- Table of Contents
-
- 07-IP Multicast Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-Multicast Overview
- 02-IGMP snooping configuration
- 03-PIM snooping configuration
- 04-Multicast VLAN configuration
- 05-Multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 06-IGMP configuration
- 07-PIM configuration
- 08-MSDP configuration
- 09-Multicast VPN configuration
- 10-MLD snooping configuration
- 11-IPv6 PIM snooping configuration
- 12-IPv6 multicast VLAN configuration
- 13-IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding configuration
- 14-MLD configuration
- 15-IPv6 PIM configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-PIM snooping configuration | 114.88 KB |
Displaying and maintaining PIM snooping
PIM snooping configuration example
PIM snooping does not work on a Layer 2 device
Configuring PIM snooping
Overview
PIM snooping runs on Layer 2 devices. It works with IGMP snooping to analyze received PIM messages, and adds the ports that are interested in specific multicast data to a PIM snooping routing entry. In this way, the multicast data can be forwarded to only the ports that are interested in the data.
Figure 1 Multicast packet transmission without or with PIM snooping
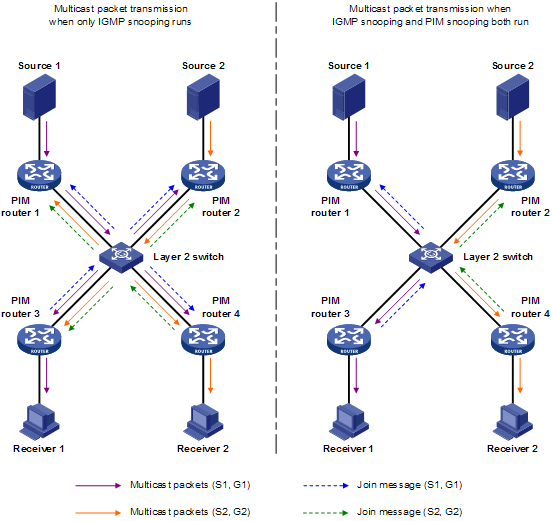
As shown in Figure 1, Source 1 sends multicast data to multicast group G1, and Source 2 sends multicast data to multicast group G2. Receiver 1 belongs to G1, and Receiver 2 belongs to G2. The Layer 2 switch's interfaces that connect to the PIM routers are in the same VLAN.
· When the Layer 2 switch runs only IGMP snooping, it performs the following actions:
a. Maintains the router ports according to the received PIM hello messages that PIM routers send.
b. Floods all other types of received PIM messages except PIM hello messages in the VLAN.
c. Forwards all multicast data to all router ports in the VLAN.
Each PIM router in the VLAN, whether interested in the multicast data or not, can receive all multicast data and all PIM messages except PIM hello messages.
· When the Layer 2 switch runs both IGMP snooping and PIM snooping, it performs the following actions:
a. Examines whether a PIM router is interested in the multicast data addressed to a multicast group according to the received PIM messages that the router send.
b. Adds only the ports that connect to the router and are interested in the data to a PIM snooping routing entry.
c. Forwards PIM messages and multicast data to only the routers that are interested in the data, which saves network bandwidth.
For more information about IGMP snooping and the router port, see "Configuring IGMP snooping."
PIM snooping can run in PIM-SM and PIM-SSM networks. Do not configure PIM snooping in PIM-DM or BIDIR-PIM networks. For more information about PIM, see "Configuring PIM."
Configuring PIM snooping
|
|
IMPORTANT: · Do not configure PIM snooping in secondary VLANs because PIM snooping does not take effect in secondary VLANs. For more information about secondary VLANs, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide. · Make sure the IP packet length of join/prune messages is less than the MTU of receiver-side PIM interfaces that connect to PIM snooping devices. Otherwise, multicast data might not be correctly forwarded. The IP packet length of join/prune messages is the packet length of join/prune messages plus the IP header length. To set the maximum size of join/prune messages, use the jp-pkt-size command. To set the MTU for an Ethernet interface, use the mtu command. For more information about the command, see Interface Command Reference. |
To configure PIM snooping for a VLAN, you must enable IGMP snooping globally on the Layer 2 device, and then enable IGMP snooping and PIM snooping for the VLAN.
To configure PIM snooping:
|
Step |
Command |
Remarks |
|
1. Enter system view. |
system-view |
N/A |
|
2. Enable IGMP snooping globally and enter IGMP-snooping view. |
igmp-snooping |
By default, IGMP snooping is disabled. |
|
3. Return to system view. |
quit |
N/A |
|
4. Enter VLAN view. |
vlan vlan-id |
N/A |
|
5. Enable IGMP snooping for the VLAN. |
igmp-snooping enable |
By default, IGMP snooping is disabled in a VLAN. |
|
6. Enable PIM snooping for the VLAN. |
pim-snooping enable |
By default, PIM snooping is disabled in a VLAN. |
|
7. (Optional.) Set the aging time for global neighbor ports on the new active MPU after an active/standby switchover. |
pim-snooping graceful-restart neighbor-aging-time interval |
The default setting is 105 seconds. A global neighbor port is a Layer 2 aggregate interface that acts as a neighbor port. |
|
8. (Optional.) Set the aging time for global downstream ports and global router ports on the new active MPU after an active/standby switchover. |
pim-snooping graceful-restart join-aging-time interval |
The default setting is 210 seconds. A global downstream port or a global router port is a Layer 2 aggregate interface that acts as a downstream port or router port. |
Displaying and maintaining PIM snooping
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Command |
|
|
Display PIM snooping neighbor information (in standalone mode). |
display pim-snooping neighbor [ vlan vlan-id ] [ slot slot-number ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display PIM snooping neighbor information (in IRF mode). |
display pim-snooping neighbor [ vlan vlan-id ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display PIM snooping router port information (in standalone mode). |
display pim-snooping router-port [ vlan vlan-id ] [ slot slot-number ] |
|
Display PIM snooping router port information (in IRF mode). |
display pim-snooping router-port [ vlan vlan-id ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] |
|
Display PIM snooping routing entries (in standalone mode). |
display pim-snooping routing-table [ vlan vlan-id ] [ slot slot-number ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display PIM snooping routing entries (in IRF mode). |
display pim-snooping routing-table [ vlan vlan-id ] [ chassis chassis-number slot slot-number ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display statistics for the PIM messages learned through PIM snooping. |
display pim-snooping statistics |
|
Clear statistics for the PIM messages learned through PIM snooping. |
reset pim-snooping statistics |
PIM snooping configuration example
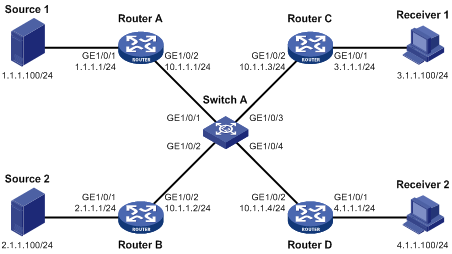
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2:
· OSPF runs on the network.
· Source 1 sends multicast data to multicast group 224.1.1.1, and Source 2 sends multicast data to multicast group 225.1.1.1.
· Receiver 1 belongs to multicast group 224.1.1.1, and Receiver 2 belongs to multicast group 225.1.1.1.
· Router C and Router D run IGMP on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. Router A, Router B, Router C, and Router D run PIM-SM.
· GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 on Router A acts as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
Configure IGMP snooping and PIM snooping on Switch A. Then, Switch A forwards PIM protocol packets and multicast data packets to routers that connect to receivers.
Configuration procedure
1. Assign an IP address and subnet mask to each interface according to Figure 2. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure OSPF on the routers. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure Router A:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterA> system-view
[RouterA] multicast routing
[RouterA-mrib] quit
# Enable PIM-SM on each interface.
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] pim sm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] pim sm
[RouterA-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 as a C-BSR and a C-RP.
[RouterA] pim
[RouterA-pim] c-bsr 10.1.1.1
[RouterA-pim] c-rp 10.1.1.1
[RouterA-pim] quit
4. Configure Router B:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterB> system-view
[RouterB] multicast routing
[RouterB-mrib] quit
# Enable PIM-SM on each interface.
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] pim sm
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[RouterB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] pim sm
[RouterB-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
5. Configure Router C:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterC> system-view
[RouterC] multicast routing
[RouterC-mrib] quit
# Enable IGMP on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[RouterC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] igmp enable
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable PIM-SM on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[RouterC] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] pim sm
[RouterC-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
6. Configure Router D:
# Enable IP multicast routing.
<RouterD> system-view
[RouterD] multicast routing
[RouterD-mrib] quit
# Enable IGMP on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[RouterD] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[RouterD-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] igmp enable
[RouterD-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Enable PIM-SM on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[RouterD] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[RouterD-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] pim sm
[RouterD-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
7. Configure Switch A:
# Enable IGMP snooping globally.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] igmp-snooping
[SwitchA-igmp-snooping] quit
# Create VLAN 100, assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 through GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to the VLAN, and enable IGMP snooping and PIM snooping for the VLAN.
[SwitchA] vlan 100
[SwitchA-vlan100] port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[SwitchA-vlan100] igmp-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan100] pim-snooping enable
[SwitchA-vlan100] quit
Verifying the configuration
# On Switch A, display information about PIM snooping neighbors for VLAN 100.
[SwitchA] display pim-snooping neighbor vlan 100
Total 4 neighbors.
VLAN 100: Total 4 neighbors.
10.1.1.1
Slots (0 in total):
Ports (1 in total):
GE1/0/1 (00:32:43)
10.1.1.2
Slots (0 in total):
Ports (1 in total):
GE1/0/2 (00:32:43)
10.1.1.3
Slots (0 in total):
Ports (1 in total):
GE1/0/3 (00:32:43)
10.1.1.4
Slots (0 in total):
Ports (1 in total):
GE1/0/4 (00:32:43)
The output shows that Router A, Router B, Router C, and Router D are PIM snooping neighbors.
# On Switch A, display information about PIM snooping routing entries for VLAN 100.
[SwitchA] display pim-snooping routing-table vlan 100
Total 2 entries.
FSM Flag: NI-no info, J-join, PP-prune pending
VLAN 100: Total 2 entries.
(*, 224.1.1.1)
Upstream neighbor: 10.1.1.1
Upstream Slots (0 in total):
Upstream Ports (1 in total):
GE1/0/1
Downstream Slots (0 in total):
Downstream Ports (1 in total):
GE1/0/3
Expires: 00:03:01, FSM: J
(*, 225.1.1.1)
Upstream neighbor: 10.1.1.2
Upstream Slots (0 in total):
Upstream Ports (1 in total):
GE1/0/2
Downstream Slots (0 in total):
Downstream Ports (1 in total):
GE1/0/4
Expires: 00:03:11, FSM: J
· Switch A will forward the multicast data intended for multicast group 224.1.1.1 to only Router C.
· Switch A will forward the multicast data intended for multicast group 225.1.1.1 to only Router D.
Troubleshooting PIM snooping
PIM snooping does not work on a Layer 2 device
Symptom
PIM snooping does not work on a Layer 2 device.
Solution
To resolve the problem:
1. Use the display current-configuration command to display information about IGMP snooping and PIM snooping.
2. If IGMP snooping is not enabled, enable IGMP snooping globally, and then enable IGMP snooping and PIM snooping for the VLAN.
3. If PIM snooping is not enabled, enable PIM snooping for the VLAN.
4. If the problem persists, contact H3C Support.

