- Table of Contents
-
- 09-Security Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-AAA configuration
- 02-802.1X configuration
- 03-MAC authentication configuration
- 04-Portal configuration
- 05-Web authentication configuration
- 06-Triple authentication configuration
- 07-Port security configuration
- 08-User profile configuration
- 09-Password control configuration
- 10-Keychain configuration
- 11-Public key management
- 12-PKI configuration
- 13-IPsec configuration
- 14-SSH configuration
- 15-SSL configuration
- 16-Attack detection and prevention configuration
- 17-TCP attack prevention configuration
- 18-IP source guard configuration
- 19-ARP attack protection configuration
- 20-ND attack defense configuration
- 21-uRPF configuration
- 22-SAVI configuration
- 23-SAVA configuration
- 24-MFF configuration
- 25-Crypto engine configuration
- 26-FIPS configuration
- 27-MACsec configuration
- 28-802.1X client configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 27-MACsec configuration | 186.86 KB |
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with MACsec
Configuring the MKA key server priority
Configuring MACsec protection parameters
About MACsec protection parameters
Restrictions and guidelines for MACsec protection parameter configuration
Configuring MACsec protection parameters in interface view
Configuring MACsec protection parameters by MKA policy
Display and maintenance commands for MACsec
Example: Configuring client-oriented MACsec
Example: Configuring device-oriented MACsec
Cannot establish MKA sessions between MACsec devices
Configuring MACsec
About MACsec
Media Access Control Security (MACsec) secures data communication on IEEE 802 LANs. MACsec provides services such as data encryption, frame integrity check, and data origin validation for frames on the MAC sublayer of the Data Link Layer. MACsec usually cooperates with 802.1X authentication to use the keys generated from MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) negotiation for authenticated users' data encryption and integrity check. This collaboration can prevent ports from processing packets from unauthenticated users or tampered packets.
Basic concepts
CA
Connectivity association (CA) is a group of participants that use the same key and key algorithm. The encryption key used by the CA participants is called a connectivity association key (CAK). The following types of CAKs are available:
· Pairwise CAK—Used by CAs that have two participants.
· Group CAK—Used by CAs that have more than two participants.
The pairwise CAK is used most often because MACsec is typically applied to point-to-point networks.
A CAK can be an encryption key generated during 802.1X authentication or a user-configured preshared key. The user-configured preshared key takes precedence over the 802.1X-generated key.
SA
Secure association (SA) is an agreement negotiated by CA participants. The agreement includes a cipher suite and keys for integrity check.
A secure channel can contain more than one SA. Each SA uses a unique secure association key (SAK). The SAK is generated from the CAK, and MACsec uses the SAK to encrypt data transmitted along the secure channel.
MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) limits the number of packets that can be encrypted by an SAK. When the limit is exceeded, the SAK will be refreshed. For example, when packets with the minimum size are sent on a 10-Gbps link, an SAK rekey occurs about every 300 seconds.
MKA life time
The participants at each end of a secure session exchange MKA protocol packets to keep the session alive.
MKA life time sets the session keepalive timer for participants. The timer starts on a participant when the participant receives the first MKA protocol packet from its peer. If the participant does not receive any subsequent MKA protocol packets from that peer before the timer expires, the participant determines that the session is insecure and then removes the session.
In client-oriented mode, the MKA life time is 6 seconds and is not user configurable.
In device-oriented mode, the MKA life time is user configurable. By default, the MKA life time is 6 seconds.
MACsec services
Data encryption
MACsec enables a port to encrypt outbound frames and decrypt MACsec-encrypted inbound frames. The keys for encryption and decryption are negotiated by MKA.
Integrity check
MACsec performs integrity check when the device receives a MACsec-encrypted frame. The integrity check uses the following process:
· Uses a key negotiated by MKA to calculate an integrity check value (ICV) for the frame.
· Compares the calculated ICV with the ICV in the frame trailer.
¡ If the ICVs are the same, the device verifies the frame as legal.
¡ If the ICVs are different, the device determines whether to drop the frame based on the validation mode. The device supports the following validation modes:
- check—Performs validation only, and does not drop illegal frames.
- disabled—Does not perform validation.
- strict—Performs validation, and drops illegal frames.
Replay protection
When MACsec frames are transmitted over the network, frame disorder might occur. MACsec replay protection allows the device to accept the out-of-order packets within the replay protection window size and drop other out-of-order packets.
MACsec application modes
MACsec supports client-oriented and device-oriented modes.
Client-oriented mode
As shown in Figure 1, MACsec secures data transmission between the client and the access device. In this mode, MACsec must operate with 802.1X authentication.
Client-oriented MACsec includes the following entities:
· Client (supplicant)—A user terminal seeking access to the LAN. The terminal must have 802.1X software to authenticate to the access device. The terminal also performs CAK negotiation and packet encryption.
· Access device (authenticator)—Authenticates the client to control access to the LAN and performs CAK negotiation and packet encryption.
· Authentication server—Provides AAA services for the access device. The authentication server is typically a RADIUS server. After the client passes authentication, the authentication server generates and distributes the CAK to the client and the access device.
|
|
NOTE: In client-oriented mode, an MKA-enabled port on the access device must perform port-based 802.1X access control. The authentication method must be EAP relay. |
Device-oriented mode
As shown in Figure 2, MACsec secures data transmission between devices. In this mode, the same preshared key must be configured on the MACsec ports that connect the devices. The devices use the configured preshared key as the CAK.
MACsec operating mechanism
Operating mechanism for client-oriented mode
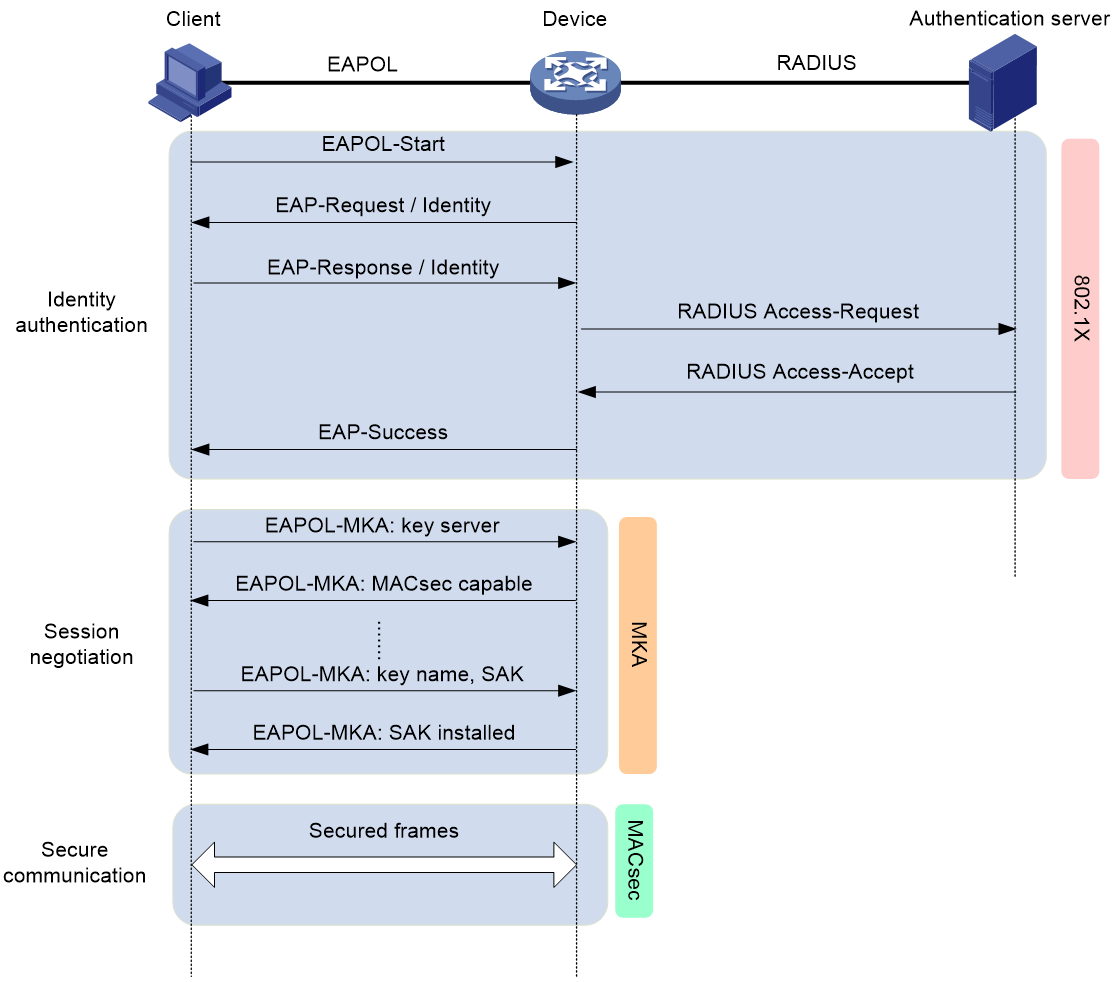
Figure 3 illustrates how MACsec operates in client-oriented mode.
Figure 3 MACsec interactive process in client-oriented mode
The following shows the MACsec process:
1. After the client passes 802.1X authentication, the RADIUS server distributes the generated CAK to the client and the access device.
2. After receiving the CAK, the client and the access device exchange EAPOL-MKA packets.
The client and the access device exchange the MACsec capability and required parameters for session establishment. The parameters include MKA key server priority and MACsec desire.
During the negotiation process, the access device automatically becomes the key server. The key server generates an SAK from the CAK for packet encryption, and it distributes the SAK to the client.
3. The client and the access device use the SAK to encrypt packets, and they send and receive the encrypted packets in secure channels.
4. When the access device receives a logoff request from the client, it immediately removes the associated secure session from the port. The remove operation prevents an unauthorized client from using the secure session established by the previous authorized client to access the network.
Operating mechanism for device-oriented mode
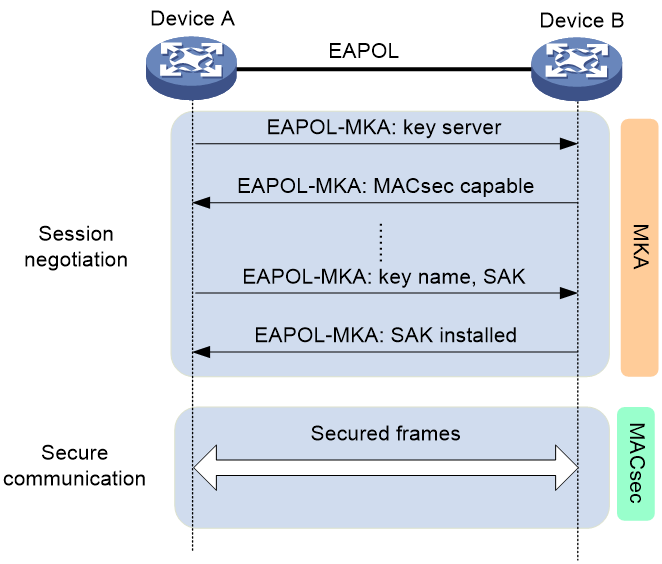
As shown in Figure 4, the devices use the configured preshared key to start session negotiation.
Figure 4 MACsec interactive process in device-oriented mode
The following shows the MACsec process:
1. The devices use the configured preshared key as the CAK to exchange EAPOL-MKA packets.
They exchange the MACsec capability and required parameters for session establishment. The parameters include MKA key server priority and MACsec desire.
During the negotiation process, the port with higher MKA key server priority becomes the key server. The key server generates and distributes an SAK.
2. The devices use the SAK to encrypt packets, and they send and receive the encrypted packets in secure channels.
3. When a device receives a logoff request from the peer, it immediately deletes the associated secure session.
Protocols and standards
IEEE 802.1X-2010, Port-Based Network Access Control
IEEE 802.1AE-2006, Media Access Control (MAC) Security
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with MACsec
MACsec is supported on the following ports:
· The highest numbered eight GE ports on the front panel. Combo interfaces among the eight ports also support MACsec.
· Ports on the LSWM4SP8PM, LSWM2SP2PM, and LSWM2XGT2PM modules.
An interface module is not hot swappable if it has MACsec-capable ports with MACsec enabled.
You cannot enable MKA on a MACsec-incapable port.
MACsec tasks at a glance
To configure MACsec, perform the following tasks:
1. Enabling MKA
3. Configuring a preshared key
This task is required in device-oriented mode. Do not perform this task in client-oriented mode.
4. (Optional.) Configuring the MKA key server priority
5. (Optional.) Setting the MKA life time
This task is applicable only in device-oriented mode.
6. (Optional.) Configuring MACsec protection parameters
Choose one of the following tasks:
¡ Configuring MACsec protection parameters in interface view
¡ Configuring MACsec protection parameters by MKA policy
7. (Optional.) Enabling MKA session logging
Enabling MKA
About this task
MKA establishes and manages MACsec secure channels on a port. It also negotiates keys used by MACsec.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable MKA.
mka enable
By default, MKA is disabled on the port.
Enabling MACsec desire
About this task
The MACsec desire feature expects MACsec protection for outbound frames. The key server determines whether MACsec protects the outbound frames.
MACsec protects the outbound frames of a port when the following requirements are met:
· The key server is MACsec capable.
· Both the local participant and its peer are MACsec capable.
· A minimum of one participant is enabled with MACsec desire.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Enable MACsec desire.
macsec desire
By default, the port does not expect MACsec protection for outbound frames.
Configuring a preshared key
Restrictions and guidelines
In device-oriented mode, configure a preshared key as the CAK. To successfully establish an MKA session between two devices, make sure the following requirements are met:
· The connected MACsec ports are configured with the same CAK name (CKN) and CAK.
· Only the ports are configured with the same CKN in the network.
A user-configured preshared key has higher priority than the 802.1X-generated CAK. To ensure a successful MKA session establishment, do not configure a preshared key in client-oriented mode.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set a preshared key.
mka psk ckn name cak { cipher | simple } string
By default, no MKA preshared key exists.
Configuring the MKA key server priority
Restrictions and guidelines
When you configure the MKA key server priority, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· In client-oriented mode, the access device port automatically becomes the key server. You do not have to configure the MKA key server priority.
· In device-oriented mode, the port that has higher priority becomes the key server. The lower the priority value, the higher the priority. If a port and its peers have the same priority, MACsec compares the secure channel identifier (SCI) values on the ports. The port with the lowest SCI value (a combination of MAC address and port ID) becomes the key server.
· A port with priority 255 cannot become the key server. For a successful key server selection, make sure a minimum of one participant's key server priority is not 255.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set the MKA key server priority.
mka priority priority-value
The default setting is 0.
Setting the MKA life time
Restrictions and guidelines
This task is applicable only in device-oriented mode.
Make sure the participants at each end of a secure session have the same MKA life time.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set the MKA life time.
mka timer mka-life seconds
By default, the MKA life time is 6 seconds.
Configuring MACsec protection parameters
About MACsec protection parameters
You can set the following MACsec protection parameters:
· MACsec confidentiality offset—Specifies the number of bytes starting from the frame header. MACsec encrypts only the bytes after the offset in a frame. The offset value can be 0, 30, or 50.
· MACsec replay protection—Allows a MACsec port to accept a number of out-of-order or repeated inbound frames.
· MACsec validation—Allows a port to perform integrity check based on the validation modes.
Restrictions and guidelines for MACsec protection parameter configuration
You can configure MACsec protection parameters either in interface view or through MKA policies.
The use of MKA policies provides a centralized method to configure MACsec protection parameters. When you need to configure the same settings for MACsec protection parameters on multiple ports, you can configure them in an MKA policy and apply the policy to the ports.
If you configure a protection parameter in interface view after applying an MKA policy, the configuration in interface view overwrites the configuration of that parameter in the MKA policy. The other protection parameters in the MKA policy still take effect.
If you apply an MKA policy to a port after configuring protection parameters on the port, the settings in the policy overwrite all protection parameter settings in interface view. The protection parameters not configured in the policy are restored to the default.
Configuring MACsec protection parameters in interface view
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
3. Set the MACsec confidentiality offset.
macsec confidentiality-offset offset-value
The default setting is 0, and the entire frame needs to be encrypted.
MACsec uses the confidentiality offset propagated by the key server.
4. Configure MACsec replay protection:
a. Enable MACsec replay protection.
macsec replay-protection enable
By default, MACsec replay protection is enabled on the port.
b. Set the MACsec replay protection window size.
macsec replay-protection window-size size-value
The default setting is 0. The device accepts only frames that arrive in the correct order. Out-of-order or duplicated frames will be dropped.
The configured replay protection window size takes effect only when MACsec replay protection is enabled.
5. Set a MACsec validation mode.
macsec validation mode { check | disabled| strict }
The default setting is check.
The S5560X-EI switch series and ES5500 switch series do not support the disabled keyword.
To avoid data loss, use the display macsec command to verify that MKA negotiation with the peer device has succeeded before you change the mode to strict.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
check |
Verifies incoming frames but does not drop illegal frames. |
|
disabled |
Disables MACsec validation for incoming frames. |
|
strict |
Configuring MACsec protection parameters by MKA policy
Restrictions and guidelines
An MKA policy can be applied to a port or multiple ports. When you apply an MKA policy to a port, follow these restrictions and guidelines:
· The settings in the MKA policy overwrite all protection parameter settings configured in interface view. The protection parameters not configured in the policy are restored to the default.
· Any modifications to the MKA policy take effect immediately.
· When you remove an MKA policy application from the port, the MACsec parameter settings on the port restore to the default.
· When you apply a nonexistent MKA policy to the port, the port automatically uses the system-defined MKA policy named default-policy. If you create the policy, the policy will be automatically applied to the port.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an MKA policy and enter its view.
mka policy policy-name
By default, a system-defined MKA policy exists. The policy name is default-policy.
The settings for parameters in the system-defined policy are the same as the default settings for the parameters on a port.
You cannot delete or modify the system-defined MKA policy.
You can create multiple MKA policies.
3. Set the MACsec confidentiality offset.
confidentiality-offset offset-value
The default setting is 0, and the entire frame needs to be encrypted.
MACsec uses the confidentiality offset propagated by the key server.
4. Configure MACsec replay protection:
a. Enable MACsec replay protection.
replay-protection enable
By default, MACsec replay protection is enabled.
b. Set the replay protection window size.
replay-protection window-size size-value
The default replay protection window size is 0. The device accepts only frames that arrive in the correct order. Out-of-order or duplicated frames will be dropped.
5. Set a MACsec validation mode.
validation mode { check | disabled | strict }
The default setting is check.
The S5560X-EI switch series and ES5500 switch series do not support the disabled keyword.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
check |
Verifies incoming frames but does not drop illegal frames. |
|
disabled |
Disables MACsec validation for incoming frames. |
|
strict |
Verifies incoming frames and drops illegal frames. |
6. Apply an MKA policy:
a. Return to system view.
quit
b. Enter interface view.
interface interface-type interface-number
c. Apply the MKA policy to the port.
mka apply policy policy-name
By default, no MKA policy is applied to a port.
Enabling MKA session logging
About this task
This feature enables the device to generate logs for MKA session changes, such as peer aging and SAK updates. The logs are sent to the information center of the device. For the logs to be output correctly, you must also configure the information center on the device. For more information about information center configuration, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Restrictions and guidelines
As a best practice, disable this feature to prevent excessive MKA session log output.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable MKA session logging.
macsec mka-session log enable
By default, MKA session logging is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for MACsec
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display MACsec information on ports. |
display macsec [ interface interface-type interface-number ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display MKA policy information. |
display mka { default-policy | policy [ name policy-name ] } |
|
Display MKA session information. |
display mka session [ interface interface-type interface-number | local-sci sci-id ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display MKA statistics on ports. |
display mka statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Reset MKA sessions on ports. |
reset mka session [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Clear MKA statistics on ports. |
reset mka statistics [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
MACsec configuration examples
Example: Configuring client-oriented MACsec
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 5, the host accesses the network through GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. The device performs RADIUS-based 802.1X authentication for the host to control user access to the Internet.
To ensure secure communication between the host and device, perform the following tasks on the device:
· Enable MACsec desire, and configure MKA to negotiate SAKs for packet encryption.
· Set the MACsec confidentiality offset to 30 bytes.
· Enable MACsec replay protection, and set the replay protection window size to 100.
· Set the MACsec validation mode to strict.
Procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for the Ethernet ports. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure the RADIUS server to provide authentication, authorization, and accounting services. Add a user account for the host. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure AAA:
# Enter system view.
<Device> system-view
# Configure RADIUS scheme radius1.
[Device] radius scheme radius1
[Device-radius-radius1] primary authentication 10.1.1.1
[Device-radius-radius1] primary accounting 10.1.1.1
[Device-radius-radius1] key authentication simple name
[Device-radius-radius1] key accounting simple name
[Device-radius-radius1] user-name-format without-domain
[Device-radius-radius1] quit
# Configure authentication domain bbb for 802.1X users.
[Device] domain bbb
[Device-isp-bbb] authentication lan-access radius-scheme radius1
[Device-isp-bbb] authorization lan-access radius-scheme radius1
[Device-isp-bbb] accounting lan-access radius-scheme radius1
[Device-isp-bbb] quit
4. Configure 802.1X:
# Enable 802.1X on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x
# Implement port-based access control on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x port-method portbased
# Specify bbb as the mandatory authentication domain for 802.1X users on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] dot1x mandatory-domain bbb
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable 802.1X globally, and sets the device to relay EAP packets.
[Device] dot1x
[Device] dot1x authentication-method eap
5. Configure MACsec:
# Create an MKA policy named pls.
[Device] mka policy pls
# Set the MACsec confidentiality offset to 30 bytes.
[Device-mka-policy-pls] confidentiality-offset 30
# Enable MACsec replay protection.
[Device-mka-policy-pls] replay-protection enable
# Set the MACsec replay protection window size to 100.
[Device-mka-policy-pls] replay-protection window-size 100
# Set the MACsec validation mode to strict.
[Device-mka-policy-pls] validation mode strict
[Device-mka-policy-pls] quit
# Apply the MKA policy to GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mka apply policy pls
# Configure MACsec desire and enable MKA on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec desire
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mka enable
[Device-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display MACsec information on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device] display macsec interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 verbose
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Protect frames : Yes
Active MKA policy : pls
Replay protection : Enabled
Replay window size : 100 frames
Confidentiality offset : 30 bytes
Validation mode : Strict
Included SCI : No
SCI conflict : No
Cipher suite : GCM-AES-128
MKA life time : 6 seconds
Transmit secure channel:
SCI : 00E00100000A0006
Elapsed time: 00h:02m:07s
Current SA : AN 0 PN 1
Receive secure channels:
SCI : 00E0020000000106
Elapsed time: 00h:02m:03s
Current SA : AN 0 LPN 1
Previous SA : AN N/A LPN N/A
# Display MKA session information on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 after a user logs in.
[Device] display mka session interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 verbose
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Tx-SCI : 00E00100000A0006
Priority : 0
Capability: 3
CKN for participant: 1234
Key server : Yes
MI (MN) : A1E0D2897596817209CD2307 (2509)
Live peers : 1
Potential peers : 0
Principal actor : Yes
MKA session status : Secured
Confidentiality offset: 30 bytes
Current SAK status : Rx & Tx
Current SAK AN : 0
Current SAK KI (KN) : A1E0D2897596817209CD230700000002 (2)
Previous SAK status : N/A
Previous SAK AN : N/A
Previous SAK KI (KN) : N/A
Live peer list:
MI MN Priority Capability Rx-SCI
B2CAF896C9BFE2ABFB135E63 2512 0 3 00E0020000000106
Example: Configuring device-oriented MACsec
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 6, Device A is the MACsec key server.
To secure data transmission between the two devices by MACsec, perform the following tasks on Device A and Device B, respectively:
· Set the MACsec confidentiality offset to 30 bytes.
· Enable MACsec replay protection, and set the replay protection window size to 100.
· Set the MACsec validation mode to strict.
· Configure the CAK name (CKN) and the CAK as E9AC and 09DB3EF1, respectively.
Procedure
1. Configure Device A:
# Enter system view.
<DeviceA> system-view
# Enter GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 interface view.
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
# Enable MACsec desire on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec desire
# Set the MKA key server priority to 5.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mka priority 5
# Configure the CKN as E9AC and the CAK as 09DB3EF1 in plain text.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mka psk ckn E9AC cak simple 09DB3EF1
# Set the MACsec confidentiality offset to 30 bytes.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec confidentiality-offset 30
# Enable MACsec replay protection.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec replay-protection enable
# Set the MACsec replay protection window size to 100.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec replay-protection window-size 100
# Set the MACsec validation mode to strict.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec validation mode strict
# Enable MKA on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mka enable
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
2. Configure Device B:
# Enter system view.
<DeviceB> system-view
# Enter GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 interface view.
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
# Enable MACsec desire on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec desire
# Set the MKA key server priority to 10.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mka priority 10
# Configure the CKN as E9AC and the CAK as 09DB3EF1 in plain text.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mka psk ckn E9AC cak simple 09DB3EF1
# Set the MACsec confidentiality offset to 30 bytes.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec confidentiality-offset 30
# Enable MACsec replay protection.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec replay-protection enable
# Set the MACsec replay protection window size to 100.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec replay-protection window-size 100
# Set the MACsec validation mode to strict.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] macsec validation mode strict
# Enable MKA on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] mka enable
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display MACsec information on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device A.
[DeviceA] display macsec interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 verbose
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Protect frames : Yes
Replay protection : Enabled
Replay window size : 100 frames
Confidentiality offset : 30 bytes
Validation mode : Strict
Included SCI : No
SCI conflict : No
Cipher suite : GCM-AES-128
MKA life time : 6 seconds
Transmit secure channel:
SCI : 00E00100000A0006
Elapsed time: 00h:05m:00s
Current SA : AN 0 PN 1
Receive secure channels:
SCI : 00E0020000000106
Elapsed time: 00h:03m:18s
Current SA : AN 0 LPN 1
Previous SA : AN N/A LPN N/A
# Display MKA session information on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device A.
[DeviceA] display mka session interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 verbose
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Tx-SCI : 00E00100000A0006
Priority : 5
Capability: 3
CKN for participant: E9AC
Key server : Yes
MI (MN) : 85E004AF49934720AC5131D3 (182)
Live peers : 1
Potential peers : 0
Principal actor : Yes
MKA session status : Secured
Confidentiality offset: 30 bytes
Current SAK status : Rx & Tx
Current SAK AN : 0
Current SAK KI (KN) : 85E004AF49934720AC5131D300000003 (3)
Previous SAK status : N/A
Previous SAK AN : N/A
Previous SAK KI (KN) : N/A
Live peer list:
MI MN Priority Capability Rx-SCI
12A1677D59DD211AE86A0128 182 10 3 00E0020000000106
# Display MACsec information on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device B.
[DeviceB] display macsec interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 verbose
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Protect frames : Yes
Replay protection : Enabled
Replay window size : 100 frames
Confidentiality offset : 30 bytes
Validation mode : Strict
Included SCI : No
SCI conflict : No
Cipher suite : GCM-AES-128
MKA life time : 6 seconds
Transmit secure channel:
SCI : 00E0020000000106
Elapsed time: 00h:05m:36s
Current SA : AN 0 PN 1
Receive secure channels:
SCI : 00E00100000A0006
Elapsed time: 00h:03m:21s
Current SA : AN 0 LPN 1
Previous SA : AN N/A LPN N/A
# Display MKA session information on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device B.
[DeviceB] display mka session interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 verbose
Interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
Tx-SCI : 00E0020000000106
Priority : 10
Capability: 3
CKN for participant: E9AC
Key server : No
MI (MN) : 12A1677D59DD211AE86A0128 (1219)
Live peers : 1
Potential peers : 0
Principal actor : Yes
MKA session status : Secured
Confidentiality offset: 30 bytes
Current SAK status : Rx & Tx
Current SAK AN : 0
Current SAK KI (KN) : 85E004AF49934720AC5131D300000003 (3)
Previous SAK status : N/A
Previous SAK AN : N/A
Previous SAK KI (KN) : N/A
Live peer list:
MI MN Priority Capability Rx-SCI
85E004AF49934720AC5131D3 1216 5 3 00E00100000A0006
Troubleshooting MACsec
Cannot establish MKA sessions between MACsec devices
Symptom
The devices cannot establish MKA sessions when the following conditions exist:
· The link connecting the devices is up.
· The ports at the ends of the link are MACsec capable.
Analysis
The symptom might occur for the following reasons:
· The ports at the link are not enabled with MKA.
· A port at the link is not configured with a preshared key or configured with a preshared key different from the peer.
Solution
To resolve the issue:
1. Enter interface view.
2. Use the display this command to check the MACsec configuration:
¡ If MKA is not enabled on the port, execute the mka enable command.
¡ If a preshared key is not configured or the preshared key is different from the peer, use the mka psk command to configure a preshared key. Make sure the preshared key is the same as the preshared key on the peer.
3. If the issue persists, contact H3C Support.