- Table of Contents
-
- 13-Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide
- 00-Preface
- 01-System maintenance and debugging configuration
- 02-NQA configuration
- 03-iNQA configuration
- 04-NTP configuration
- 05-PTP configuration
- 06-SNMP configuration
- 07-RMON configuration
- 08-NETCONF configuration
- 09-EAA configuration
- 10-Process monitoring and maintenance configuration
- 11-Sampler configuration
- 12-Mirroring configuration
- 13-sFlow configuration
- 14-Information center configuration
- 15-GOLD configuration
- 16-Packet capture configuration
- 17-VCF fabric configuration
- 18-CWMP configuration
- 19-SmartMC configuration
- 20-Event MIB configuration
- 21-SQA configuration
- 22-eMDI configuration
- 23-Performance management configuration
- 24-Ansible configuration
- 25-EPS agent configuration
- 26-Cloud connection configuration
- 27-EPA configuration
- 28-Packet trace configuration
- 29-IPv6 NetStream configuration
- 30-NetStream configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 28-Packet trace configuration | 142.51 KB |
Restrictions and guidelines: Packet trace configuration
Configuring a TCP or UDP packet profile for packet trace
Configuring an ICMP packet profile for packet trace
Configuring a raw packet profile for packet trace
Executing a packet trace operation
Display and maintenance commands for packet trace
Packet trace configuration examples
Example: Executing a packet trace operation (TCP packet profile)
Example: Executing a packet trace operation (ICMP packet profile)
Example: Executing a packet trace operation (raw packet profile)
Configuring packet trace
About packet trace
Packet trace uses a packet profile to construct traced packets, injects the packets to the device from an ingress interface, simulates the packet forwarding process, and traces the forwarding process. This feature can identify whether the device can forward packets correctly and whether packet loss has occurred during the forwarding process. If packets are lost, the feature can assist in locating the packet loss cause.
Application scenario
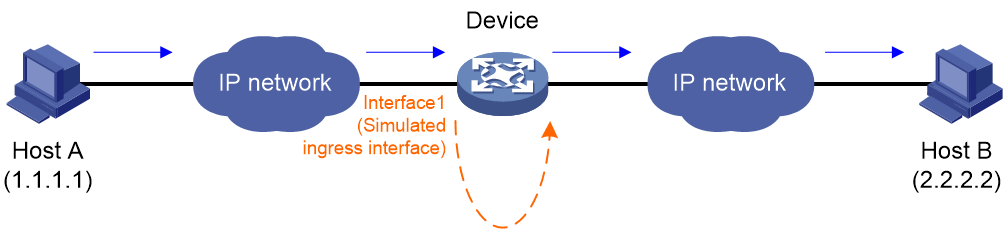
As shown in Figure 1, you can use packet trace as follows:
1. Capture a packet sent from Host A to Host B on Interface 1 of the device.
2. Configure a packet profile on the device according to the field values in the captured packet.
3. Execute a packet trace operation. In the operation, specify the profile to construct traced packets and injects the packets to the device from Interface 1. The device simulates the packet forwarding process and traces the entire packet forwarding process, including the packets are injected, processed by software and hardware, and sent out of the device.
4. View the packet trace operation result, obtain the forwarding process of the packets, identify whether packets are lost, and locate the packet drop reason.
Packet profile
A packet profile contains a set of parameters used to construct traced packets. You can configure the parameters based on the characteristic parameters of service packets.
The following types of packet profiles are available:
· Protocol packet profile—In this type of profiles, you can simulate ICMP, TCP, or UDP protocol packets by defining values for the required fields of the protocol packets. The device automatically pads values for fields that are not defined. The configuration is simple.
· Raw packet profile—In this type of profiles, the entire content of traced packets is user configured. The protocol type of traced packets and all field values are user defined. You must first use a packet capture tool to capture a packet in hexadecimal notation and copy the entire packet to the raw packet view of a raw packet profile.
Restrictions and guidelines: Packet trace configuration
In order to truly present the processing process of service packets within the device, construct traced packets based on the corresponding field values in real service packets. Make sure the traced packets are the same as the real service packets. A violation might bring in inaccurate packet trace operation result because the simulated packet processing process might be different from the real packet processing process.
Configuring a TCP or UDP packet profile for packet trace
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a TCP or UDP packet profile for packet trace and enter its view.
packet-trace profile profile-name type { tcp | udp }
3. Configure Layer 2 parameters for traced packets.
source-mac src-mac destination-mac dest-mac [ vlan vlan-id [ dot1p dot1p-value ] | service-vlan vlan-id [ service-dot1p dot1p-value ] customer-vlan vlan-id [ customer-dot1p dot1p-value ] ]
By default, no Layer 2 parameters are configured for traced packets in a packet profile.
4. Configure Layer 3 parameters for traced packets.
source-ip src-ip destination-ip dest-ip [ dscp dscp-value ] [ ttl ttl-value ]
By default, no Layer 3 parameters are configured for traced packets in a packet profile.
5. Configure the source and destination port numbers of traced packets.
source-port src-port destination-port dest-port
By default, no source or destination port number is configured for traced packets in a packet profile.
6. Enter TCP or UDP packet profile payload view and configure the payload of traced packets.
payload
In TCP or UDP packet profile payload view, you can input a string of hexadecimal characters. The string must contain an even number of hexadecimal characters. The length of the string varies by packet profile type. For more information, see the command reference.
If you input the hexadecimal characters with spaces in multiple lines, the device automatically removes the line breakers and spaces from the string in the input order when saving the payload.
7. Exit TCP or UDP packet profile payload view. Use one of the following options:
¡ Save the configuration in TCP or UDP packet profile payload view and exit the view.
payload-end
¡ Exit TCP or UDP packet profile payload view without saving the configuration in the view.
quit
Configuring an ICMP packet profile for packet trace
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create an ICMP packet profile for packet trace and enter its view.
packet-trace profile profile-name type icmp
3. Configure Layer 2 parameters for traced packets.
source-mac src-mac destination-mac dest-mac [ vlan vlan-id [ dot1p dot1p-value ] | service-vlan vlan-id [ service-dot1p dot1p-value ] customer-vlan vlan-id [ customer-dot1p dot1p-value ] ]
By default, no Layer 2 parameters are configured for traced packets in a packet profile.
4. Configure Layer 3 parameters for traced packets.
source-ip src-ip destination-ip dest-ip [ dscp dscp-value ] [ ttl ttl-value ]
By default, no Layer 3 parameters are configured for traced packets in a packet profile.
5. Configure the ICMP message type and message code for traced packets.
icmp-type icmp-type icmp-code icmp-code
By default, no ICMP message type or message code is configured for traced packets in a packet profile.
6. Enter ICMP packet profile payload view and configure the payload of traced packets.
payload
In ICMP packet profile payload view, you can input a string of hexadecimal characters. The string must contain an even number of hexadecimal characters. For information about the length of the string, see the command reference.
If you input the hexadecimal characters with spaces in multiple lines, the device automatically removes the line breakers and spaces from the string in the input order when saving the payload.
7. Exit ICMP packet profile payload view. Use one of the following options:
¡ Save the configuration in ICMP packet profile payload view and exit the view.
payload-end
¡ Exit ICMP packet profile payload view without saving the configuration in the view.
quit
Configuring a raw packet profile for packet trace
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a raw packet profile for packet trace and enter its view.
packet-trace profile profile-name type raw
3. Enter raw packet profile raw packet view and configure the content of traced raw packets.
raw-packet
In raw packet profile raw packet view, you can input a string of 128 to 3036 hexadecimal characters. The string must contain an even number of hexadecimal characters. If you input the hexadecimal characters with spaces in multiple lines, the device automatically removes the line breakers and spaces from the string in the input order when saving the content.
You can use a packet capture tool (for example, Wireshark) to capture a packet in string format and copy the packet to the raw packet profile raw packet view.
4. Exit raw packet profile raw packet view. Use one of the following options:
¡ Save the configuration in raw packet profile raw packet view and exit the view.
raw-packet-end
¡ Exit raw packet profile raw packet view without saving the configuration in the view.
quit
Executing a packet trace operation
About this task
This task constructs traced packets based on a packet profile, injects the packets to the device from an ingress interface, simulates the packet forwarding process, and traces the forwarding process.
Restrictions and guidelines
To ensure that the packet trace operation can succeed, the specified ingress interface must be up.
You can use only Ethernet interfaces as ingress interfaces.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Execute a packet trace operation.
packet-trace execute profile profile-name interface interface-type interface-number
Display and maintenance commands for packet trace
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display information about packet profiles. |
display packet-trace profile [ profile-name ] |
|
Display history packet trace operation results. |
display packet-trace history profile profile-name [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
|
Clear history packet trace operation results. |
reset packet-trace history profile profile-name [ interface interface-type interface-number ] |
Packet trace configuration examples
Example: Executing a packet trace operation (TCP packet profile)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 2, the Telnet client Telnets to the Telnet server. The Telnet connection is flapping.
Use the packet trace feature to identify whether Telnet packets are dropped when the packets pass through the device. If the packets are dropped on the device, locate the packet drop reason.
Prerequisites
# Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Configure static routes or a dynamic routing protocol to make sure the client, device, and server have routes to reach one another. (Details not shown.)
Procedure
# Configure a TCP packet profile.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] packet-trace profile t1 type tcp
# Configure Layer 2 parameters for traced TCP packets. The source MAC address and destination MAC address are 2-2-1 and 2-2-2, respectively.
[Sysname-packet-trace-t1-tcp] source-mac 2-2-1 destination-mac 2-2-2
# Configure Layer 3 parameters for traced TCP packets. The source IP address, destination IP address, DSCP value, and TTL value are 2.2.2.1, 1.1.1.2, 10, and 100, respectively.
[Sysname-packet-trace-t1-tcp] source-ip 2.2.2.1 destination-ip 1.1.1.2 dscp 10 ttl 100
# Configure the source and destination port numbers of traced TCP packets as 1000 and 23, respectively.
[Sysname-packet-trace-t1-tcp] source-port 1000 destination-port 23
[Sysname-packet-trace-t1-tcp] quit
# Execute a packet trace operation.
[Sysname] packet-trace execute profile t1 interface hundredgige 3/0/1
Packet Trace Result:
Forwarding path:
ForwardingVlanValid
L2DstHit
L3SrcHostHit
L3DestHostHit
L3DestRouteHit
L2SrcMiss
MystationHit
Packet resolution:
KnownL3UcPkt
Source port STP state: Forward
Egress interface info:
Destination mod:40 port:0
l3 egress intf show 100001
Packet drop reason:
NoDrop
Verifying the configuration
# Display results about packet trace operations that use packet profile t1.
[Sysname] display packet-trace history profile t1
Ingress interface: HundredGigE3/0/1
Packet trace result 1:
Forwarding path:
ForwardingVlanValid
L2DstHit
L3SrcHostHit
L3DestHostHit
L3DestRouteHit
L2SrcMiss
MystationHit
Packet resolution:
KnownL3UcPkt
Source port STP state: Forward
Egress interface info:
Destination mod:40 port:0
l3 egress intf show 100001
Packet drop reason:
NoDrop
The output shows that the device can correctly forward the Telnet packets sent from the Telnet client to the Telnet server without packet loss. Packet loss occurred at other locations.
Example: Executing a packet trace operation (ICMP packet profile)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 3, when Host A pings Host B, packets are lost. Use the packet trace feature to identify whether ping packets are dropped when the packets pass through the device. If the packets are dropped on the device, locate the packet drop reason.
Prerequisites
# Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Configure static routes or a dynamic routing protocol to make sure the hosts and device have routes to reach one another. (Details not shown.)
Procedure
# Configure an ICMP packet profile for packet trace.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] packet-trace profile testicmp type icmp
# Configure Layer 2 parameters for traced ICMP packets. The source MAC address and destination MAC address are 2-2-1 and 2-2-2, respectively.
[Sysname-packet-trace-testicmp-icmp] source-mac 2-2-1 destination-mac 2-2-2
# Configure Layer 3 parameters for traced ICMP packets. The source IP address, destination IP address, DSCP value, and TTL value are 2.2.2.1, 1.1.1.2, 10, and 100, respectively.
[Sysname-packet-trace-testicmp-icmp] source-ip 2.2.2.1 destination-ip 1.1.1.2 dscp 10 ttl 100
# Configure the ICMP message type and code of traced ICMP packets as 1 and 255, respectively.
[Sysname-packet-trace-testicmp-icmp] icmp-type 1 icmp-code 255
# Execute a packet trace operation.
[Sysname] packet-trace execute profile testicmp interface hundredgige 3/0/1
Packet Trace Result:
Forwarding path:
ForwardingVlanValid
L2DstHit
L3SrcHostHit
L3DestHostHit
L3DestRouteHit
L2SrcMiss
MystationHit
Packet resolution:
KnownL3UcPkt
Source port STP state: Forward
Egress interface info:
Destination mod:40 port:0
l3 egress intf show 100001
Packet drop reason:
NoDrop
Verifying the configuration
# Display results about packet trace operations that use packet profile testicmp.
[Sysname] display packet-trace history profile testicmp
Ingress interface: HundredGigE3/0/1
Packet trace result 1:
Forwarding path:
ForwardingVlanValid
L2DstHit
L3SrcHostHit
L3DestHostHit
L3DestRouteHit
L2SrcMiss
MystationHit
Packet resolution:
KnownL3UcPkt
Source port STP state: Forward
Egress interface info:
Destination mod:40 port:0
l3 egress intf show 100001
Packet drop reason:
NoDrop
The output shows that the device can correctly forward the ping packets sent from Host A to Host B without packet loss. Packet loss occurred at other locations.
Example: Executing a packet trace operation (raw packet profile)
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 4, the FTP client downloads files from the FTP server. Data packets are lost.
Use the packet trace feature to identify whether data packets are dropped when the packets pass through the device. If the packets are dropped on the device, locate the packet drop reason.
Prerequisites
# Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
# Configure static routes or a dynamic routing protocol to make sure the client, device, and server have routes to reach one another. (Details not shown.)
Procedure
# Configure a raw packet profile.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] packet-trace profile r1 type raw
# Configure the content of traced raw packets.
[Sysname-packet-trace-r1-raw] raw-packet
[Sysname-packet-trace-r1-raw-packet] 90e7106017f800465900a03208004500002800004000ff0677cb0101010201010101271027100000001500000000500000005dab000000000000000000000000
[Sysname-packet-trace-r1-raw-packet] raw-packet-end
[Sysname-packet-trace-r1-raw] quit
# Execute a packet trace operation.
[Sysname] packet-trace execute profile r1 interface hundredgige 3/0/1
Packet Trace Result:
Forwarding path:
ForwardingVlanValid
L2DstHit
L3SrcHostHit
L3DestHostHit
L3DestRouteHit
L2SrcMiss
MystationHit
Packet resolution:
KnownL3UcPkt
Source port STP state: Forward
Egress interface info:
Destination mod:40 port:0
l3 egress intf show 100001
Packet drop reason:
NoDrop
Verifying the configuration
# Display results about packet trace operations that use packet profile r1.
[Sysname] display packet-trace history profile r1
Ingress interface: HundredGigE3/0/1
Packet trace result 1:
Forwarding path:
ForwardingVlanValid
L2DstHit
L3SrcHostHit
L3DestHostHit
L3DestRouteHit
L2SrcMiss
MystationHit
Packet resolution:
KnownL3UcPkt
Source port STP state: Forward
Egress interface info:
Destination mod:40 port:0
l3 egress intf show 100001
Packet drop reason:
NoDrop
The output shows that the device can correctly forward the data packets sent between the FTP client and the FTP server without packet loss. Packet loss occurred at other locations.