- Table of Contents
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 01-Hardware Information and Specifications | 2.19 MB |
Contents
1 Chassis views and technical specifications
Module power consumption and system power consumption
2 FRUs and compatibility matrixes
Switch fabric module status LEDs
Switch fabric module status LEDs
Switch fabric module status LEDs on a fan tray
Making an Ethernet twisted pair cable
1 Chassis views and technical specifications
H3C S10500X-G switch series is a set of core switching products designed for the cloud computing data centers. It uses the advanced multi-stage multi-plane CLOS architecture to deliver the industry's highest switching performance, port density, availability, and most abundant cloud computing features.
The S10500X-G switch series includes the S10506X-G, S10506X-G-PoE, S10508X-G, and S10512X-G models.
Chassis views
The switch has an MPU section, service module section, switch fabric module section, power supply section, and fan tray section.
|
|
NOTE: The chassis view figures are for illustration only. |
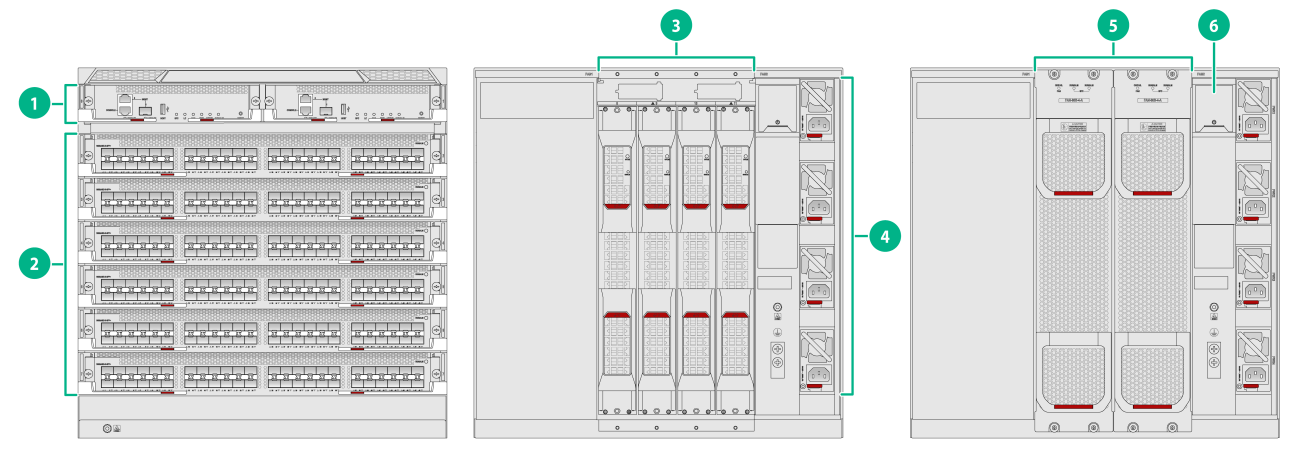
Figure1-1 S10506X-G front and rear panels
|
(1) MPU section |
(2) Service module section |
|
(3) Switch fabric module section |
(4) Power supply section |
|
(5) Fan tray section |
(6) Power switches |
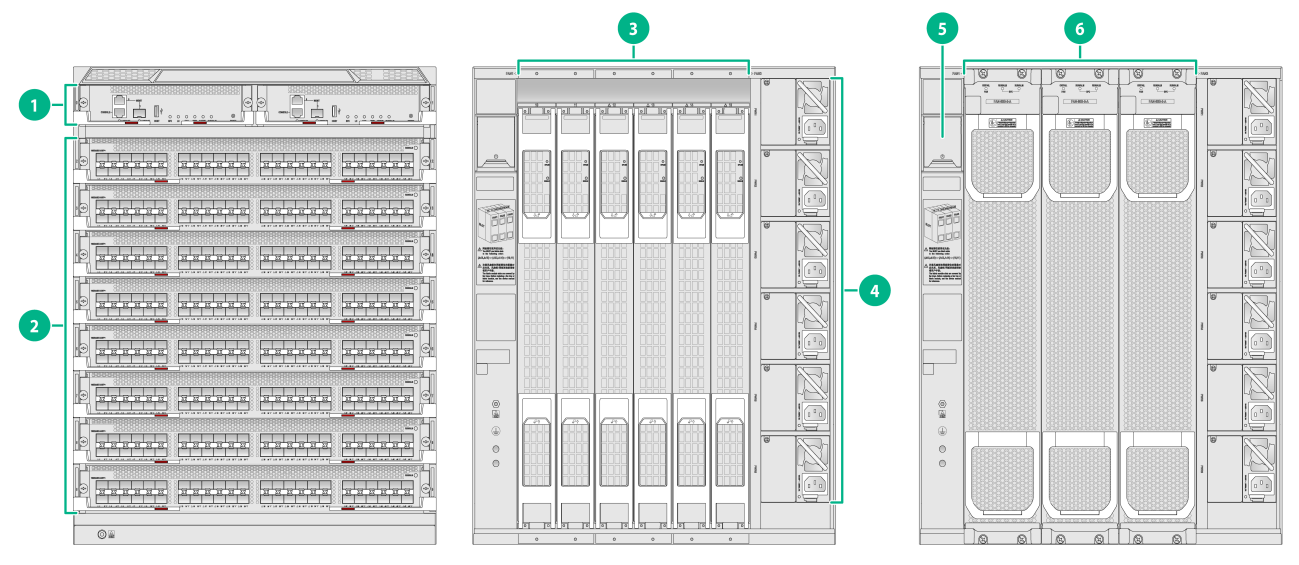
Figure1-2 S10506X-G-PoE switch front and rear panels
|
(1) MPU section |
(2) Service module section |
|
(3) PoE power supply section |
(4) Switch fabric module section |
|
(5) Power supply section |
(6) Fan tray section |
|
(7) Power switches |
|
Figure1-3 S10508X-G switch front and rear panels
|
(1) MPU section |
(2) Service module section |
|
(3) Switch fabric module section |
(4) Power supply section |
|
(5) Power switches |
(6) Fan tray section |
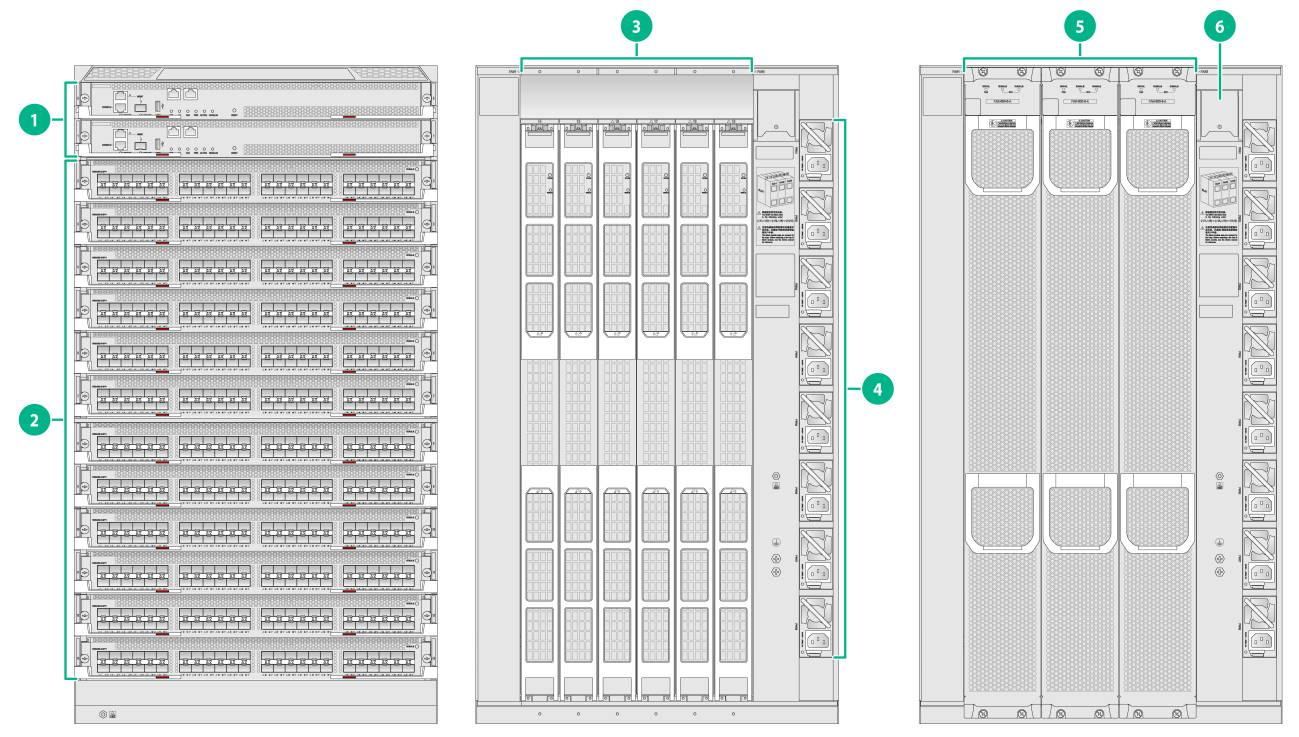
Figure1-4 S10512X-G front and rear panels
|
(1) MPU section |
(2) Service module section |
|
(3) Switch fabric module section |
(4) Power supply section |
|
(5) Fan tray section |
(6) Power switches |
Table1-1 Description for the switch sections
|
Section |
Installation description |
|
MPU section |
No MPUs are provided with the switch. Purchase MPUs yourself. The switch has two MPU slots. You can install one MPU, or two MPUs for redundancy. To install only one MPU for the switch, you can install it in either of the MPU slots. |
|
Service module section |
No service modules are provided with the switch. · S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE—6 service module slots. Select the service module model and quantity as are needed. · S10508X-G—8 service module slots. Select the service module model and quantity as are needed. · S10512X-G—12 service module slots. Select the service module model and quantity as needed. You can install a service module in any of the empty service module slots. |
|
Power supply section |
No power supplies are provided with the switch. · S10506X-G—4 power supply slots, on the right side of the rear panel. · S10506X-G-PoE—4 power supply slots and 8 PoE power supply slots on the left and rights sides of the rear panel. · S10508X-G—6 power supply slots, on the right side of the rear panel. · S10512X-G—8 power supply slots, on the right side of the rear panel. The switch supports N+N (dual power input sources) and N+1 (single power input source) power redundancy. Determine the number of power supplies based on power supply mode and the system power consumption. You can install a power supply in any of the empty power supply slots. |
|
Switch fabric module section |
No switch fabric modules are provided with the switch. · S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE—Install 1 to 4 switch fabric modules. · S10508X-G—Install 1 to 6 switch fabric modules. · S10512X-G—Install 1 to 6 switch fabric modules. Install filler panels in the empty switch fabric module slots. Read the priority instructions about switch fabric module slots on the rear panel of the chassis. Insert switch fabric modules according to the instructions. Before you replace a switch fabric module, remove the fan tray that covers it. |
|
Fan tray section |
No fan trays are provided with the switch. · S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE—Two fan tray slots FAN 1 and FAN 2. · S10508X-G—Three fan tray slots FAN 1, FAN 2, and FAN 3. · S10512X-G—Three fan tray slots FAN 1, FAN 2, and FAN 3. You must install a fan tray in each slot. |
|
Power switches |
To power on the switch, turn on both power switches. To power off the switch, turn off both power switches. |
For the modules, fan trays, and power supplies available for the switch, see "FRUs and compatibility matrixes."
Table1-2 describes the slot arrangements for FRUs.
|
Model |
MPU |
Service module |
Switch fabric module |
Power supply |
Fan tray |
|
S10506X-G |
Slots 0 and 1 |
Slots 2 to 7 |
Slots 8 to 11 Slots 8 and 9 are covered by FAN 1. Slots 10 and 11 are covered by FAN 2. |
PWR 1 to PWR 4 |
FAN 1 and FAN 2 |
|
S10506X-G-PoE |
Slots 0 and 1 |
Slots 2 to 7 |
Slots 8 to 11 Slots 8 and 9 are covered by FAN 1. Slots 10 and 11 are covered by FAN 2. |
· PWR 1 to PWR 4 · PWR-PoE 1 to PWR-PoE 8 |
FAN 1 and FAN 2 |
|
S10508X-G |
Slots 0 and 1 |
Slots 2 to 9 |
Slots 10 to 15 Slots 10 and 11 are covered by FAN 1. Slots 12 and 13 are covered by FAN 2. Slots 14 and 15 are covered by FAN 3. |
PWR 1 to PWR 6 |
FAN 1 to FAN 3 |
|
S10512X-G |
Slots 0 and 1 |
Slots 2 to 13 |
Slots 14 to 19 Slots 14 and 15 are covered by FAN 1. Slots 16 and 17 are covered by FAN 2. Slots 18 and 19 are covered by FAN 3 |
PWR 1 to PWR 8 |
FAN 1 to FAN 3 |
Weights and dimensions
Table1-3 Chassis weights and dimensions
|
Model |
Net weight |
Max weight (fully configured) |
Height |
Width |
Depth |
|
S10506X-G |
30.5 kg (67.24 lb) |
< 85 kg (187.39 lb) |
442 mm (17.40 in)/10 RU |
440 mm (17.32 in) |
520 mm (20.47 in) |
|
S10506X-G-PoE |
33.0 kg (72.75 lb) |
< 95 kg (209.44 lb) |
442 mm (17.40 in)/10 RU |
440 mm (17.32 in) |
520 mm (20.47 in) |
|
S10508X-G |
46.5 kg (102.51 lb) |
< 130 kg (286.60 lb) |
531 mm (20.91 in)/12 RU |
440 mm (17.32 in) |
640 mm (25.20 in) |
|
S10512X-G |
58.5 kg (128.97 lb) |
< 180 kg (396.83 lb) |
796 mm (31.34 in)/18 RU |
440 mm (17.32 in) |
640 mm (25.20 in) |
|
|
NOTE: · Rack height is measured in RUs. One RU is 44.45 mm (1.75 in). · Table1-3 lists dimensions for the switch, excluding the mounting brackets, cable management brackets, modules, and power supplies. |
Table1-4 Module weights and dimensions
|
Model |
Weight |
Height |
Width |
Depth |
|
LSEM1SUPA0 |
1.90 kg (4.19 lb) |
45 mm (1.77 in) |
208 mm (8.19 in) |
269 mm (10.59 in) |
|
LSEM3SUPA0 |
1.95 kg (4.30 lb) |
45 mm (1.77 in) |
208 mm (8.19 in) |
269 mm (10.59 in) |
|
LSEM1SUPB0 |
3.00 kg (6.62 lb) |
45 mm (1.77 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
269 mm (10.59 in) |
|
LSEM3SUPB0 |
2.95 kg (6.50 lb) |
45 mm (1.77 in) |
208 mm (8.19 in) |
269 mm (10.59 in) |
|
LSEM1SF06D0 |
3.35 kg (7.39 lb) |
46 mm (1.81 in) |
368 mm (14.49 in) |
198 mm (7.80 in) |
|
LSEM1SF08C0 |
4.30 kg (9.48 lb) |
46 mm (1.81 in) |
467 mm (18.39 in) |
273 mm (10.75 in) |
|
LSEM1SF12B0 |
6.50 kg (14.33 lb) |
46 mm (1.81 in) |
698 mm (27.48 in) |
273 mm (10.75 in) |
|
LSEM1TGS24SD0 |
3.35 kg (7.39 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1TGS48SD0 |
3.50 kg (7.72 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1GT48TSSD0 |
3.25 kg (7.16 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1GV48TSSD0 |
3.35 kg (7.39 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1GT24GP16TSSD0 |
3.35 kg (7.39 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1TGS16GP32SD0 |
3.50 kg (7.72 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1GT48TS24QSSD0 |
3.90 kg (8.60 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1TGS48QSSF0 |
4.50 kg (9.92 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM3TGS48QSSF0 |
4.30 kg (9.48 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1QGS16SF0 |
3.95 kg (8.71 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM3QGS16SF0 |
4.05 kg (8.93 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1YGS48CQSF0 |
4.20 kg (9.26 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM3YGS48CQSF0 |
4.30 kg (9.48 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1CGQ16SF0 |
3.95 kg (8.71 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM3CGQ16SF0 |
3.95 kg (8.71 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1CGQ36SF0 |
4.45 kg (9.81 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
LSEM1CDQ2SF0 |
3.30 kg (7.28 lb) |
51 mm (2.01 in) |
423 mm (16.65 in) |
270 mm (10.63 in) |
|
|
NOTE: Module dimensions are expressed in Height (H) × Width (W) × Depth (D) format: · Height—Height of the front panel of the module. · Width—Width of the front panel of the module. · Depth—Depth from the front panel of the module to the connector (Including the connector, but excluding the ejector levers and captive screws). |
Table1-5 Power supply weights and dimensions
|
Model |
Weight |
Height |
Width |
Depth |
|
PSR1600B-12A-B |
1.10 kg (2.43 lb) |
74 mm (2.91 in) |
225 mm (8.86 in) |
|
|
PSR1600-54A-B |
0.95 kg (2.10 lb) |
40 mm (1.57 in) |
74 mm (2.91 in) |
185 mm (7.28 in) |
|
PSR2000-12D-B |
1.10 kg (2.43 lb) |
40 mm (1.57 in) |
74 mm (2.91 in) |
225 mm (8.86 in) |
Table1-6 Fan tray weights and dimensions
|
Model |
Weight |
Height |
Width |
Depth |
|
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE fan tray —FAN-80B-4-A |
2.75 kg (6.06 lb) |
93 mm (3.66 in) |
432 mm (17.01 in) |
143 mm (5.63 in) |
|
S10508X-G fan tray -FAN-80B-5-A |
3.85 kg (8.49 lb) |
93 mm (3.66 in) |
527 mm (20.75 in) |
162 mm (6.38 in) |
|
S10512X-G fan tray-FAN-80B-8-A |
5.25 kg (11.57 lb) |
93 mm (3.66 in) |
788 mm (31.02 in) |
162 mm (6.38 in) |
Module power consumption and system power consumption
Module power consumption
The switch supports varieties of modules that are different in power consumptions. For a same module, the power consumption varies by its state. Table1-7 shows the power consumption for different module models.
· The static power consumption of a module refers to the power consumed by the module when the module is running but all its ports are down and its fiber ports are not installed with transceiver modules.
· The dynamic power consumption of a module refers to the power consumed by the module when all the ports on the module are link up and send broadcasts.
Table1-7 Module power consumption
|
Model |
Static power consumption (minimum) |
Dynamic power consumption (maximum) |
|
LSEM1SUPA0 |
22 W |
30 W |
|
LSEM3SUPA0 |
22 W |
33 W |
|
LSEM1SUPB0 |
27 W |
170 W |
|
LSEM3SUPB0 |
22 W |
33 W |
|
LSEM1SF06D0 |
55 W |
95 W |
|
LSEM1SF08C0 |
61 W |
112 W |
|
LSEM1SF12B0 |
62 W |
126 W |
|
LSEM1TGS24SD0 |
24 W |
56 W |
|
LSEM1TGS48SD0 |
40 W |
93 W |
|
LSEM1GT48TSSD0 |
28 W |
55 W |
|
LSEM1GV48TSSD0 |
28 W |
55 W |
|
LSEM1GT24GP16TSSD0 |
28 W |
62 W |
|
LSEM1TGS16GP32SD0 |
39 W |
80 W |
|
LSEM1GT48TS24QSSD0 |
52 W |
115 W |
|
LSEM1TGS48QSSF0 |
71 W |
175 W |
|
LSEM3TGS48QSSF0 |
71 W |
178 W |
|
LSEM1QGS16SF0 |
71 W |
172 W |
|
LSEM3QGS16SF0 |
71 W |
175 W |
|
LSEM1YGS48CQSF0 |
75 W |
218 W |
|
LSEM3YGS48CQSF0 |
75 W |
221 W |
|
LSEM1CGQ16SF0 |
70 W |
197 W |
|
LSEM3CGQ16SF0 |
70 W |
200 W |
|
LSEM1CGQ36SF0 |
121 W |
348 W |
|
LSEM1CDQ2SF0 |
67 W |
133 W |
Fan tray power consumption
The switch uses fan trays that can automatically adjust the fan speed based on the switch temperature. The power consumed by a fan tray depends on the fan speed.
Table1-8 Fan tray power consumption
|
Switch model |
Fan tray model |
Minimum fan tray power consumption |
Maximum fan tray power consumption |
|
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE |
FAN-80B-4-A |
30 W |
230 W |
|
S10508X-G |
FAN-80B-5-A |
34 W |
276 W |
|
S10512X-G |
FAN-80B-8-A |
53 W |
425 W |
System power consumption
The system power consumption of the switch depends on the type and number of modules and the fan tray power consumption.
· The minimum system power consumption is the total static power consumption of all modules plus the minimum fan tray power consumption.
· The maximum system power consumption is the total dynamic power consumption of all modules plus the maximum fan tray power consumption.
For example, for an S10506X-G switch that has two LSEM1SUPA0 MPUs, two LSEM1GT48TSSD0 service modules, two LSEM1SF06D0 switch fabric modules, and two FAN-80B-4-A fan trays, the minimum system power consumption of the switch is 2 × 22 + 2 × 28 + 2 × 55 + 2 × 30 = 270 W. The maximum system power consumption of the switch is 2 × 30 + 2 × 55 + 2 × 95 + 2 × 230 = 820 W.
The maximum power consumption is the maximum power input to the device when the device is fully configured with modules with the maximum power consumption.
Maximum module and fan tray power consumption is power consumed by all modules and fan trays when the device is fully configured with modules and fan trays with the maximum power consumption.
Heat dissipation
Heat dissipation is measured in BTU/h, and 1 W equals 3.4121 BTU/h.
The heat dissipation of a switch depends on its power consumption. To calculate heat dissipation of the switch, assume 90% power consumption is converted to heat, and the conversion efficiency of the power supplies is 90%. Heat dissipation/hour of the switch is 0.9 × (total power consumption of the modules plus power consumption of the fan tray)/0.9 × 3.4121.
For the power consumption of the modules and fan trays of the H3C S10500X-G switches, see "Module power consumption and system power consumption."
Table1-9 Heat dissipation
|
Switch module |
Heat dissipation (BTU/H) |
|
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE |
10216 |
|
S10508X-G |
14843 |
|
S10512X-G |
121405 |
Environmental specifications
Table1-10 Environmental specifications
|
Description |
Operating |
Storage |
|
Temperature |
0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) |
–40°C to +70°C (–40°F to +158°F) |
|
Relative humidity (noncondensing) |
5% to 95% |
5% to 95% |
Noise
The switch uses fan trays that can automatically adjust the fan speed based on the switch temperature The sound pressure levels vary by fan speed. For more information, see Table1-11.
Table1-11 Sound pressure levels
|
Switch model |
Fan tray model |
Sound pressure level in the acceptable temperature range |
Sound pressure level when the fan tray operates at full speed |
|
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE (fully configured with fan trays) |
FAN-80B-4-A |
57.7 dBA |
79.1 dBA |
|
S10508X-G (fully configured with fan trays) |
FAN-80B-5-A |
58.6 dBA |
81.9 dBA |
|
S10512X-G (fully configured with fan trays) |
FAN-80B-8-A |
62.1 dBA |
82.6 dBA |
|
|
NOTE: The sound pressure levels are measured based on the method specified in ISO 7779 at bystander positions. |
Chassis ordering information
To purchase an S10500X-G chassis, contact the sales agent or H3C sales personnel.
Table1-12 S10500X-G chassis ordering information
|
Product name |
Description |
|
S10506X-G |
H3C S10506X-G Ethernet Switch Chassis |
|
S10506X-G-PoE |
H3C S10506X-G-PoE Ethernet Switch Chassis |
|
S10508X-G |
H3C S10508X-G Ethernet Switch Chassis |
|
S10512X-G |
H3C S10512X-G Ethernet Switch Chassis |
2 FRUs and compatibility matrixes
For the transceiver modules and cables available for the modules, see H3C S10500X-G Switch Series Cards and Transceiver Modules Compatibility Matrixes.
MPUs
The switch uses an MPU for control and management. You can install one MPU, or two MPUs for redundancy on the switch. Do not install MPUs of different models on the same switch.
Table2-1 MPU ordering guide
|
Switch model |
Available MPUs |
|
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE/S10508X-G |
LSEM1SUPA0 |
|
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE/S10508X-G |
LSEM3SUPA0 |
|
S10512X-G |
LSEM1SUPB0 |
|
S10512X-G |
LSEM3SUPB0 |
|
Item |
LSEM1SUPA0 |
LSEM1SUPB0 |
LSEM3SUPA0 |
LSEM3SUPB0 |
|
Processor |
Quad core, 1.8 GHz |
Quad core, 2.2 GHz |
||
|
SDRAM |
8 GB |
8 GB |
||
|
Flash |
8 GB |
2 GB |
||
|
NVRAM |
1 MB |
1 MB |
||
|
Connector type |
· RJ-45 · LC · USB (Type A) |
· RJ-45 · LC · USB (Type A) |
||
|
Ports |
· 1 × console port · 1 × USB port · 2 × management ports, including one RJ-45 port and one SFP port |
· 1 × console port · 1 × USB port · 2 × management ports, including one RJ-45 port and one SFP port |
||
|
Transmission rate |
· Console port: 9600 bps (default) to 115200 bps · RJ-45 management port: 10/100/1000 Mbps, half/full duplex · SFP management port: 1000 Mbps |
· Console port: 9600 bps (default) to 115200 bps · RJ-45 management port: 10/100/1000 Mbps, half/full duplex · SFP management port: 1000 Mbps |
||
|
IMPORTANT: · To verify compatibility of the module with the software release you are using, see the release notes. · The USB port outputs power as prescribed by USB 2.0. You can only install a USB 2.0-compliant device in the USB port. · Set the same speed and duplex mode for a management Ethernet port and its peer port. · If the two management ports are connected to one remote switch, you must assign their peer ports to different VLANs. Login or file transfer will fail if the peer ports are in the same VLAN. · When using the BootWare menu to upgrade software or BootWare, make sure you use 10/100/1000BASE-T port M0/0/0 for image transferring. |
Service modules
Table2-3 Service module specifications
|
Service module |
Port quantity |
Port type |
Available transceiver modules and cables |
|
LSEM1TGS24SD0 |
24 |
24 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ fiber ports |
· 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · GE SFP transceiver modules |
|
LSEM1TGS48SD0 |
48 |
48 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ fiber ports |
· 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · GE SFP transceiver modules |
|
LSEM1GT48TSSD0 |
52 |
· 4 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ fiber ports · 48 × 10M/100M/1000M autosensing RJ-45 copper ports |
· 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · FE/GE SFP transceiver modules · Category 5 twisted pair cables |
|
LSEM1GV48TSSD0 |
52 |
· 4 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ fiber ports · 48 × 10/100/1000 BASE-T-PoE+ copper ports |
· 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · FE/GE SFP transceiver modules · Category 5 twisted pair cables |
|
LSEM1GT24GP16TSSD0 |
52 |
· 12 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ ports · 16 × 1000BASE-X-SFP ports · 24 × 10/100/1000BASE-T ports |
· 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · FE/GE SFP transceiver modules · Category 5 twisted pair cables |
|
LSEM1TGS16GP32SD0 |
48 |
· 16 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ fiber ports · 32 × 1000BASE-X-SFP ports |
· 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · FE/GE SFP transceiver modules |
|
LSEM1GT48TS24QSSD0 |
74 |
· 2 × 40GBASE-R-QSFP+ ports · 24 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ ports · 48 × 10/100/1000BASE-T ports |
· QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables · 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · GE SFP transceiver modules · Category 5 twisted pair cables |
|
LSEM1TGS48QSSF0 |
52 |
· 48 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ fiber ports · 4 × 40GBASE-R-QSFP+ ports |
· QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables · 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · GE SFP transceiver modules |
|
LSEM3TGS48QSSF0 |
52 |
· 48 × 10GBASE-R-SFP+ fiber ports · 4 × 40GBASE-R-QSFP+ ports |
· QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables · 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · GE SFP transceiver modules |
|
LSEM1QGS16SF0 |
16 |
16 × 40GBASE-R-QSFP+ ports |
· QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables |
|
LSEM3QGS16SF0 |
16 |
16 × 40GBASE-R-QSFP+ ports |
· QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables |
|
LSEM1YGS48CQSF0 |
52 |
· 4 × 100G QSFP28 fiber ports · 48 × 25G SFP28 fiber ports |
· QSFP28 transceiver modules · QSFP28 DAC cables · QSFP28 AOC cables · QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP28 to SFP28 DAC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables · SFP28 transceiver modules · SFP28 DAC cables · SFP28 AOC cables · 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · GE SFP transceiver modules |
|
LSEM3YGS48CQSF0 |
52 |
· 4 × 100G QSFP28 fiber ports · 48 × 25G SFP28 fiber ports |
· QSFP28 transceiver modules · QSFP28 DAC cables · QSFP28 AOC cables · QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP28 to SFP28 DAC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables · SFP28 transceiver modules · SFP28 DAC cables · SFP28 AOC cables · 10-GE SFP+ transceiver modules · 10-GE SFP+ DAC cables · GE SFP transceiver modules |
|
LSEM1CGQ16SF0 |
16 |
16 × 100GBASE-R-QSFP28 fiber ports |
· QSFP28 transceiver modules · QSFP28 DAC cables · QSFP28 AOC cables · QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP28 to SFP28 DAC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables |
|
LSEM3CGQ16SF0 |
16 |
16 × 100GBASE-R-QSFP28 fiber ports |
· QSFP28 transceiver modules · QSFP28 DAC cables · QSFP28 AOC cables · QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP28 to SFP28 DAC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables |
|
LSEM1CGQ36SF0 |
36 |
36 × 100GBASE-R-QSFP28 ports |
· QSFP28 transceiver modules · QSFP28 DAC cables · QSFP28 AOC cables · QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables · QSFP28 to SFP28 DAC cables · QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cables |
|
LSEM1CDQ2SF0 |
2 |
2 × 400GBASE-R-QSFP-DD fiber ports |
· QSFP-DD transceiver modules · QSFP-DD DAC cables · QSFP28 transceiver modules · QSFP28 DAC cables · QSFP28 AOC cables · QSFP+ transceiver modules · QSFP+ DAC cables · QSFP+ AOC cables |
Switch fabric modules
Table2-4 Switch fabric module ordering guide
|
Switch model |
Available switch fabric modules |
Switch fabric module quantity per switch |
|
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE |
LSEM1SF06D0 |
1 to 4 |
|
S10508X-G |
LSEM1SF08C0 |
1 to 6 |
|
S10512X-G |
LSEM1SF12B0 |
1 to 6 |
Slide rails
No slide rails are shipped with the switch. Select slide rails for the switch as required. Table2-5 describes the slide rails available for the switch.
Table2-5 Slide rails available for the switch
|
Item |
LSEM1BSR |
LSXM1BSR |
LSTM2KSGD0 |
|
Part No. |
0231AJAP |
0231A4EK |
0231A0PL |
|
Adjustment range |
380 mm to 630 mm (14.96 in to 24.80 in) |
630 mm to 900 mm (24.80 in to 35.43 in) |
500 mm to 800 mm (19.69 to 31.50 in) |
|
Load bearing capacity |
100 kg (220.46 lb) |
400 kg (881.83 lb) |
200 kg (440.92 lb) |
|
Occupied space |
N/A |
1 U |
2 U |
|
Applicable rack depth |
0.6 m (1.97 ft), 0.8 m (2.62 ft) |
1.0 m (3.28 ft), 1.2 m (3.94 ft) |
0.8 m (2.62 ft), 1.0 m (3.28 ft) |
|
Applicable switch model |
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE |
All S10500X-G switch models |
All S10500X-G switch models |
|
|
NOTE: The applicable rack depths in Table2-5 are for your reference only. Before you install slide rails, make sure the rack depth is in the adjustment range of the slide rails. |
Power supplies
The switch supports N+N (dual power input sources) or N+1 (single power input source) power supply redundancy. Determine the number of power supplies based on the power supply mode and system power consumption. Make sure the maximum total output power of the installed power supplies is greater than the system power consumption. Reserve a 20% power surplus as a best practice.
Table2-6 describes the power supplies available for the switch.
Table2-6 Power supplies available for the switch
|
Switch model |
Available power supplies |
Power supply quantity per switch |
|
S10506X-G |
· PSR1600B-12A-B · PSR2000-12D-B |
2 to 4 |
|
S10506X-G-PoE |
· PSR1600B-12A-B · PSR2000-12D-B · PoE: PSR1600-54A-B |
· 2 to 4 · PoE: 2 to 8 |
|
S10508X-G |
· PSR1600B-12A-B · PSR2000-12D-B |
2 to 6 |
|
S10512X-G |
· PSR1600B-12A-B · PSR2000-12D-B |
2 to 8 |
Table2-7 PSR1600B-12A-B power supply specifications
|
Item |
Specifications |
|
|
Rated input voltage |
· 100 to 240 VAC @ 50 or 60 Hz, 10 A · 240 VDC @ 8 A |
|
|
Rated output voltage |
12 V |
|
|
Maximum output current |
131 A (12 V) |
|
|
Maximum output power |
· 786 W @ 110 VAC · 1572 W @ 220 VAC · 1572 W @ 240 VDC |
|
|
Dimensions (H × W × D) |
40 × 74 × 225 mm (1.57 × 2.91 × 8.86 in) |
|
|
Ambient temperature |
Operating temperature |
–10°C to +55°C (14°F to 131°F) |
|
Storage temperature |
–40°C to +70°C (–40°F to +158°F) |
|
|
Compatible devices |
All device models |
|
Table2-8 PSR1600-54A-B power supply specifications
|
Item |
Specifications |
|
|
Rated input voltage |
· 100 to 130 VAC @ 50 or 60 Hz, 12 A · 200 to 240 VAC @ 50 or 60 Hz, 10 A · 240 VDC @ 8 A |
|
|
Rated output voltage |
56 V |
|
|
Maximum output current |
29 A |
|
|
Maximum output power |
· 950 W @ 110 VAC · 1600 W @ 220 VAC · 1600 W @ 240 VDC |
|
|
Dimensions (H × W × D) |
40 × 74 × 185 mm (1.57 × 2.91 × 7.28 in) |
|
|
Ambient temperature |
Operating temperature |
–10°C to +55°C (14°F to 131°F) |
|
Storage temperature |
–40°C to +70°C (–40°F to +158°F) |
|
|
Compatible devices |
S10506X-G-PoE |
|
Table2-9 PSR2000-12D-B power supply specifications
|
Item |
Specifications |
|
|
Rated input voltage |
–48 to –60 VDC @ 60 A |
|
|
Rated output voltage |
12 V |
|
|
Maximum output current |
167 A |
|
|
Maximum output power |
2000 W |
|
|
Dimensions (H × W × D) |
40 × 74 × 225 mm (1.57 × 2.91 × 8.86 in) |
|
|
Ambient temperature |
Operating temperature |
–10°C to +55°C (14°F to 131°F) |
|
Storage temperature |
–40°C to +70°C (–40°F to +158°F) |
|
|
Compatible devices |
All device models |
|
|
|
NOTE: The power supply shuts down automatically when its temperature exceeds the acceptable range. When the temperature returns to the acceptable range, the power supply automatically restarts. |
Fan trays
Table2-10 Fan tray specifications
|
Model |
Available fan trays |
Number of fans |
Fan diameter |
Maximum air flow rate |
|
S10506X-G/S10506X-G-PoE |
FAN-80B-4-A |
4 |
80 mm (3.15 in) |
420 CFM |
|
S10508X-G |
FAN-80B-5-A |
5 |
80 mm (3.15 in) |
525 CFM |
|
S10512X-G |
FAN-80B-8-A |
8 |
80 mm (3.15 in) |
840 CFM |
DC power cords
A DC power cord connects a DC power supply to an external DC power source.
Table2-11 DC power cords available for the power supplies
|
DC power supply |
DC power cord length |
|
PSR2000-12D-B |
3 m (9.84 ft) |
|
15 m (49.21 ft) |
AC power cords
An AC power cords is used for connecting an AC power supply on the switch to the external AC power supply system. Select an AC power cord with a current-carrying capacity that meets the power supply requirement.
For a PSR1600B-12A-B power supply, use an IEC 60320 standard-compliant power cord that has a C13 connector (connected to the power supply). For a PSR1600-54A-B power supply, use an IEC 60320 standard-compliant power cord that has a C15 connector (connected to the power supply).
The type of the connector (connected to the power source) varies by country or region. Select a compliant connector type as needed. For the connector types of different countries or regions and the power cord codes, see H3C Power Cords & Cables User Guide.
3 LEDs
Table3-1 lists the LEDs available for the switch.
Table3-1 LEDs at a glance
|
LEDs |
|
|
· Management Ethernet port LEDs |
|
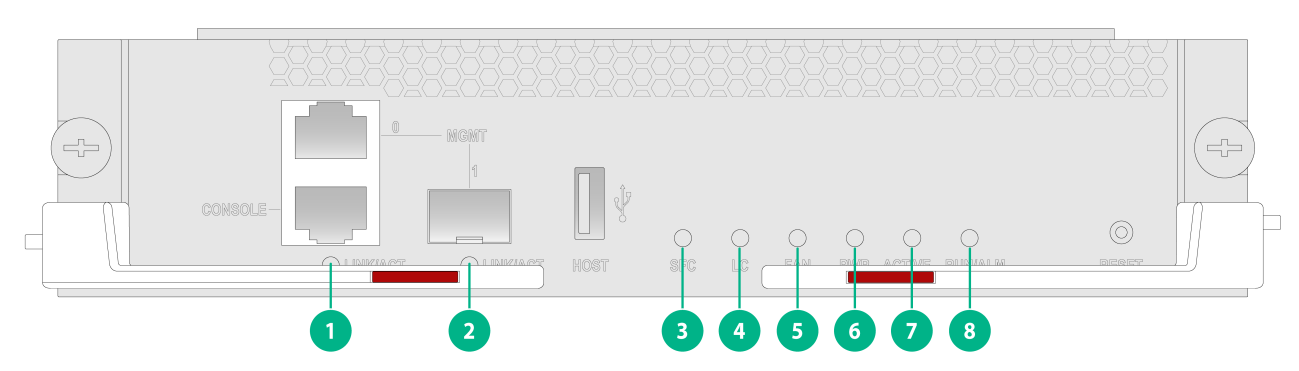
MPU LEDs
|
(1) 10/100/1000BASE-T management Ethernet port LED |
(2) SFP management Ethernet port LED |
|
(3) Switch fabric module status LED (SFC) |
(4) Service module status LED (LC) |
|
(5) Fan tray status LED (FAN) |
(6) Power supply status LED (PWR) |
|
(7) MPU active/standby status LED (ACTIVE) |
(8) MPU status LED (RUN/ALM) |
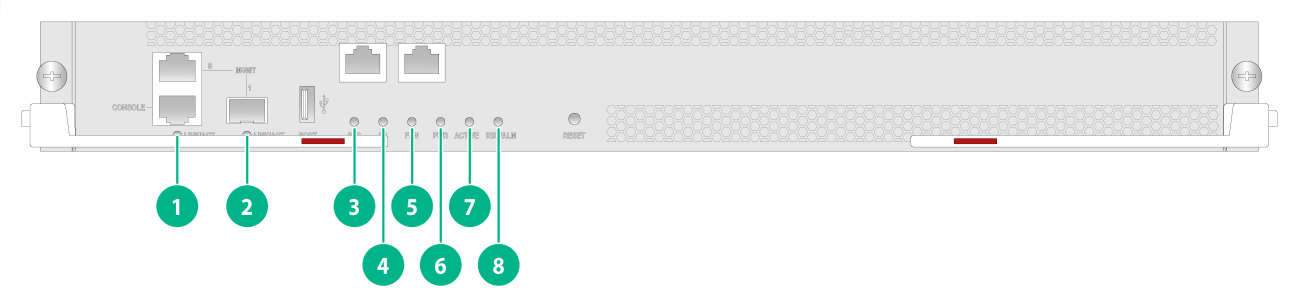
Figure3-2 LSEM1SUPB0 MPU LEDs
|
(1) 10/100/1000BASE-T management Ethernet port LED |
(2) SFP management Ethernet port LED |
|
(3) Switch fabric module status LED (SFC) |
(4) Service module status LED (LC) |
|
(5) Fan tray status LED (FAN) |
(6) Power supply status LED (PWR) |
|
(7) MPU active/standby status LED (ACTIVE) |
(8) MPU status LED (RUN/ALM) |
Management Ethernet port LEDs
10/100/1000BASE-T management Ethernet port LEDs
The MPU provides a LED for the 10/100/1000BASE-T management Ethernet port to indicate the link status and data forwarding status of the port.
Table3-2 10/100/1000BASE-T management Ethernet port LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Flashing |
The management Ethernet port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
|
NOTE: The data rate of a 10/100/1000BASE-T management Ethernet port is 1 Gbps when its LED is green and 10/100 Mbps when its LED is yellow. |
SFP management Ethernet port LEDs
The MPU provides a LED for the SFP management Ethernet port to indicate the link status and data forwarding status of the port.
Table3-3 SFP management Ethernet port LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Flashing |
The SFP port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
|
NOTE: When a link is present on an SFP management Ethernet port, the LED is green and the port is operating at 1 Gbps. |
Fan tray status LEDs
The MPU provides a fan tray status LED to indicate the status of the fan trays.
Table3-4 Fan tray status LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Steady green |
All fan trays are operating correctly. |
|
Steady red |
A fan tray is faulty or only one fan tray or no fan tray is operating correctly. |
|
Off |
The switch is not powered on. |
Power supply status LEDs
The MPU provides a power supply status LED to indicate the status of the power supplies.
Table3-5 Power supply status LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Steady green |
All power supplies are operating correctly. |
|
Steady red |
A minimum of one power supply is faulty. |
|
Off |
The switch is not powered on. |
|
|
NOTE: The power supply status LED is steady green only when all the power supplies are operating correctly. When a power supply is faulty, the power supply status LED is steady red. |
Service module status LEDs
The MPU provides a service module status LED (LC) to indicate the status of the service modules.
Table3-6 Service module status LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Flashing green (once per two seconds) |
All service modules are operating correctly. |
|
Steady red |
Possible reasons are as follows: · A minimum of one service module is starting up or loading software. · A high severity alarm has occurred on a minimum of one service module or a minimum of one service module is faulty. · The temperature of a service module has exceeded the upper warning threshold or fell below the lower warning threshold. |
|
Off |
No service module is present. |
MPU status LEDs
The MPU provides an MPU status LED (RUN/ALM) to indicate its operating status.
Table3-7 MPU status LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Flashing green (once per two seconds) |
The MPU is operating correctly. |
|
Flashing green (four times per second) |
The MPU is loading software. |
|
Steady green |
The MPU is starting up. |
|
Steady red |
A high severity alarm has occurred on the MPU or the MPU is faulty. |
|
Flashing red (once per four seconds) |
The MPU temperature has exceeded the upper warning threshold or fell below the lower warning threshold. |
|
Off |
The MPU is not in position or is faulty. |
MPU active/standby status LED
The MPU has one ACTIVE LED to indicate the active or standby status of the MPU.
Table3-8 MPU ACTIVE LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
On |
The MPU is active. |
|
Off |
· The MPU is in standby status. · The MPU is faulty. Examine the MPU status LED to further determine the MPU status. |
Switch fabric module status LEDs
The MPU provides a switch fabric module status LED (SFC) to indicate the status of the switch fabric modules.
Table3-9 Switch fabric module status LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Flashing green (once per two seconds) |
All switch fabric modules are operating correctly. |
|
Steady green |
A minimum of one switch fabric module has been isolated. |
|
Steady red |
Possible reasons are as follows: · A minimum of one switch fabric module is starting up or loading software. · A high severity alarm has occurred on a minimum of one switch fabric module or a minimum of one switch fabric module is faulty. · The temperature of a switch fabric module has exceeded the upper warning threshold or fell below the lower warning threshold. |
|
Off |
No switch fabric module is present or all present switch fabric modules are faulty. |
|
|
NOTE: If an alarm with a higher priority has occurred on a switch fabric module when the SFC LED is steady green, the LED becomes steady red. |
Service module LEDs
Service module status LEDs
Each service module provides a RUN/ALM LED to indicate their operating status.
Table3-10 Service module status LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Flashing green (once per two seconds) |
The service module is operating correctly. |
|
Flashing green (four times per second) |
The service module is loading software. |
|
Steady green |
The service module is starting up. |
|
Steady red |
A high severity alarm has occurred on the service module or the service module is faulty. |
|
Flashing red (four times per second) |
The service module temperature has exceeded the upper warning threshold or fell below the lower warning threshold. |
|
Off |
The service module is not in position or is faulty. |
RJ-45 port LEDs
The service modules provide one LED for each RJ-45 port to indicate the link status and data receiving/transmitting status of the RJ-45 ports.
Table3-11 RJ-45 port LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Flashing |
The RJ-45 port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
SFP port LEDs
The service modules provide one LED for each SFP port to indicate the link status and data receiving/transmitting status of the SFP ports.
Table3-12 SFP port LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Flashing |
The SFP port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
SFP+ port LEDs
The service modules provide one LED for each SFP+ port to indicate the link status and data receiving/transmitting status of the SFP+ ports.
Table3-13 SFP+ port LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Flashing |
The SFP+ port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
|
NOTE: The data rate of an SFP+ port is 1 Gbps when its LED is green and 100 Mbps when its LED is yellow. |
SFP28 port LEDs
The service modules provide one LED for each SFP28 port to indicate the link status and data receiving/transmitting status of the SFP28 ports.
Table3-14 SFP28 port LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Flashing |
The SFP28 port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
QSFP+ port LEDs
The service modules provide one LED for each QSFP+ port to indicate the link status and data receiving/transmitting status of the QSFP+ ports.
Table3-15 QSFP+ port LED description
|
QSFP+ port operating mode |
LED status |
Description |
|
Non-breakout mode |
Flashing |
The QSFP+ port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present. |
|
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
|
Breakout mode |
Flashing |
The QSFP+ port is receiving or sending data on a minimum of one link. |
|
On |
A minimum of one link is present. |
|
|
Off |
No link is present. |
QSFP28 port LEDs
The service modules provide one LED for each QSFP28 port to indicate the link status and data receiving/transmitting status of the QSFP28 ports.
Table3-16 QSFP28 port LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Flashing |
The QSFP28 port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present. |
|
Off |
No link is present. |
|
|
NOTE: The LED for a QSFP28 port is yellow if the port supports data rate change from 100 Gbps to 40 Gbps and is green if the port does not support data rate change from 100 Gbps to 40 Gbps. |
QSFP-DD port LEDs
The service modules provide a LED for each QSFP-DD port to indicate the link status and data receiving/transmitting status of the QSFP-DD ports.
Table3-17 QSFP-DD port LED description
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Flashing |
The QSFP-DD port is receiving or sending data. |
|
On |
A link is present on the QSFP-DD port. |
|
Off |
No link is present on the QSFP-DD port. |
Switch fabric module status LEDs
A switch fabric module has a RUN/ALM LED to indicate its operating status.
Table3-18 Description for the RUN/ALM LED on a switch fabric module
|
LED status |
Description |
|
Flashing green (once per two seconds) |
The switch fabric module is operating correctly. |
|
Flashing green (four times per second) |
The switch fabric module is starting up. |
|
Steady green |
The switch fabric module has been isolated. |
|
Steady red |
A high severity alarm has occurred on the switch fabric module or the switch fabric module is faulty. |
|
Flashing red (once per four seconds) |
The switch fabric module temperature has exceeded the upper warning threshold or fell below the lower warning threshold. |
|
Off |
The switch fabric module is not in position or is faulty. |
Fan tray LEDs
Fan tray status LEDs
A fan tray uses an OK/FAIL LED to indicate its operating status.
Table3-19 Fan tray status LED description
|
Status |
Description |
|
Steady green |
The fan tray is operating correctly. |
|
Steady red |
The fan tray is faulty. |
|
Off |
The fan tray is not powered on. |
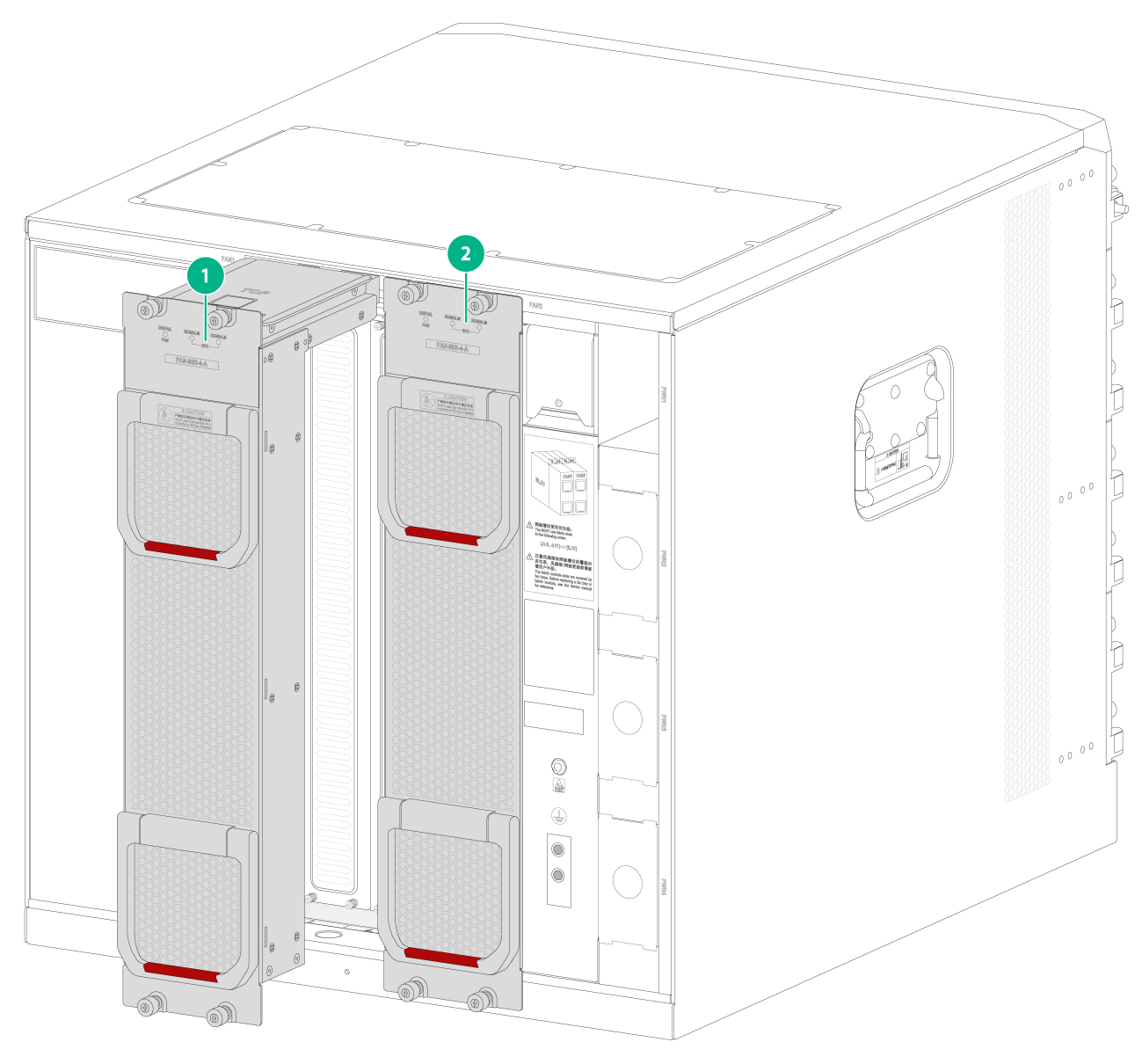
Switch fabric module status LEDs on a fan tray
A fan tray provides a RUN/ALM LED for each switch fabric module it covers.
Table3-20 Description for switch fabric module status LEDs on a fan tray
|
Status |
Description |
|
Flashing green (once per two seconds) |
The switch fabric module is operating correctly. |
|
Flashing green (four times per second) |
The switch fabric module is starting up. |
|
Steady green |
The switch fabric module has been isolated. |
|
Steady red |
A high severity alarm has occurred on the switch fabric module or the switch fabric module is faulty. |
|
Flashing red (once per four seconds) |
The switch fabric module temperature has exceeded the upper warning threshold or fell below the lower warning threshold. |
|
Off |
The switch fabric module is not in position or is faulty. |
|
|
NOTE: The switch fabric module LEDs on a fan tray indicate the status of the switch fabric modules the fan tray covers from left to right. |
Figure3-3 Relations between the LEDs and switch fabric module slots (S10506X-G as an example)
|
(1) LEDs for the switch fabric module slots 8 and 9 |
|
(2) LEDs for the switch fabric module slots 10 and 11 |
Power supply LEDs
Table3-21 Power supply LED description
|
Power supply model |
LED mark/LED status |
Description |
|
|
PSR1600B-12A-B |
Steady green |
The power supply is operating correctly. |
|
|
Flashing green (once per two seconds) |
The power supply has correct power input and is in standby state with 12 V standby output and without 12 V main output. |
||
|
Flashing green (twice per second) |
The power supply is updating software. |
||
|
Flashing green (once per three seconds) |
The power supply has entered cold redundancy state. |
||
|
Steady yellow |
The power supply is faulty. |
||
|
Flashing yellow (once per second) |
· The power supply is operating correctly, but an alarm has occurred (such as input undervoltage, output overcurrent, and overtemperature). · The power supply does not have power input, but the backup power supplies have correct power input. |
||
|
Off |
No power input. |
||
|
PSR1600-54A-B |
OUT OK |
Steady green |
Normal power output. |
|
Flashing green |
Normal power input, and 12 V output disabled. |
||
|
Steady red |
The power supply has entered protection state (no power output). |
||
|
Alternating between red and green (once per second) |
Abnormal power input and output. |
||
|
Off |
No power output. |
||
|
IN OK |
Steady green |
Normal power input. |
|
|
Steady red |
Abnormal power input. |
||
|
Off |
No power input. |
||
|
PSR2000-12D-B |
Steady green |
The power supply is operating correctly. |
|
|
Flashing green (once per second) |
The power supply is updating software. |
||
|
Flashing green (once per two seconds) |
The power supply has correct power input and is in standby state with 12 V standby output and without 12 V main output. |
||
|
Steady red |
The power supply is faulty. |
||
|
Flashing yellow (once per second) |
The power supply does not have power input, but the backup power supplies have correct power input. |
||
|
Flashing yellow (twice per second) |
The power supply is operating correctly, but an alarm has occurred (such as input undervoltage, output overcurrent, and overtemperature). |
||
|
Off |
No power input. |
||
4 Cables
This chapter describes cables used for connecting network ports.
Table4-1 Cable description
|
Cable |
Port type |
Application |
|
RJ-45 Ethernet port at one end and DB-9 port at the other end |
Connects the console port of the switch to the console terminal. |
|
|
RJ-45 Ethernet ports |
Connects RJ-45 Ethernet ports to transmit data. |
|
|
SFP/SFP+ ports |
Connects the fiber ports to transmit data. |
|
|
SFP+ ports |
Connects SFP+ ports to transmit data. |
|
|
SFP28 ports |
Connects SFP28 ports to transmit data. |
|
|
SFP28 ports |
Connects SFP28 ports to transmit data. |
|
|
QSFP+ ports |
Connects QSFP+ ports to transmit data. |
|
|
QSFP+ ports |
Connects QSFP+ ports to transmit data. |
|
|
QSFP28 ports |
Connects QSFP28 ports to transmit data. |
|
|
QSFP28 ports |
Connects QSFP28 ports to transmit data. |
|
|
QSFP+ port at one end and SFP+ ports at the other end |
Connects the QSFP+ port and SFP+ ports to transmit data. |
|
|
QSFP28 port at one end and SFP28 ports at the other end |
Connects the QSFP28 port and SFP28 ports to transmit data. |
|
|
QSFP-DD ports |
Connects QSFP-DD ports to transmit data. |
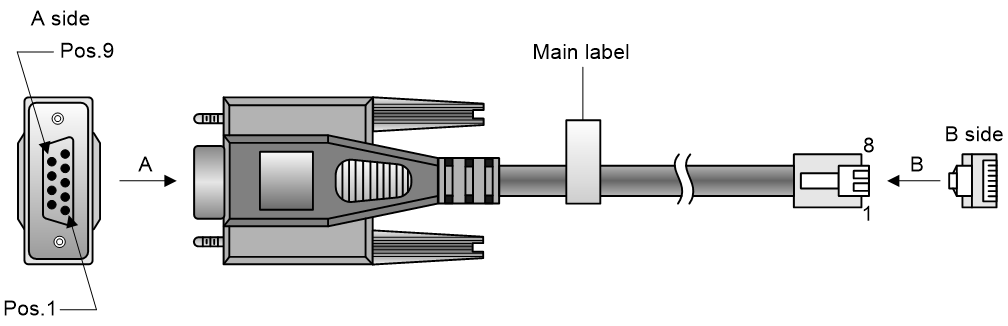
Console cable
A console cable is an 8-core shielded cable, with a crimped RJ-45 connector at one end for connecting to the console port of the switch, and a DB-9 female connector at the other end for connecting to the serial port on the console terminal.
Figure4-1 Console cable
Table4-2 Connection between the console ports on the switch and console ports on a PC (terminal)
|
RJ-45 |
Signal |
DB-9 |
Signal |
|
1 |
RTS |
8 |
CTS |
|
2 |
DTR |
6 |
DSR |
|
3 |
TXD |
2 |
RXD |
|
4 |
SG |
5 |
SG |
|
5 |
SG |
5 |
SG |
|
6 |
RXD |
3 |
TXD |
|
7 |
DSR |
4 |
DTR |
|
8 |
CTS |
7 |
RTS |
Ethernet twisted pair cable
An Ethernet twisted pair cable consists of four pairs of insulated wires twisted together. It mainly transmits analog signals and is advantageous in transmitting data over shorter distances. The maximum transmission distance is 100 m (328.08 ft). To increase the transmission distance, you can install a maximum of four repeaters between two Ethernet twisted pair cables. With four repeaters installed, the maximum transmission distance can reach 500 m (1640.42 ft).
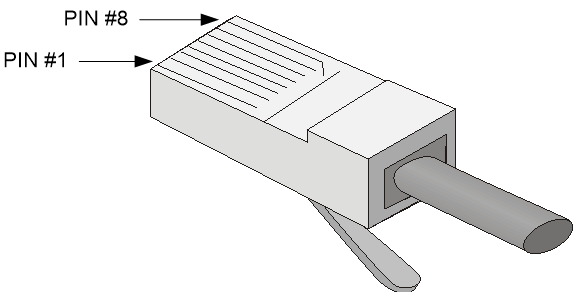
RJ-45 connector
An Ethernet twisted pair cable connects network devices through the RJ-45 connectors at the two ends. Figure4-2 shows the pinouts of an RJ-45 connector.
Figure4-2 RJ-45 connector pinout diagram
Cable pinouts
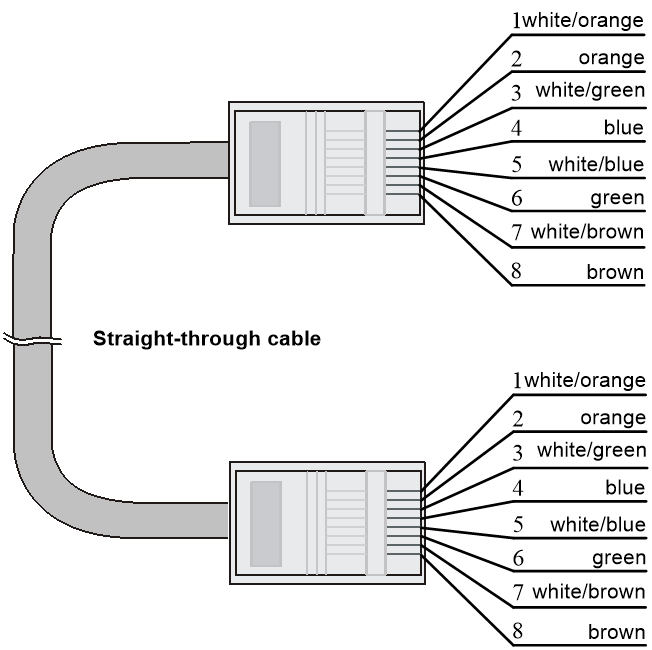
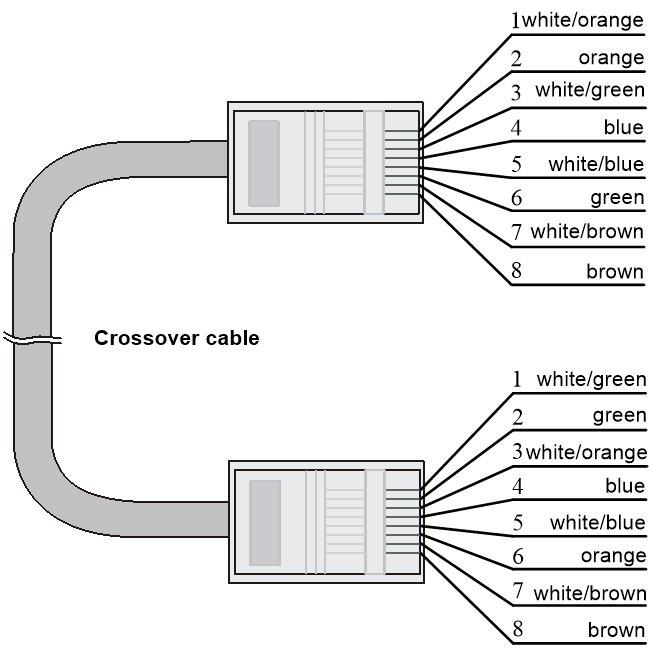
EIA/TIA cabling specifications define two standards: 568A and 568B for cable pinouts.
· Standard 568A—pin 1: white/green stripe, pin 2: green solid, pin 3: white/orange stripe, pin 4: blue solid, pin 5: white/blue stripe, pin 6: orange solid, pin 7: white/brown stripe, pin 8: brown solid.
· Standard 568B—pin 1: white/orange stripe, pin 2: orange solid, pin 3: white/green stripe, pin 4: blue solid, pin 5: white/blue stripe, pin 6: green solid, pin 7: white/brown stripe, pin 8: brown solid.
Cable type
Based on performance
Table4-3 Ethernet cable description
|
Type |
Description |
|
Category 5 |
Transmits data at a maximum speed of 100 Mbps, with a bandwidth of 100 MHz. |
|
Category 5e |
Transmits data at a maximum speed of 1000 Mbps, with a bandwidth of 100 MHz. |
|
Category 6 |
Transmits data at a speed higher than 1 Gbps, with a bandwidth of 250 MHz. |
|
Category 6A |
Transmits data at a speed higher than 10 Gbps, with a bandwidth of 500 MHz. |
|
Category 7 |
Transmits data at a speed higher than 10 Gbps, with a bandwidth of 600 MHz. |
Based on pinouts
Ethernet twisted pair cables can be classified into straight through and crossover cables based on their pinouts.
· Straight-through—The pinouts at both ends comply with standard 568B, as shown in Figure4-3.
· Crossover—The pinouts at one end comply with standard 568B, and those at the other end comply with standard 568A, as shown in Figure4-4.
Figure4-3 Straight-through cable
Pin assignments
Select an Ethernet twisted pair cable according to the RJ-45 Ethernet interface type on your device. An RJ-45 Ethernet interface can be MDI (for routers and PCs) or MDIX (for switches). For the pinouts of RJ-45 Ethernet interfaces, see Table4-4 and Table4-5.
Table4-4 RJ-45 MDI interface pinouts
|
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX |
1000BASE-T |
|||
|
Signal |
Function |
Signal |
Function |
|
|
1 |
Tx+ |
Send data |
BIDA+ |
Bi-directional data cable A+ |
|
2 |
Tx- |
Send data |
BIDA- |
Bi-directional data cable A- |
|
3 |
Rx+ |
Receive data |
BIDB+ |
Bi-directional data cable B+ |
|
4 |
Reserved |
N/A |
BIDC+ |
Bi-directional data cable C+ |
|
5 |
Reserved |
N/A |
BIDC- |
Bi-directional data cable C- |
|
6 |
Rx- |
Receive data |
BIDB- |
Bi-directional data cable B- |
|
7 |
Reserved |
N/A |
BIDD+ |
Bi-directional data cable D+ |
|
8 |
Reserved |
N/A |
BIDD- |
Bi-directional data cable D- |
Table4-5 RJ-45 MDI-X interface pinouts
|
Pin |
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX |
1000BASE-T |
||
|
Signal |
Function |
Signal |
Function |
|
|
1 |
Rx+ |
Receive data |
BIDB+ |
Bi-directional data cable B+ |
|
2 |
Rx- |
Receive data |
BIDB- |
Bi-directional data cable B- |
|
3 |
Tx+ |
Send data |
BIDA+ |
Bi-directional data cable A+ |
|
4 |
Reserved |
N/A |
BIDD+ |
Bi-directional data cable D+ |
|
5 |
Reserved |
N/A |
BIDD- |
Bi-directional data cable D- |
|
6 |
Tx- |
Send data |
BIDA- |
Bi-directional data cable A- |
|
7 |
Reserved |
N/A |
BIDC+ |
Bi-directional data cable C+ |
|
8 |
Reserved |
N/A |
BIDC- |
Bi-directional data cable C- |
To ensure normal communication, the pins for sending data on one port should correspond to the pins for receiving data on the peer port. When both of the ports on the two devices are MDI or MDIX, a crossover Ethernet cable is needed. A cross-over cable connects devices of the same type. When one port is MDI and the other is MDIX, a straight-through Ethernet cable is needed. A straight-through cable connects devices of different types.
An RJ-45 Ethernet interface with MDI/MDIX autosensing enabled can automatically negotiate pin roles. The S10500X-G RJ-45 Ethernet interfaces support MDI/MDIX. By default, MDI/MDIX is enabled on a port.
Making an Ethernet twisted pair cable
1. Cut the cable to length with the crimping pliers.
2. Strip off an appropriate length of the cable sheath. The length is typically that of the RJ-45 connector.
3. Untwist the pairs so that they can lie flat, and arrange the colored wires based on the wiring specifications.
4. Cut the top of the wires even with one another. Insert the wires into the RJ-45 end and make sure the wires extend to the front of the RJ-45 end and make good contact with the metal contacts in the RJ-45 end and in the correct order.
5. Crimp the RJ-45 connector with the crimping pliers until you hear a click.
6. Repeat the above steps with the other end of the cable.
7. Use a cable tester to verify the connectivity of the cable.
Optical fiber
|
CAUTION: Use the same types of transceiver modules, pigtail cords, patch cords, and fiber cables. If you use single-mode optical fibers, the transceiver modules, pigtail cords, patch cords, and fiber cables must be single-mode. |
Optical fiber
Optical fibers are widely used in fiber-optic communications, which are advantageous for long-distance communications.
Optical fibers can be classified into the following types:
· Single mode fiber—It has a core size of 10 µm or smaller, and has a lower modal dispersion. It carries only a single ray of light. It is mostly used for communication over longer distances.
· Multi-mode fiber—It has a core size of 50 µm or 62.5 µm or higher, and has a higher modal dispersion than single-mode optical fiber. It is mostly used for communication over shorter distances.
Table4-6 Allowed maximum tensile force and crush load
|
Period of force |
Tensile load (N) |
Crush load (N/mm) |
|
Short period |
150 |
500 |
|
Long term |
80 |
100 |
Optical fiber cable
An optical fiber cable is a cable containing one or more optical fibers. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube. Optical fiber cables fall into single-mode and multi-mode.
Patch cord
A fiber that has connectors at both ends is called a patch cord. A patch cord connects one optical device to another for signal routing. Patch cords fall into single-mode and multi-mode patch cords.
· Single-mode patch cord—The jacket is yellow. It permits transmission over longer distances.
· Multi-mode patch cord—The jacket is orange. It permits transmission over shorter distances.
Patch cords are classified into SC, LC, FC, and so on based on interface type. The length of a patch cord can be 0.5 m (1.64 ft), 1 m (3.28 ft), 2 m (6.56 ft), 3 m (9.84 ft), 5 m (16.40 ft), 10 m (32.81 ft), and so on.
Pigtail cord
A pigtail cord is an optical fiber that has an optical connector on one end and a length of exposed fiber on the other. The end of the pigtail is fusion spliced to a fiber, connecting the fiber cable and transceiver.
Pigtail cords fall into single-mode (yellow) and multi-mode (orange), and can also be classified into SC, LC, FC, and so on based on interface type.
Fiber connector
Figure4-5 MPO connector
Precautions
· Make sure the fiber connector and fiber type match the transceiver module type.
· The fiber ports on the switch are provided with dust plugs. Insert the dust plugs into the fiber ports that you are not to use, to prevent particles from entering the ports.
· Fiber connectors must be protected under safe and reliable outer packing, and be fitted with dust caps. Fiber connectors must be installed with dust caps when they are not in use. Take care not to scratch their end face. Replace the dust cap if it is loose or polluted.
· Before connecting a fiber, use dust free paper and absolute alcohol to clean the end face of the fiber connector. You can brush the end face only in one direction. You also need to brush the end face of the fiber port.
· If the fiber has to pass through a metallic board hole, the hole must have a sleek and fully filleted surface (the filleting radius must be not less than 2 mm). When passing through a metallic board hole or bending along the acute side of mechanical parts, the fiber must wear jackets or cushions.
· Insert and remove a plug with care. Never exert a fierce force to the fiber or plug; otherwise the plug might be damaged or the fiber might be broken. Never pull, press or extrude the fiber fiercely. For the allowed maximum tensile load and crush load, see Table4-6.
SFP+ DAC cable
You can use SFP+ DAC cables to connect SFP+ ports.
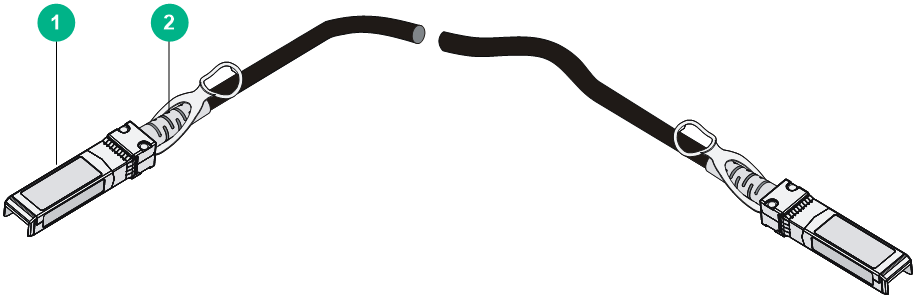
The SFP+ DAC cables available for the switch series are 10G SFP+ Cu cables, as shown in Figure4-7.
|
(1) Connector |
(2) Pull latch |
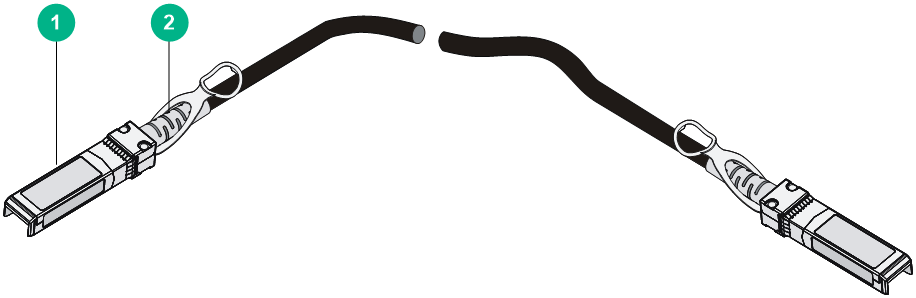
SFP28 DAC cable
You can use an SFP28 DAC cable to connect SFP28 ports.
Figure4-8 SFP28 DAC cable
|
(1) Connector |
(2) Pull latch |
SFP28 AOC cable
You can use an SFP28 AOC cable to connect SFP28 ports.
Figure4-9 SFP28 AOC cable
|
(1) Connector |
(2) Pull latch |
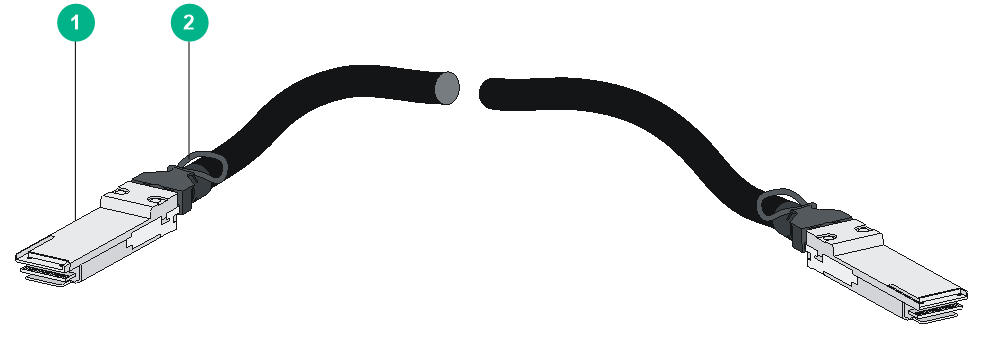
QSFP+ DAC cable
You can use a QSFP+ DAC cable to connect QSFP+ ports.
Figure4-10 QSFP+ DAC cable
|
(1) Connector |
(2) Pull latch |
QSFP+ AOC cable
You can use a QSFP+ AOC cable to connect QSFP+ ports
Figure4-11 QSFP+ AOC cable
|
(1) Connector |
(2) Pull latch |
QSFP28 DAC cable
You can use a QSFP28 DAC cable to connect QSFP28 ports.
Figure4-12 QSFP28 DAC cable
|
(1) Connector |
(2) Pull latch |
QSFP28 AOC cable
You can use a QSFP28 AOC cable to connect QSFP28 AOC ports.
Figure4-13 QSFP28 AOC cable
|
(1) Connector |
(2) Pull latch |
QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cable
You can use a QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cable to connect a QSFP+ port at one end and four SFP+ ports at the other end.
Figure4-14 QSFP+ to SFP+ DAC cable
|
(1) QSFP+ connector |
(2) QSFP+ connector pull latch |
|
(3) SFP+ connector |
(4) SFP+ connector pull latch |
QSFP28 to SFP28 DAC cable
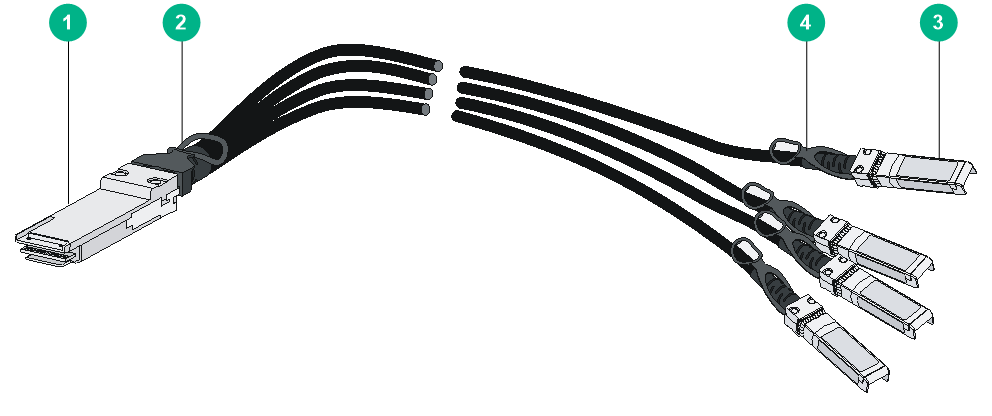
You can use a QSFP28 to SFP28 DAC cable to connect a QSFP28 port at one end and four SFP28 ports at the other end.
Figure4-15 QSFP28 to SFP28 DAC cable
|
(1) QSFP28 connector |
(2) QSFP28 connector pull latch |
|
(3) SFP28 connector |
(4) SFP28 connector pull latch |
QSFP-DD copper cable
You can use a QSFP-DD copper cable to connect QSFP-DD ports.
Figure4-16 QSFP-DD copper cable