agent discovery
IP-Address MAC-Address OS-Type OS-ver Vendor Product
100.100.100.100 cc:ef:48:9b:5f:c1 IOS 12.X Cisco C3560E